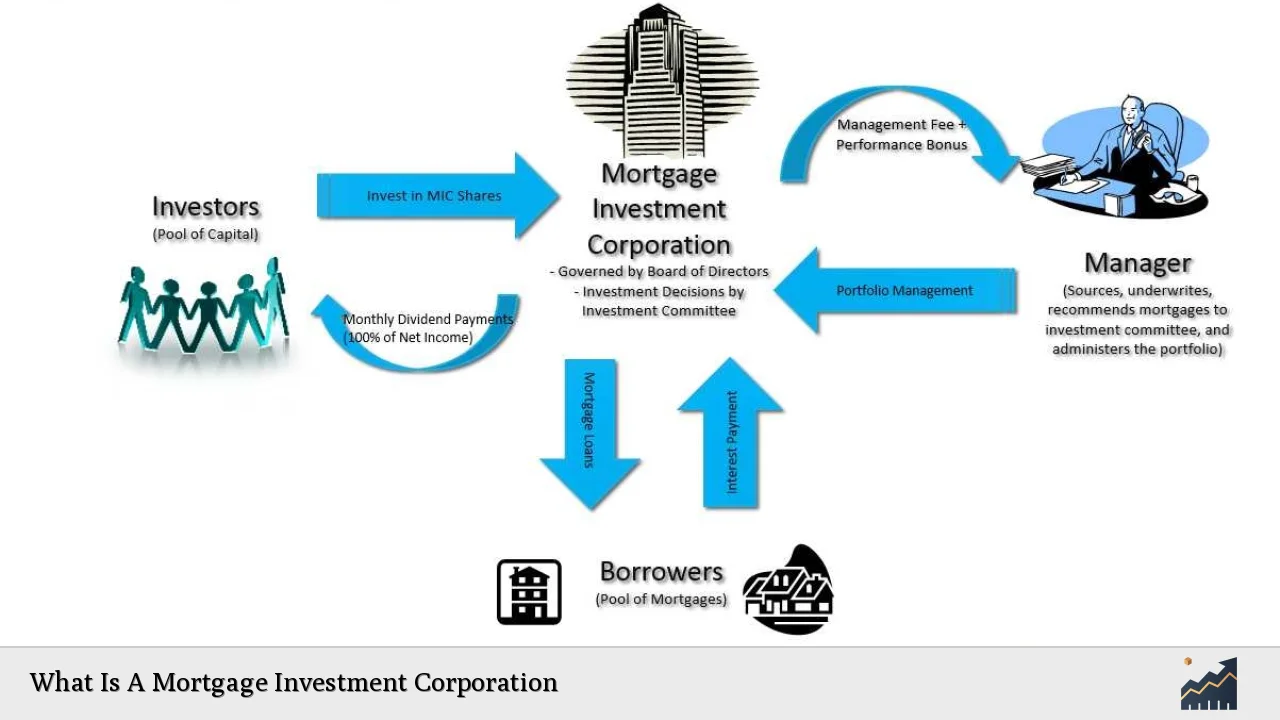
A Mortgage Investment Corporation (MIC) is a unique investment vehicle that allows individuals to pool their funds and invest in a diversified portfolio of mortgages. Originating in Canada through the Income Tax Act of 1973, MICs have become increasingly popular among investors seeking exposure to the real estate market without directly owning property. These corporations offer a way to participate in mortgage lending while potentially benefiting from regular income streams and tax advantages.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Investment Structure | Pooled funds used to invest in a diversified mortgage portfolio |
| Income Generation | Regular dividend payments from mortgage interest and fees |
| Tax Treatment | Flow-through entity, avoiding double taxation |
| Risk Profile | Generally higher risk than traditional fixed-income investments |
| Regulatory Oversight | Subject to specific rules under the Income Tax Act and securities regulations |
Market Analysis and Trends
The MIC market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by several factors:
Low Interest Rate Environment: In the prolonged low interest rate environment, investors have been seeking alternative income-generating investments. MICs have attracted attention due to their potential for higher yields compared to traditional fixed-income securities.
Real Estate Market Dynamics: The Canadian real estate market has remained robust, with property values in major urban centers continuing to appreciate. This trend has increased demand for mortgage financing, benefiting MICs that focus on these markets.
Tightening Bank Lending Standards: As traditional banks have tightened their lending criteria, particularly for self-employed individuals and those with non-traditional income sources, MICs have filled a gap in the market by providing alternative financing options.
According to recent data from the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC), the assets under management of the top 25 MICs in Canada increased by 4.9% year-over-year in the second quarter of 2024, reaching $10.691 billion. This growth outpaced the national residential mortgage debt increase of 3.5% during the same period, indicating a shift in market share towards alternative lenders.
Implementation Strategies
For investors considering MICs, several implementation strategies can be employed:
1. Direct Investment in MIC Shares
Investors can purchase shares in publicly traded MICs listed on stock exchanges or invest in private MICs through offering memorandums. This approach provides direct exposure to the MIC’s mortgage portfolio and dividend stream.
