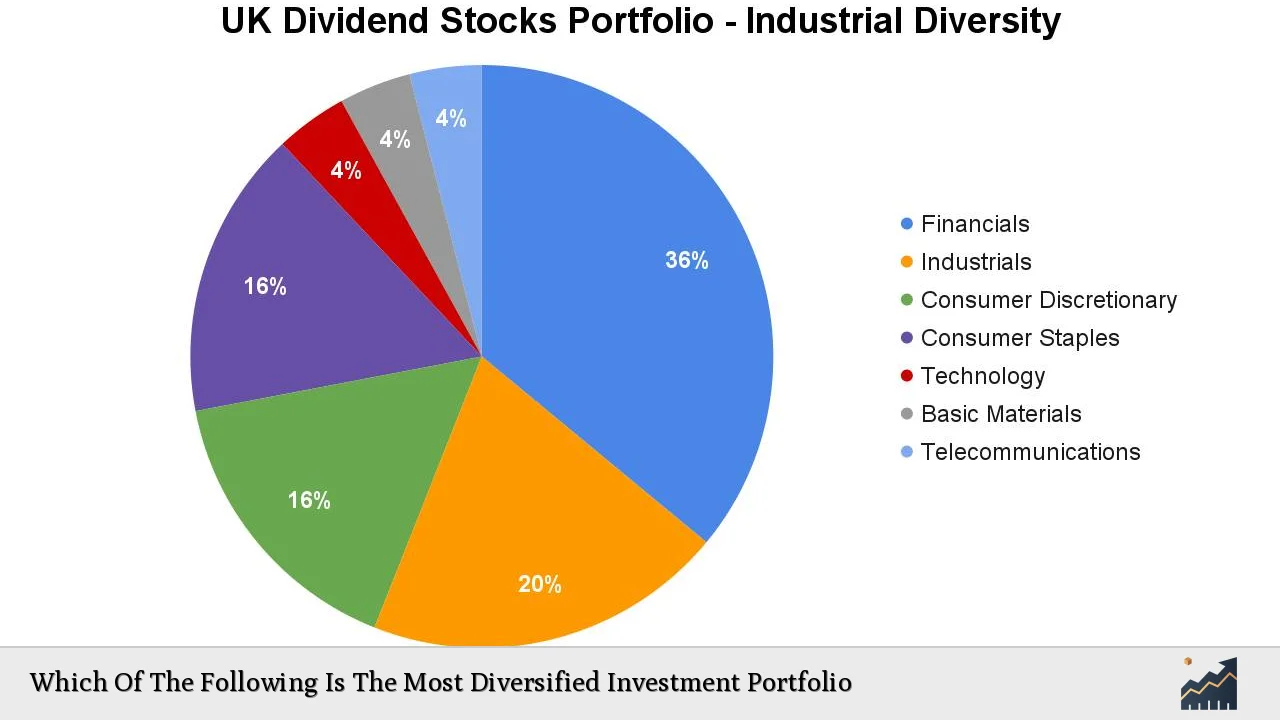
A well-diversified investment portfolio is essential for managing risk and optimizing returns in an unpredictable market environment. Diversification involves spreading investments across various asset classes, sectors, and geographies to mitigate the impact of poor performance from any single investment. This article explores the most diversified investment portfolios, analyzing current market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Diversification | Spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and enhance returns. |
| Asset Allocation | The process of dividing investments among different categories such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. |
| Geographic Diversification | Investing in assets from various countries to mitigate risks associated with specific regions. |
| Sector Diversification | Distributing investments across various industries to reduce exposure to economic downturns in specific sectors. |
| Risk Management | Strategies employed to minimize potential losses in an investment portfolio. |
Market Analysis and Trends
As of late 2024, the investment landscape is characterized by significant volatility driven by geopolitical tensions, inflationary pressures, and rapid technological advancements. Key trends influencing portfolio diversification include:
- Increased Interest in Alternative Investments: Investors are increasingly allocating funds to alternative assets such as private equity, real estate, and commodities. These assets often have low correlation with traditional equities and bonds, enhancing overall portfolio diversification.
- Rise of ESG Investing: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are becoming crucial in investment decisions. Portfolios that include ESG-compliant assets can mitigate risks associated with regulatory changes and reputational damage.
- Technological Integration: The use of advanced analytics and AI in portfolio management allows for more sophisticated risk assessments and dynamic asset allocation strategies.
