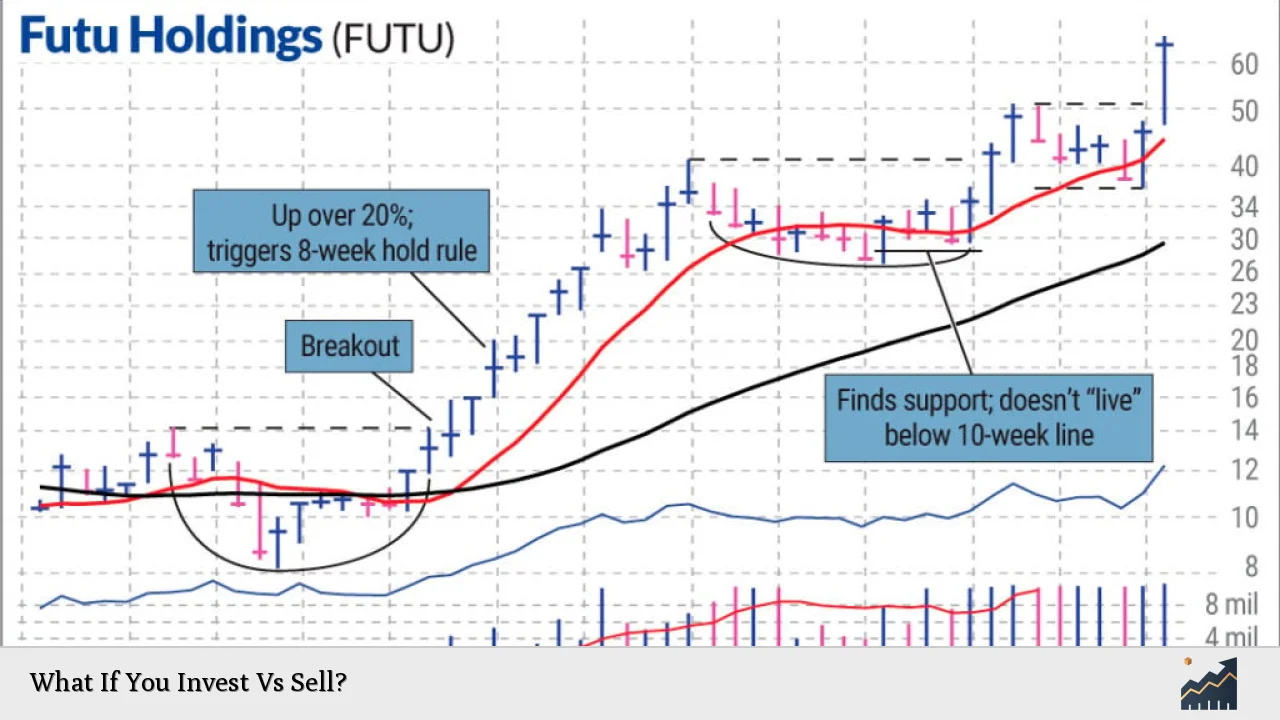
Deciding whether to invest or sell is a crucial consideration for anyone involved in the financial markets. The choice between holding onto an investment for potential future gains or selling it for immediate cash can significantly impact your financial health. This article explores the implications of both strategies, helping investors understand the benefits and risks associated with each option.
Investing typically involves purchasing assets with the expectation of generating returns over time. This strategy is often linked to long-term wealth accumulation, where patience and market understanding play vital roles. Conversely, selling signifies liquidating an asset to realize gains or cut losses. Each approach has its own set of advantages and challenges, which can vary based on individual circumstances and market conditions.
The decision-making process involves analyzing various factors, including market trends, personal financial goals, and risk tolerance. Understanding these elements can guide investors in making informed choices that align with their financial objectives.
| Investing | Selling |
|---|---|
| Focus on long-term growth | Realizing immediate cash flow |
| Potential for compound returns | Mitigating losses on underperforming assets |
| Requires patience and strategy | Involves timing the market |
Understanding Investment Strategies
Investment strategies vary widely, catering to different goals and risk tolerances. Long-term investing is characterized by buying assets and holding them for extended periods, often years or decades. This approach allows investors to benefit from compound interest and market appreciation over time.
Short-term trading, on the other hand, focuses on capitalizing on price fluctuations within shorter timeframes. Traders frequently buy and sell stocks, bonds, or other assets to take advantage of market volatility. While this can lead to quick profits, it also comes with higher risks due to the unpredictable nature of short-term price movements.
Investors must assess their financial goals when choosing a strategy. For those saving for retirement or major life events, a long-term approach may be more appropriate. In contrast, individuals seeking immediate gains might favor short-term trading.
The psychological aspect of investing cannot be overlooked either. Many investors struggle with emotional decision-making, often leading them to sell during downturns or hold onto losing investments in hopes of recovery. Establishing a clear investment plan helps mitigate these emotional responses.
