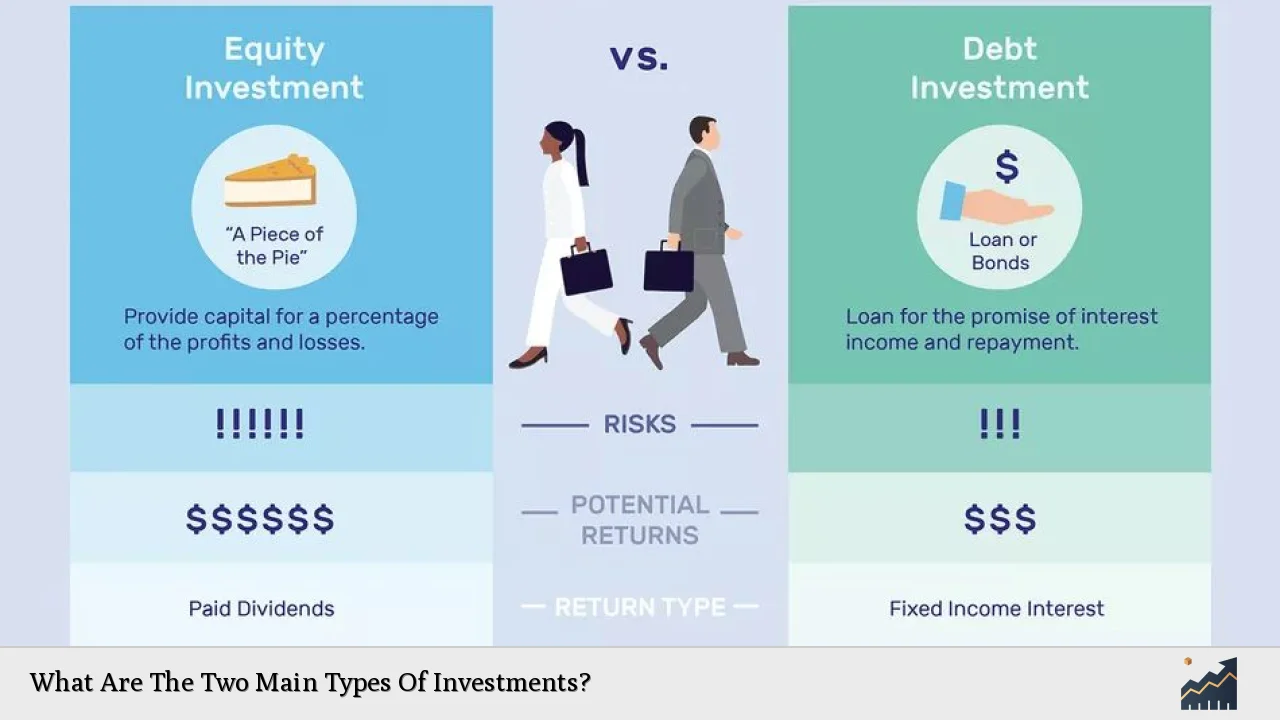
Investing is a fundamental aspect of personal finance that allows individuals to grow their wealth over time. Understanding the different types of investments is crucial for making informed financial decisions. The two main types of investments are equity investments and fixed-income investments. Each type has unique characteristics, risk profiles, and potential returns, making them suitable for different investment strategies and goals.
Equity investments involve purchasing shares of a company, giving investors ownership stakes in that company. This type of investment can yield high returns, especially in a growing economy, but it also carries higher risks due to market volatility. Conversely, fixed-income investments, such as bonds, provide more stable returns and lower risk. They involve lending money to an entity in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal at maturity.
Understanding these two main types of investments is essential for anyone looking to build a diversified portfolio that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
| Type of Investment | Description |
|---|---|
| Equity Investments | Ownership in a company through stocks; potential for high returns but higher risk. |
| Fixed-Income Investments | Lending money to entities (governments or corporations) for interest payments; lower risk and stable returns. |
Equity Investments
Equity investments represent ownership in a company through the purchase of its stock. When you buy shares, you become a shareholder and have a claim on the company's assets and earnings. Equity investments can be further categorized into common stocks and preferred stocks.
