Investing is a fundamental aspect of personal finance and wealth building, characterized by the allocation of resources, typically money, with the expectation of generating an income or profit. The foundation concept of investing revolves around understanding the principles that govern investment decisions, risk management, market dynamics, and the long-term growth potential of various asset classes. This comprehensive overview will explore these foundational concepts, current market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks to equip investors with a robust framework for making informed investment choices.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
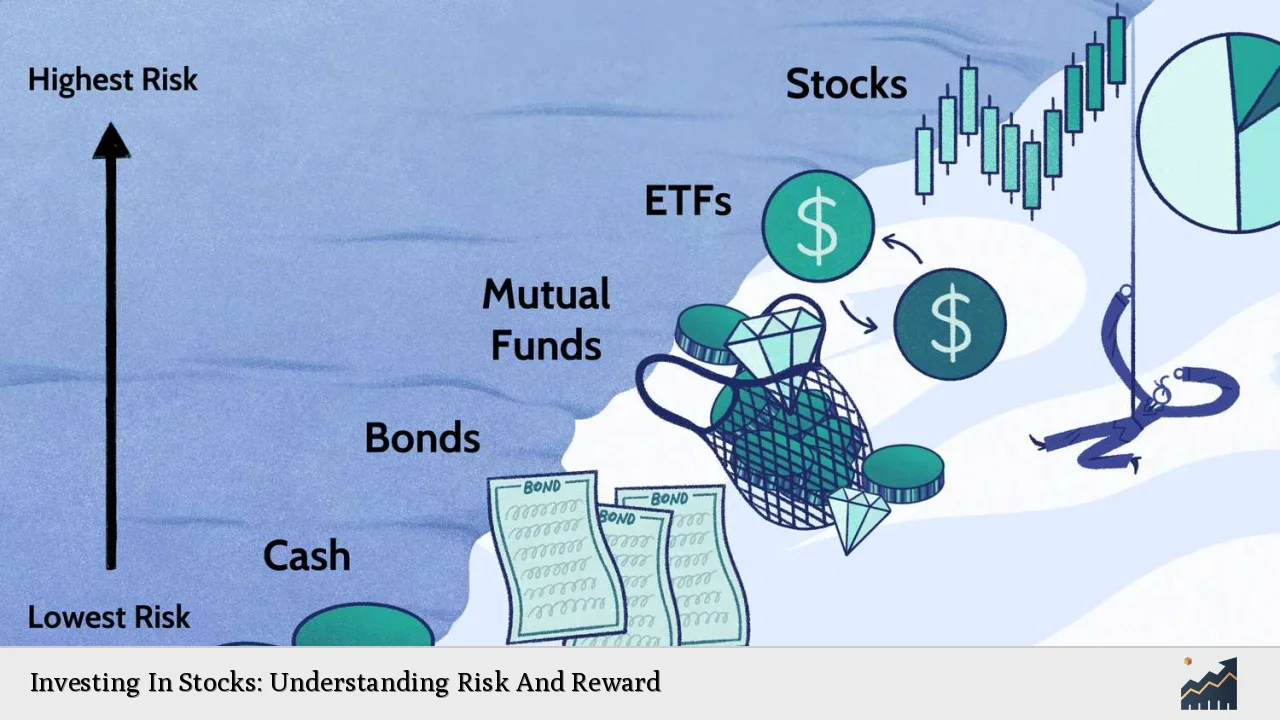
| Risk and Return Trade-off | The principle that potential return rises with an increase in risk. Investors must balance their desire for the highest possible return against their tolerance for risk. |
| Diversification | A strategy to reduce risk by allocating investments among various financial instruments, industries, and other categories. |
| Asset Allocation | The process of dividing investments among different asset categories to optimize the risk-return profile based on individual goals and risk tolerance. |
| Market Efficiency | The hypothesis that stock prices reflect all available information. In an efficient market, it is impossible to “beat the market” consistently on a risk-adjusted basis. |
| Time Horizon | The length of time an investor expects to hold an investment before taking the money out. Longer time horizons can typically withstand more volatility. |
| Fundamental Analysis vs. Technical Analysis | Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company’s financial health and intrinsic value, while technical analysis focuses on statistical trends from trading activity. |
| Behavioral Finance | A field that examines how psychological influences and cognitive biases affect the financial behaviors of investors. |
Market Analysis and Trends
Current market conditions are shaped by various macroeconomic factors including inflation rates, interest rates, and geopolitical events. As of late 2024, global equities have reached an all-time high of approximately USD 78.4 trillion, marking a nearly 10% increase from December 2023. This growth is largely attributed to advancements in technology sectors, particularly those related to artificial intelligence (AI) .
