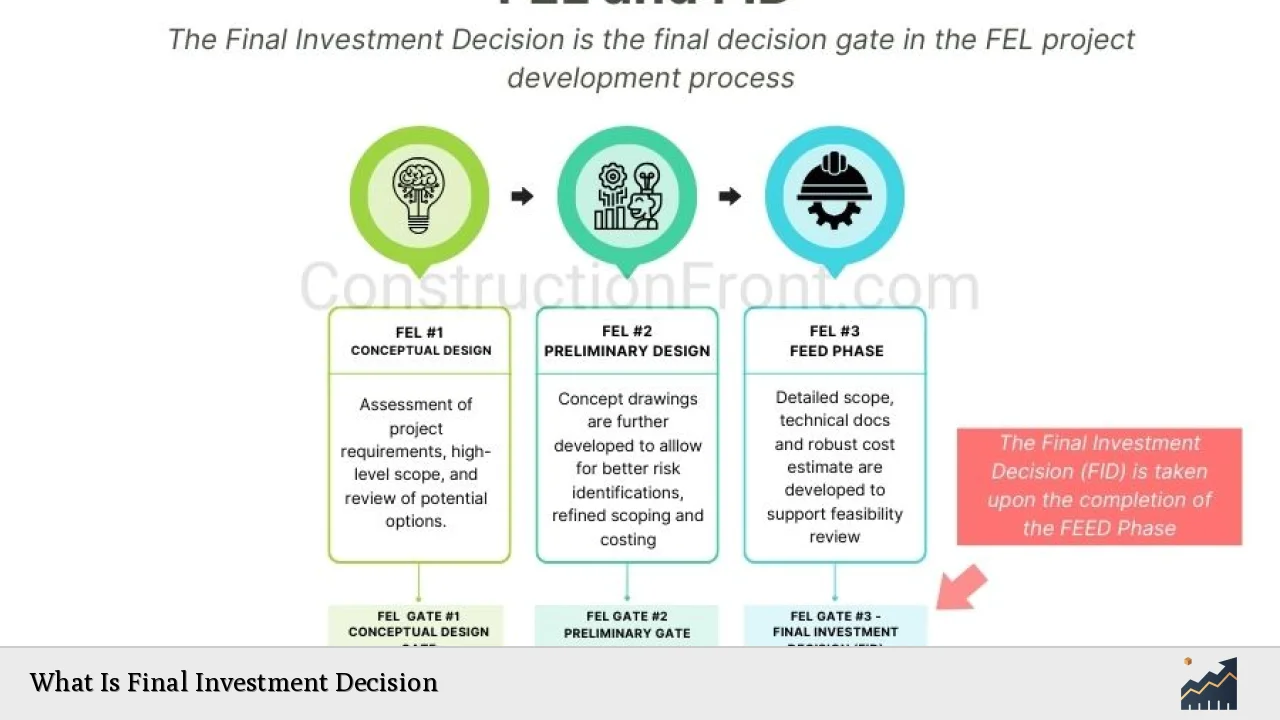
The Final Investment Decision (FID) represents a pivotal moment in the lifecycle of capital projects, particularly in sectors such as energy, infrastructure, and manufacturing. This decision marks the point at which stakeholders commit to significant financial investments, transitioning from the planning phase to full-scale implementation. The FID is crucial as it encapsulates the culmination of extensive feasibility studies, risk assessments, and economic analyses that determine whether a project is viable and aligned with strategic goals.
The FID process involves a thorough evaluation of various factors, including technical feasibility, economic viability, risk management, and regulatory compliance. Once the FID is made, it signals the start of procurement and construction activities, impacting various stakeholders such as investors, contractors, local communities, and governments.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Technical Feasibility | Assessment of whether the project can be executed with available technology and resources. |
| Economic Analysis | Evaluation of financial returns against capital and operational expenditures to justify investment. |
| Risk Assessment | Identification and mitigation strategies for potential risks including market volatility and regulatory changes. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensuring all legal requirements are met before project execution to avoid future liabilities. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Involvement of all relevant parties to ensure alignment and support for the project. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The landscape surrounding FIDs is influenced by several market trends that can significantly impact investment decisions:
- Increased Demand for Renewable Energy: As global energy policies shift towards sustainability, projects related to renewable energy sources are gaining traction. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that renewable energy investments will reach $1 trillion annually by 2030.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in technology are enabling more efficient project execution and monitoring. For instance, advancements in AI and data analytics are helping firms better predict project outcomes and manage risks.
