Investing your 401(k) is a crucial step towards securing your financial future in retirement. A 401(k) is a tax-advantaged retirement savings plan sponsored by employers, allowing employees to save and invest a portion of their paycheck before taxes are taken out. When you invest your 401(k), you’re not just saving money; you’re potentially growing your wealth over time through the power of compound interest and market returns.
The decision to invest your 401(k) can have a significant impact on your retirement readiness. By choosing to invest, you’re taking advantage of the opportunity to grow your money faster than it would in a traditional savings account. This growth is essential for keeping pace with inflation and ensuring that your retirement savings maintain their purchasing power over time.
| 401(k) Investment | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Diversified Portfolio | Reduced Risk |
| Compound Interest | Accelerated Growth |
| Tax-Deferred Growth | More Money Working for You |
| Employer Match | Free Money |
Understanding 401(k) Investment Options
When you decide to invest your 401(k), you’ll typically be presented with a range of investment options. These options usually include a mix of mutual funds, which can be broadly categorized into stock funds, bond funds, and balanced funds. Each type of fund comes with its own level of risk and potential for return.
Stock funds, also known as equity funds, invest in shares of companies and tend to offer the highest potential for growth over the long term. However, they also come with higher short-term volatility. These funds can be further divided into categories such as large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap, international, and emerging markets.
Bond funds, on the other hand, invest in fixed-income securities and are generally considered less risky than stock funds. They typically offer more stable, albeit lower, returns. Bond funds can include government bonds, corporate bonds, or a mix of both.
Balanced funds, including target-date funds, offer a mix of stocks and bonds. Target-date funds automatically adjust their asset allocation to become more conservative as you approach retirement age. These funds can be an excellent option for investors who prefer a “set it and forget it” approach to their 401(k) investments.
It’s important to note that your 401(k) plan may also offer other investment options, such as company stock or stable value funds. While company stock can align your interests with your employer’s success, it’s generally recommended to limit your exposure to any single company to reduce risk.
Strategies for Investing Your 401(k)
Developing a sound investment strategy for your 401(k) is crucial for maximizing your retirement savings. Here are some key strategies to consider:
1. Diversification: Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk. This means investing in a mix of stock funds, bond funds, and potentially other asset classes available in your plan.
2. Asset Allocation: Determine the right balance of stocks and bonds based on your risk tolerance and time horizon. Generally, younger investors can afford to take on more risk with a higher allocation to stocks.
3. Regular Rebalancing: Review and adjust your portfolio periodically to maintain your desired asset allocation. This helps ensure that your investment mix stays aligned with your goals as market conditions change.
4. Maximize Employer Match: If your employer offers a match on your contributions, aim to contribute at least enough to take full advantage of this “free money”.
5. Consider Your Risk Tolerance: Choose investments that align with your comfort level for risk. While higher-risk investments may offer greater potential returns, they can also lead to significant losses in the short term.
6. Stay Informed: Educate yourself about the investment options available in your plan and stay updated on any changes or new offerings.
7. Avoid Emotional Decisions: Resist the urge to make drastic changes to your investments based on short-term market fluctuations. Stick to your long-term strategy.
Remember, the key to successful 401(k) investing is to start early and contribute consistently. Even small contributions can grow significantly over time due to the power of compound interest.
The Impact of Fees on Your 401(k) Investments
When investing your 401(k), it’s crucial to be aware of the fees associated with your investment choices. These fees can have a significant impact on your long-term returns. There are two main types of fees to consider:
1. Plan Administration Fees: These are charged by your employer or the plan administrator to cover the costs of running the 401(k) plan. These fees are often paid by the employer but may sometimes be passed on to participants.
