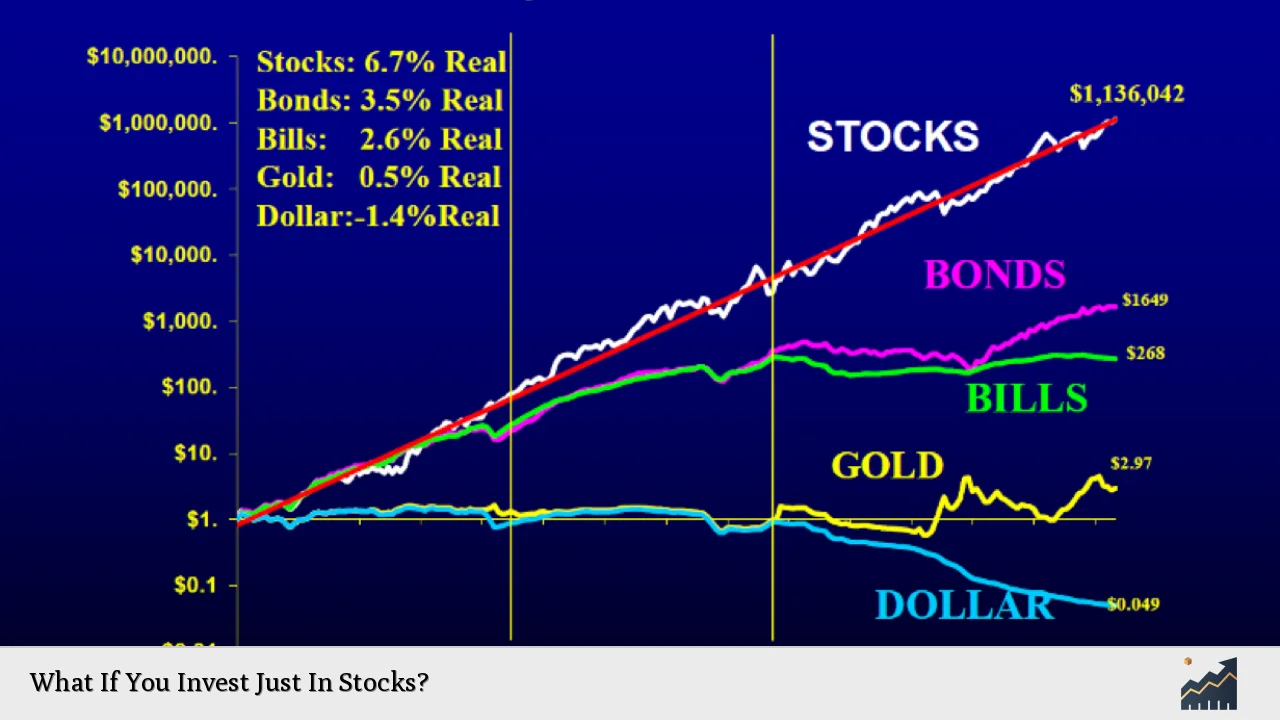
Investing solely in stocks can be a compelling strategy for individuals looking to grow their wealth over time. Stocks represent ownership in a company, and investing in them allows you to participate in the company’s growth and profits. However, this approach comes with its own set of risks and rewards that investors need to understand thoroughly.
When you invest in stocks, you essentially buy shares of a company, hoping that its value will increase over time. The stock market can be volatile, with prices fluctuating based on various factors such as economic conditions, company performance, and investor sentiment. Therefore, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of how stock investments work, the potential benefits, and the inherent risks involved.
This article will explore the implications of investing exclusively in stocks, including strategies for success, types of stocks to consider, and the importance of diversification. We will also discuss potential pitfalls and how to navigate them effectively.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Ownership | Buying shares means owning a part of the company. |
| Growth Potential | Stocks can provide significant returns over time. |
| Volatility | Stock prices can fluctuate widely. |
Understanding Stock Investments
Investing in stocks involves purchasing shares from publicly traded companies. When you buy a stock, you become a partial owner of that company. This ownership entitles you to a portion of the profits, typically distributed as dividends. Stocks are categorized into various types based on characteristics such as growth potential and risk level.
The primary types of stocks include:
- Common Stocks: These are the most common type of stock that investors buy. Common shareholders have voting rights but are last in line during liquidation.
- Preferred Stocks: These stocks provide dividends before common stocks and have priority over assets in case of liquidation but usually do not carry voting rights.