- Global Economic Conditions: The macroeconomic environment plays a crucial role in FIDs. As of mid-2024, global equity markets reached an all-time high of $78.4 trillion, driven by strong performances in technology sectors, particularly those related to AI. However, economic uncertainties such as inflation and geopolitical tensions remain critical considerations.
- Regulatory Changes: The evolving regulatory landscape necessitates that companies stay abreast of compliance requirements. For example, the SEC’s updated regulations on ESG disclosures are impacting investment strategies across sectors.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing a successful FID requires comprehensive planning and execution strategies:
- Detailed Project Planning: Before making an FID, organizations should develop detailed project plans that outline timelines, budgets, resource allocations, and key milestones.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Engaging with stakeholders early in the process helps align interests and secure necessary approvals. This includes collaboration with governmental bodies for regulatory compliance.
- Financial Structuring: Identifying optimal financing structures—such as equity vs. debt financing—can significantly impact the project’s financial health. Companies often form joint ventures to share risks associated with large capital expenditures.
- Monitoring Mechanisms: Establishing robust monitoring systems post-FID ensures that projects remain on track regarding budget and timeline. This includes regular reviews of performance metrics against initial projections.
Risk Considerations
Risk management is essential during the FID process due to the substantial investments involved:
- Market Risks: Fluctuations in commodity prices can affect project viability. For instance, oil price volatility remains a critical factor for energy projects.
- Operational Risks: Delays in construction or unforeseen technical challenges can lead to cost overruns. Implementing contingency plans is vital for mitigating these risks.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in laws or regulations can impact project feasibility. Companies must stay informed about potential regulatory shifts that could affect their operations.
- Environmental Risks: Projects must consider environmental impacts to avoid legal challenges or reputational damage. Conducting thorough environmental assessments before FID is essential.
Regulatory Aspects
Navigating regulatory frameworks is crucial for successful FIDs:
- Permitting Requirements: Securing necessary permits is often one of the most time-consuming aspects of project development. This includes environmental assessments and zoning approvals.
- Compliance Standards: Companies must adhere to local and international standards related to safety, environmental protection, and labor laws.
- Reporting Obligations: Post-FID, companies are often required to report on progress and compliance with regulatory standards. Failure to meet these obligations can result in fines or project delays.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, several factors will shape the future of FIDs:
- Sustainability Focus: As investors increasingly prioritize ESG criteria, projects that align with sustainable practices are likely to attract more funding.
- Technological Integration: The integration of advanced technologies such as blockchain for transparency in transactions will become more prevalent in project financing.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: Global political stability will continue to influence investment flows. Companies must be agile in adapting their strategies based on geopolitical developments.
- Market Recovery Post-Pandemic: As economies recover from COVID-19 impacts, there may be increased capital available for new projects. However, companies must remain cautious about potential economic downturns.
Frequently Asked Questions About Final Investment Decision
- What is a Final Investment Decision?
The Final Investment Decision (FID) is a commitment made by stakeholders to proceed with a capital project after thorough evaluation of its feasibility and risks. - Why is FID important?
The FID signifies a transition from planning to execution for major projects, impacting funding releases and stakeholder confidence. - What factors influence an FID?
Key factors include technical feasibility, economic viability, risk assessment results, stakeholder engagement, and regulatory compliance. - How does market volatility affect FIDs?
Market volatility can impact financial projections and risk assessments; thus companies must consider these factors before making an FID. - What role do stakeholders play in the FID process?
Stakeholders provide essential insights into project viability and help secure necessary approvals; their engagement is crucial for alignment. - How can companies mitigate risks associated with FIDs?
Companies can mitigate risks through detailed planning, stakeholder collaboration, financial structuring, and establishing monitoring mechanisms. - What are common sectors where FIDs are made?
The energy sector (including oil & gas), infrastructure development (such as transportation), and manufacturing are common areas where FIDs occur. - What future trends should investors watch regarding FIDs?
Investors should monitor trends related to sustainability initiatives, technological advancements in project management, and changing regulatory landscapes.
The Final Investment Decision remains a cornerstone in capital investment strategies across industries. Understanding its implications helps investors navigate complex market dynamics while making informed decisions about future opportunities.