2. MIC Funds
Some mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) specialize in investing across multiple MICs, offering broader diversification and professional management.
3. Registered Account Investments
MIC shares are eligible investments for registered accounts such as RRSPs, RRIFs, and TFSAs in Canada, allowing for tax-advantaged growth or income.
4. Balanced Portfolio Allocation
Financial advisors often recommend allocating a portion of a diversified portfolio to MICs as part of the alternative investment or income-generating segment.
Risk Considerations
While MICs can offer attractive yields, they come with specific risks that investors should carefully consider:
Credit Risk: The quality of the mortgage portfolio is crucial. MICs that lend to higher-risk borrowers or in speculative real estate markets may face increased default rates.
Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can affect the value of the mortgage portfolio and the MIC’s ability to attract capital through new share issuances.
Liquidity Risk: Shares in private MICs may have limited liquidity, potentially making it difficult for investors to sell their holdings quickly.
Market Risk: The overall health of the real estate market can significantly impact MIC performance. A downturn in property values could lead to increased defaults and lower returns.
Regulatory Risk: Changes in tax laws or financial regulations could affect the operational model or tax advantages of MICs.
The CMHC report for Fall 2024 highlighted an increase in the risk profile of MICs, with the average delinquency rate for single-family mortgages rising to 5.0% in Q2 2024, up from 2.7% in Q2 2023. This trend underscores the importance of thorough due diligence when selecting MIC investments.
Regulatory Aspects
MICs in Canada are subject to specific regulatory requirements:
Income Tax Act Compliance: To maintain their tax-advantaged status, MICs must adhere to the rules set out in Section 130.1 of the Income Tax Act, including:
- Having at least 20 shareholders
- Investing at least 50% of funds in residential mortgages, cash, or insured deposits
- Not developing land or engaging in construction activities
- Distributing 100% of taxable income to shareholders annually
Securities Regulations: MICs are subject to provincial securities laws, which govern how they can raise capital and report to investors. Public MICs must comply with stock exchange listing requirements and continuous disclosure obligations.
Mortgage Broker Regulations: In many provinces, MICs engaged in mortgage lending activities must be licensed as mortgage brokers or administrators.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance: MICs are required to implement AML programs and report suspicious transactions to FINTRAC, Canada’s financial intelligence unit.
Future Outlook
The future of MICs is closely tied to broader economic trends and the real estate market:
Interest Rate Environment: With central banks globally navigating inflationary pressures and economic recovery, interest rate movements will play a crucial role in MIC performance. Higher rates could increase yields but may also lead to higher default risks.
Technology Integration: Many MICs are adopting fintech solutions to streamline lending processes and improve risk assessment, potentially leading to more efficient operations and better-quality loan portfolios.
Market Consolidation: As the MIC sector matures, there may be increased consolidation, with larger MICs acquiring smaller players to achieve economies of scale and diversification benefits.
Regulatory Evolution: Ongoing regulatory scrutiny of the alternative lending sector may lead to new rules or guidelines for MICs, potentially impacting operational practices and investor protections.
ESG Considerations: Growing interest in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors may influence MIC lending practices and investor preferences, potentially leading to the emergence of ESG-focused MICs.
As the real estate and financial landscapes continue to evolve, MICs are likely to remain an important part of the Canadian mortgage market. However, investors should remain vigilant, conducting thorough research and potentially seeking professional advice to navigate the complexities of this investment vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions About What Is A Mortgage Investment Corporation
- How do MICs generate returns for investors?
MICs generate returns primarily through interest and fees collected from the mortgages in their portfolio. These earnings are distributed to shareholders as dividends, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis. - Are MICs suitable for all types of investors?
MICs are generally considered more suitable for sophisticated investors who understand the risks involved in real estate lending. They may not be appropriate for conservative investors or those seeking guaranteed income. - How are MIC dividends taxed?
In Canada, MIC dividends are treated as interest income for tax purposes. When held in non-registered accounts, they are taxed at the investor’s marginal tax rate. However, MIC shares held in registered accounts (RRSPs, TFSAs) can benefit from tax-deferred or tax-free growth. - What’s the difference between a public and private MIC?
Public MICs are listed on stock exchanges, offering greater liquidity and transparency. Private MICs are not publicly traded and may have higher minimum investment requirements but potentially offer higher yields. - How do MICs compare to REITs?
While both invest in real estate, MICs focus on mortgage lending, while REITs typically own and operate income-producing properties. MICs often offer higher yields but may carry more risk, especially in terms of credit quality. - Can non-residents invest in Canadian MICs?
Yes, non-residents can invest in Canadian MICs. However, they may be subject to withholding taxes on dividends and should consult with a tax professional regarding their specific situation. - How do economic cycles affect MIC performance?
Economic cycles can significantly impact MICs. During economic downturns, default rates may increase, potentially affecting returns. Conversely, periods of economic growth and rising property values can benefit MICs through increased lending opportunities and lower default rates.