- Growth Stocks: Companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market. They typically reinvest earnings rather than paying dividends.
- Value Stocks: These are undervalued stocks that trade for less than their intrinsic value, offering potential for appreciation.
- Dividend Stocks: Companies that return a portion of profits to shareholders regularly through dividends.
Investing solely in stocks can lead to high returns but also exposes investors to significant risks. Understanding these categories helps investors make informed decisions based on their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Advantages of Investing in Stocks
Investing in stocks offers several advantages that can contribute to wealth accumulation:
- High Potential Returns: Historically, stocks have outperformed other asset classes like bonds and real estate over long periods.
- Liquidity: Stocks are generally easy to buy and sell on exchanges, providing flexibility for investors who may need quick access to cash.
- Ownership Benefits: As a shareholder, you have voting rights and can influence corporate decisions at annual meetings.
- Dividends: Many companies pay dividends, providing income alongside capital appreciation.
- Diversification Opportunities: Investing in different sectors or industries can spread risk while maximizing returns.
While these advantages are appealing, it’s essential to approach stock investments with caution and a well-thought-out strategy.
Risks Associated with Stock Investments
Despite the potential benefits, investing solely in stocks carries inherent risks:
- Market Volatility: Stock prices can fluctuate significantly due to market conditions or economic factors, leading to potential losses.
- Company-Specific Risks: Poor performance by a single company can negatively impact your investment portfolio if heavily concentrated in one stock.
- Lack of Diversification: Focusing only on stocks may expose you to higher risks compared to a diversified portfolio that includes bonds or other assets.
- Emotional Decision-Making: Investors may react emotionally during market downturns, leading to impulsive decisions that could harm long-term performance.
Understanding these risks is crucial for developing an effective investment strategy that aligns with your financial goals.
Strategies for Successful Stock Investing
To maximize your chances of success when investing solely in stocks, consider implementing these strategies:
- Buy and Hold Strategy: This long-term approach involves purchasing stocks and holding them for several years or decades. It allows you to ride out market fluctuations and benefit from compounding returns over time.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: This strategy involves investing a fixed amount regularly regardless of market conditions. It reduces the impact of volatility by averaging out purchase costs over time.
- Research and Analysis: Conduct thorough research on companies before investing. Analyze financial statements, industry trends, and market conditions to make informed decisions.
- Set Clear Goals: Define your investment objectives clearly—whether it’s capital appreciation, income generation through dividends, or both—and tailor your strategy accordingly.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market news and developments related to your investments. Staying informed allows you to adjust your strategy as needed based on changing circumstances.
Implementing these strategies can help mitigate risks while enhancing your chances for profitable stock investments.
The Importance of Diversification
While this article focuses on investing solely in stocks, it is vital to understand the role of diversification within this context. Diversification involves spreading investments across various securities or sectors rather than concentrating on a single stock or industry.
Benefits of diversification include:
- Risk Reduction: By holding different types of stocks across various sectors (e.g., technology, healthcare), you reduce exposure to any single company’s poor performance.
- Smoother Returns: A diversified portfolio tends to experience less volatility compared to individual stock holdings since losses in one area may be offset by gains in another.
- Access to Different Growth Opportunities: Investing across sectors allows you to capitalize on growth trends across various industries rather than being limited to one area.
Even if you choose not to diversify outside stocks, consider diversifying within your stock portfolio by investing in different sectors or types of companies (e.g., growth vs. value).
Conclusion
Investing solely in stocks can be a rewarding venture if approached with knowledge and strategy. Understanding the types of stocks available, recognizing the advantages and risks associated with stock investments, and implementing sound investment strategies are crucial steps toward achieving financial success through the stock market.
While focusing exclusively on stocks may seem appealing due to their growth potential, it is essential not to overlook the importance of diversification within your stock portfolio. By carefully selecting your investments and staying informed about market trends, you can navigate the complexities of stock investing effectively.
FAQs About Investing Just In Stocks
- What are the benefits of investing only in stocks?
Investing only in stocks offers high potential returns and liquidity. - What types of stocks should I consider?
Consider common stocks, preferred stocks, growth stocks, value stocks, and dividend-paying stocks. - How do I manage risk when investing in stocks?
Manage risk by diversifying within your stock portfolio and setting clear investment goals. - Is it wise to invest all my money in stocks?
It’s generally advisable not to invest all your money in one asset class; diversification is key. - What strategies can enhance my stock investment success?
Consider strategies like buy-and-hold and dollar-cost averaging for better outcomes.