Key Market Trends
- Economic Growth: The global economy is projected to grow steadily at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% from 2024 to 2028. Factors contributing to this growth include increased consumer spending and foreign trade .
- Inflation Dynamics: Inflation rates have shown signs of decline, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reflecting its lowest year-over-year pace since 2021. This trend is expected to influence Federal Reserve policies regarding interest rates .
- Investment Vehicles: There has been a notable shift towards sustainable investing and digital assets as investors seek to align their portfolios with environmental and technological advancements .
Implementation Strategies
Investors can adopt several strategies based on their individual goals and market conditions:
- Value Investing: Focuses on identifying undervalued stocks that are expected to provide returns as their true value is recognized over time.
- Growth Investing: Involves investing in companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market.
- Index Investing: A passive investment strategy where investors aim to replicate the performance of a specific index like the S&P 500.
- Robo-Advisors: Automated platforms that create diversified portfolios based on investor preferences and risk tolerance.
Steps for Effective Implementation
- Define Investment Goals: Establish clear objectives based on personal financial situations.
- Assess Risk Tolerance: Understand how much risk one is willing to take based on financial capacity and emotional comfort.
- Choose Investment Vehicles: Select appropriate asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) that align with investment goals.
- Monitor and Rebalance: Regularly review portfolio performance and make adjustments as necessary to maintain desired asset allocation.
Risk Considerations
Understanding risks is crucial for successful investing:
- Market Risk: The potential for losses due to fluctuations in market prices.
- Credit Risk: The risk that a bond issuer will default on payments.
- Liquidity Risk: The danger that an investor may not be able to sell an asset quickly without incurring significant losses.
Risk Management Techniques
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various asset classes can mitigate risks associated with individual securities.
- Hedging: Using options or futures contracts can protect against adverse price movements.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically selling a security when it reaches a certain price can limit potential losses.
Regulatory Aspects
The investment landscape is heavily influenced by regulations designed to protect investors:
- Securities Exchange Commission (SEC): Oversees securities transactions and protects investors from fraudulent practices.
- Investment Company Act of 1940: Regulates mutual funds and other investment companies to ensure transparency and fairness.
Compliance Considerations
Investment firms must stay abreast of regulatory changes that could impact operations or compliance costs. For instance, new rules under SEC Chair Gary Gensler have introduced significant changes in reporting requirements .
Future Outlook
As we look ahead into 2025 and beyond:
- Technological Integration: The rise of AI and machine learning will continue transforming investment strategies and decision-making processes.
- Sustainable Investments: There is growing demand for ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) investments as consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability in their financial decisions.
- Global Economic Shifts: Emerging markets are expected to play a larger role in global investments as they recover from recent economic challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions About What Is The Foundation Concept Of Investing
- What is the primary goal of investing?
The primary goal of investing is to grow wealth over time through returns generated from assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate. - How does diversification help reduce risk?
Diversification spreads investments across various asset classes, reducing the impact of poor performance in any single investment. - What are the different types of investment strategies?
Common strategies include value investing, growth investing, index investing, and using robo-advisors for automated management. - How can I assess my risk tolerance?
Risk tolerance can be assessed through questionnaires that evaluate your financial situation, investment goals, and emotional response to market fluctuations. - What role do regulations play in investing?
Regulations help ensure fair practices in the financial markets, protect investors from fraud, and maintain market integrity. - What are some common mistakes new investors make?
Common mistakes include lack of diversification, emotional decision-making during market volatility, and failing to conduct proper research before investing. - How important is it to monitor my investments?
Regular monitoring allows investors to assess performance against goals and make necessary adjustments based on changing market conditions. - What should I consider when creating an investment plan?
Your investment plan should consider your financial goals, time horizon, risk tolerance, and preferred investment vehicles.
This comprehensive exploration into the foundational concepts of investing provides individual investors and finance professionals with essential insights into making informed decisions in today’s complex financial landscape. Understanding these principles not only aids in navigating current market conditions but also prepares investors for future opportunities and challenges.