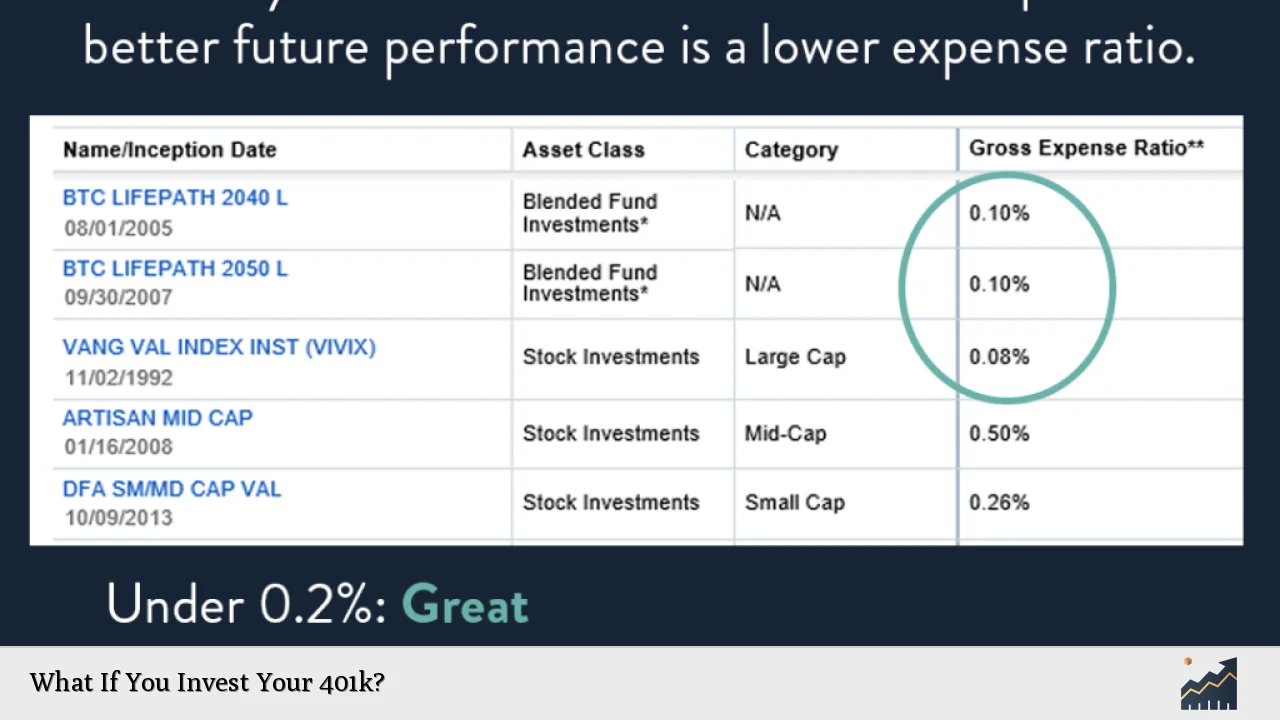
2. Investment Fees: These are charged by the mutual funds or other investment options within your plan. They’re typically expressed as an expense ratio, which is a percentage of your investment that goes towards fund management and other expenses.
Lower fees can make a substantial difference in your retirement savings over time. For example, a difference of just 0.5% in annual fees can result in tens of thousands of dollars more in your account over a 30-year period.
To minimize the impact of fees on your 401(k) investments:
- Choose low-cost index funds when available
- Compare expense ratios among similar fund options
- Be cautious of actively managed funds, which often have higher fees
- Consider whether any additional services or features justify higher fees
It’s important to note that while fees are a crucial consideration, they shouldn’t be the only factor in your investment decisions. The overall performance, risk level, and alignment with your investment goals are equally important factors to consider.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your 401(k) Investments
Investing your 401(k) isn’t a one-time decision; it requires ongoing attention and periodic adjustments. While you don’t need to obsess over daily market movements, it’s important to review your 401(k) investments regularly and make changes when necessary.
A good rule of thumb is to review your 401(k) at least once a year or when you experience significant life changes, such as:
- Getting married or divorced
- Having a child
- Changing jobs
- Approaching retirement
During these reviews, consider the following:
1. Performance: Evaluate how your investments are performing compared to relevant benchmarks. Keep in mind that short-term underperformance doesn’t necessarily indicate a need for change, especially for long-term investments.
2. Asset Allocation: Check if your current asset allocation still aligns with your risk tolerance and time horizon. As you get closer to retirement, you may want to shift towards a more conservative allocation.
3. Contribution Rate: Assess whether you can increase your contribution rate, especially if your income has increased or you’ve paid off debts.
4. New Investment Options: Review any new investment options that may have been added to your plan since your last check-in.
5. Life Changes: Consider how any major life events might impact your retirement goals and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Remember, the goal of monitoring your 401(k) investments is not to react to every market movement but to ensure your investment strategy remains aligned with your long-term goals. If you find the process overwhelming or confusing, consider seeking advice from a financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation.
FAQs About What If You Invest Your 401k
- How much should I contribute to my 401(k)?
Aim to contribute at least enough to get your full employer match, if offered. Ideally, try to save 10-15% of your income for retirement. - Can I lose money in my 401(k)?
Yes, investments can lose value. However, historically, long-term investors have benefited from market growth despite short-term fluctuations. - What happens to my 401(k) if I change jobs?
You can typically roll it over to your new employer’s plan, convert it to an IRA, or leave it with your former employer if allowed. - When can I withdraw money from my 401(k)?
You can typically start withdrawing without penalties at age 59½. Required minimum distributions generally begin at age 72. - Should I invest in a Roth 401(k) if available?
A Roth 401(k) can be beneficial if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement. Consider your current and future tax situations.