The Global Market Portfolio (GMP), which encompasses all investable assets globally, reached a valuation of approximately USD 175 trillion by mid-2024. This portfolio structure is viewed as a benchmark for diversification strategies due to its comprehensive coverage of asset classes.
Implementation Strategies
To build a highly diversified investment portfolio, consider the following strategies:
- Asset Class Diversification: Allocate investments across multiple asset classes such as equities (both domestic and international), fixed income (government and corporate bonds), real estate (REITs), and commodities (gold, oil).
- Geographic Diversification: Include international investments to hedge against domestic market fluctuations. This can involve investing in emerging markets that may offer higher growth potential.
- Sector Diversification: Invest across various sectors such as technology, healthcare, consumer goods, and utilities. This reduces the risk associated with sector-specific downturns.
- Regular Rebalancing: Periodically review and adjust the portfolio to maintain desired asset allocation percentages. This helps in capturing gains from outperforming assets while reinvesting in underperforming ones.
- Utilizing Model Portfolios: Many investors are turning to model portfolios provided by asset managers that offer pre-set allocations based on risk tolerance. These portfolios simplify diversification efforts while ensuring adherence to best practices.
Risk Considerations
While diversification can significantly reduce risk, it is essential to recognize its limitations:
- Over-Diversification: Holding too many assets can dilute potential returns. A focused approach is often more effective than trying to include every available option.
- Market Correlation: During systemic crises (e.g., financial downturns), correlations between asset classes may increase, reducing the effectiveness of diversification strategies.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in regulations can impact certain sectors or asset classes disproportionately. Staying informed about regulatory developments is crucial for maintaining a diversified portfolio.
Effective risk management strategies should include:
- Value-at-Risk (VaR) Analysis: Estimating potential losses under normal market conditions helps investors understand their exposure.
- Stress Testing: Simulating adverse market conditions can provide insights into how a portfolio would perform during crises.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory environment for investment portfolios continues to evolve. Key considerations include:
- ESG Regulations: Increased scrutiny around ESG compliance requires investors to ensure their portfolios align with sustainability criteria. This can impact investment choices significantly.
- Transparency Requirements: New regulations mandate detailed reporting on fees and performance metrics for investment funds. Compliance with these rules is essential for maintaining investor confidence.
- Liquidity Management Standards: Stricter liquidity requirements are being imposed on funds, particularly those dealing with alternative investments. Investors must ensure their portfolios meet these standards to avoid penalties.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape diversified investment portfolios:
- Continued Growth of Alternative Investments: As traditional markets face challenges, alternative investments will likely gain prominence due to their potential for higher returns and lower correlation with mainstream assets.
- Technological Advancements: AI and machine learning will play a pivotal role in optimizing portfolio management by providing real-time data analysis and predictive modeling capabilities.
- Focus on Sustainable Investments: The shift towards sustainable investing will continue as investors seek not only financial returns but also positive societal impacts.
In summary, the most diversified investment portfolios will be those that adapt to changing market conditions while balancing risk across various asset classes, geographies, and sectors. Investors should remain proactive in adjusting their strategies based on emerging trends and regulatory developments.
Frequently Asked Questions About Which Of The Following Is The Most Diversified Investment Portfolio
- What is the definition of a diversified portfolio?
A diversified portfolio spreads investments across various asset classes to reduce risk and enhance returns. - How does geographic diversification benefit my portfolio?
Geographic diversification mitigates risks associated with local economic downturns by investing in international markets. - What are some common asset classes used for diversification?
Common asset classes include stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and cash equivalents. - How often should I rebalance my portfolio?
It is generally recommended to rebalance your portfolio at least once a year or whenever your asset allocation deviates significantly from your target. - What are the risks associated with over-diversification?
Over-diversification can dilute potential returns and make it challenging to manage individual investments effectively. - How do ESG factors influence investment decisions?
ESG factors help investors assess risks related to sustainability issues that could impact long-term performance. - What role do model portfolios play in diversification?
Model portfolios provide pre-defined allocations based on risk tolerance, simplifying the process of achieving diversification. - What should I consider when selecting investments for my diversified portfolio?
You should consider your risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, and current market conditions when selecting investments.
This comprehensive analysis highlights the importance of constructing a well-diversified investment portfolio tailored to individual goals while navigating an increasingly complex financial landscape.