Factors Influencing the Decision to Sell
Several key factors influence whether an investor should sell an asset:
- Market Conditions: Economic indicators and market trends can signal whether it’s time to sell. A declining market may prompt investors to liquidate assets before further losses occur.
- Investment Performance: If an investment consistently underperforms compared to benchmarks or peers, it may be time to consider selling.
- Financial Needs: Personal circumstances such as job loss, medical expenses, or major purchases can necessitate selling investments for cash flow.
- Tax Considerations: Selling investments can have tax implications that affect overall profitability. Investors should consider potential capital gains taxes when deciding to sell.
- Portfolio Rebalancing: Over time, certain investments may grow disproportionately within a portfolio. Selling some assets allows investors to rebalance their holdings according to their risk tolerance and investment strategy.
Understanding these factors can help investors make informed decisions about when to sell their investments.
The Risks of Holding Investments
While investing offers potential rewards, it also carries inherent risks that investors must acknowledge:
- Market Volatility: The stock market can be unpredictable, with prices fluctuating based on various factors such as economic data, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment.
- Opportunity Cost: By holding onto underperforming investments, investors may miss out on better opportunities elsewhere.
- Emotional Stress: Watching investments decline in value can lead to anxiety and poor decision-making if not managed properly.
Investors should regularly evaluate their portfolios and consider whether holding certain assets aligns with their overall financial strategy.
Advantages of Long-Term Investing
Long-term investing presents several advantages that appeal to many individuals:
- Compound Growth: Over time, investments can grow exponentially through compound interest and reinvested earnings.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Frequent trading incurs transaction fees that can erode profits. Long-term investing minimizes these costs.
- Tax Benefits: Holding investments for over a year typically qualifies for lower capital gains tax rates compared to short-term trades.
- Reduced Stress: A long-term perspective helps investors avoid the emotional rollercoaster associated with daily market fluctuations.
By focusing on long-term growth rather than short-term gains, investors can build substantial wealth over time while minimizing stress associated with constant trading.
The Case for Selling Investments
Selling investments can be just as strategic as buying them. Here are some reasons why selling might be beneficial:
- Realizing Gains: If an investment has significantly appreciated in value, selling allows investors to lock in profits before potential declines occur.
- Cutting Losses: When an investment consistently underperforms or shows signs of fundamental weakness, selling can prevent further losses.
- Reallocating Capital: Selling enables investors to free up capital for new opportunities that may offer better returns or align more closely with their investment goals.
- Adjusting Risk Exposure: As markets change, so do individual risk tolerances. Selling certain assets helps maintain a balanced portfolio aligned with current risk preferences.
Understanding when and why to sell is crucial for maintaining a healthy investment portfolio.
Emotional Considerations in Investing
Emotions play a significant role in investment decisions. Fear and greed often drive behavior in financial markets:
- Fear of Loss: Many investors panic during market downturns and sell at a loss rather than waiting for recovery.
- Greed for Gains: Conversely, the desire for quick profits can lead some investors to hold onto winning stocks too long without considering market fundamentals.
Developing a disciplined approach helps mitigate these emotional influences. Establishing clear exit strategies based on predetermined criteria can guide decisions about when to sell without succumbing to emotional impulses.
Balancing Investment Strategies
Finding the right balance between investing and selling is essential for achieving financial goals:
- Diversification: A well-diversified portfolio reduces risk by spreading investments across various asset classes and sectors.
- Regular Review: Periodically reviewing investment performance helps identify underperforming assets that may need selling or reallocating funds into higher-performing areas.
- Clear Goals: Setting specific financial goals allows investors to tailor their strategies accordingly—whether focusing on long-term growth or short-term gains through strategic selling.
Balancing these elements ensures that an investor’s approach remains aligned with their overall financial objectives while adapting to changing market conditions.
FAQs About What If You Invest Vs Sell
- What are the main differences between investing and selling?
Investing focuses on acquiring assets for long-term growth while selling involves liquidating those assets for immediate cash flow. - When should I consider selling my investments?
You should consider selling if your investment underperforms significantly or if you need cash for personal reasons. - How does emotional decision-making affect investing?
Emotional decision-making can lead to impulsive actions like panic selling during downturns or holding onto losing investments too long. - What are the benefits of long-term investing?
The benefits include compound growth potential, lower transaction costs, tax advantages, and reduced stress. - How often should I review my investment portfolio?
You should review your portfolio regularly—at least annually—to ensure it aligns with your financial goals.
In conclusion, whether you choose to invest or sell depends on various factors including personal financial goals, market conditions, and emotional resilience. Understanding both strategies allows you to make informed decisions that align with your overall financial objectives while navigating the complexities of the investment landscape effectively.