Common stocks are the most prevalent form of equity investment. Shareholders benefit from price appreciation as the company's value increases and may receive dividends—periodic payments made from the company's profits. The potential for high returns exists, especially if the company performs well; however, common stockholders are last in line during liquidation events.
Preferred stocks offer a different set of benefits. These stocks typically provide fixed dividends and have priority over common stocks in asset liquidation. While preferred stockholders enjoy more stability in dividend payments, they usually do not have voting rights.
Investing in equities can be done directly by purchasing individual stocks or indirectly through investment vehicles like mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These funds pool money from multiple investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, reducing individual risk while providing exposure to various companies.
Despite their potential for high returns, equity investments come with significant risks:
- Market Volatility: Stock prices can fluctuate dramatically based on market conditions.
- Company Performance: Poor performance by the company can lead to losses.
- Economic Factors: Broader economic downturns can negatively impact stock values.
Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance when investing in equities and may choose to diversify their portfolios across various sectors to mitigate risks.
Fixed-Income Investments
Fixed-income investments are debt securities that provide investors with regular interest payments until maturity when the principal amount is returned. These investments are generally considered safer than equities and include various instruments such as bonds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and money market accounts.
Bonds are one of the most common forms of fixed-income investment. When you purchase a bond, you are essentially lending money to an issuer—such as a corporation or government—in exchange for periodic interest payments known as coupon payments. Bonds come with different maturities ranging from short-term (a few months) to long-term (several years), each offering varying levels of risk and return.
Certificates of deposit (CDs) are another fixed-income option offered by banks. They typically provide higher interest rates than regular savings accounts but require you to lock your funds for a specified period. Money market accounts offer liquidity with slightly higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts but usually lower than CDs.
The advantages of fixed-income investments include:
- Predictable Income: Investors receive regular interest payments.
- Capital Preservation: Fixed-income securities tend to be less volatile than stocks.
- Diversification: Including fixed-income assets can balance out the risks associated with equities.
However, fixed-income investments also come with risks:
- Interest Rate Risk: Rising interest rates can decrease bond prices.
- Credit Risk: The issuer may default on payments.
- Inflation Risk: Fixed income may not keep pace with inflation over time.
Investors often use fixed-income securities to create a balanced portfolio that provides steady income while mitigating risks associated with equity investments.
Comparison Between Equity and Fixed-Income Investments
To better understand the differences between equity and fixed-income investments, here’s a comparison table:
| Feature | Equity Investments | Fixed-Income Investments |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Ownership stake in a company | Lending money to an entity |
| Return Potential | Higher potential returns | Stable but lower returns |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to market volatility | Lower risk but subject to interest rate changes |
| Income Generation | Dividends based on company profits | Regular interest payments |
| Liquidity | Generally liquid; can be sold easily on exchanges | Varies; some may have penalties for early withdrawal (e.g., CDs) |
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the two main types of investments—equity and fixed income—is vital for anyone looking to build wealth through investing. Equity investments offer the potential for high returns but come with higher risks due to market fluctuations. On the other hand, fixed-income investments provide more stability and predictable income but typically yield lower returns.
Investors should assess their financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon when deciding how to allocate their assets between these two types of investments. A well-balanced portfolio often includes both equities and fixed-income securities, allowing investors to take advantage of growth opportunities while managing risks effectively.
FAQs About Types Of Investments
- What are equity investments?
Equity investments involve buying shares in a company, giving investors ownership stakes that can yield high returns. - What are fixed-income investments?
Fixed-income investments involve lending money to entities like governments or corporations for regular interest payments. - How do I choose between equity and fixed-income investments?
Your choice should depend on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. - Can I invest in both types simultaneously?
Yes, many investors use a combination of both equity and fixed-income investments for diversification. - What is the main risk associated with equity investing?
The main risk is market volatility, which can lead to significant fluctuations in stock prices.
By understanding these fundamental concepts about equity and fixed-income investments, individuals can make informed choices that align with their financial aspirations and create robust investment strategies for future success.