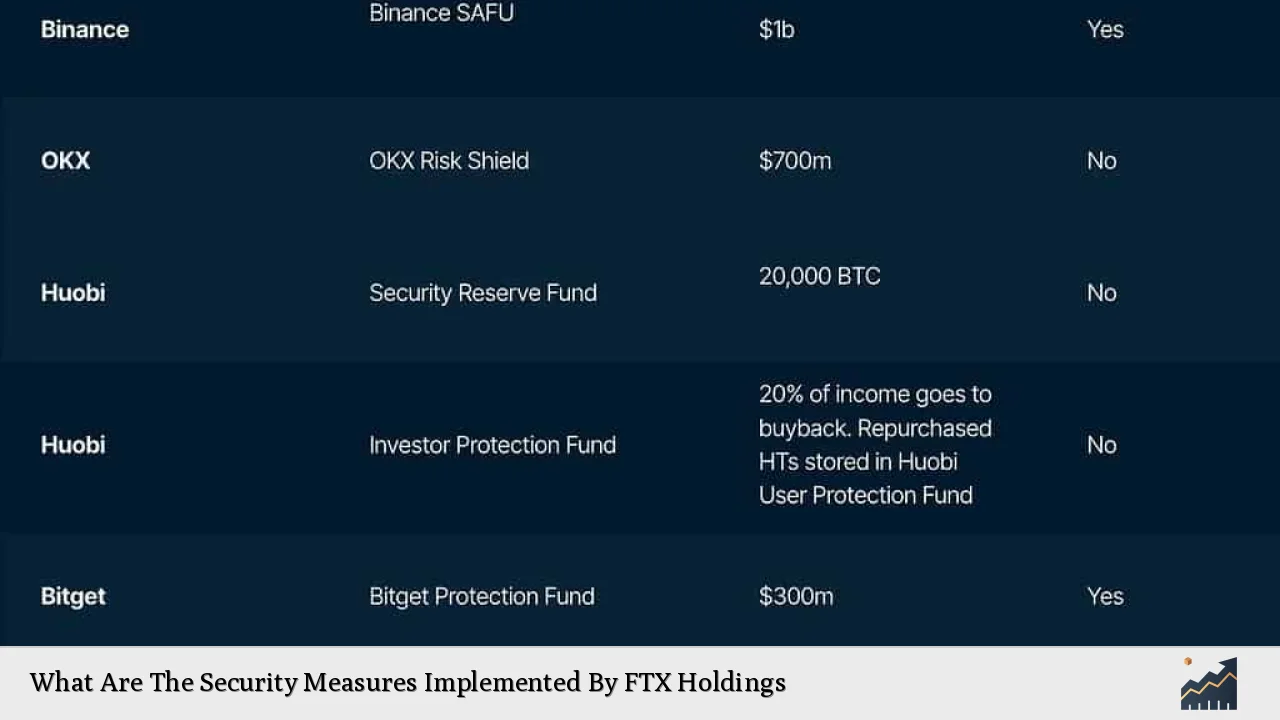
FTX Holdings, once a leading cryptocurrency exchange, implemented various security measures aimed at safeguarding user assets and maintaining operational integrity. However, the effectiveness of these measures has been called into question following the exchange’s dramatic collapse in late 2022. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the security protocols that were in place, the failures that led to significant losses, and the lessons learned from FTX’s experience.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Mandatory for user transactions to enhance account security. |
| Cold Wallet Storage | Intended to protect funds by keeping them offline; however, FTX relied heavily on hot wallets. |
| Withdrawal Locks | Temporarily disabled withdrawals after changes to account settings for added security. |
| API Key Whitelisting | Allowed users to restrict access to their accounts through specified IP addresses. |
| Transaction Monitoring | Partnership with Chainalysis for real-time monitoring of suspicious transactions. |
| Lack of Dedicated Security Team | No specialized personnel for cybersecurity, leading to inadequate risk management. |
| Hot Wallet Vulnerabilities | A significant portion of assets stored in hot wallets, exposing them to theft. |
| Inadequate Private Key Management | Private keys stored insecurely, increasing risk of unauthorized access. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The cryptocurrency market has evolved rapidly, with exchanges like FTX playing a pivotal role in its growth. As of late 2023, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization is approximately $1 trillion, reflecting a volatile yet resilient ecosystem. The demand for secure trading platforms has surged as investors become increasingly aware of security risks associated with digital assets.
Recent trends indicate a growing emphasis on regulatory compliance and enhanced security measures across the industry. Following FTX’s collapse, there has been heightened scrutiny on exchanges regarding their operational transparency and risk management practices. Investors are now prioritizing platforms that demonstrate robust security protocols and compliance with regulatory standards.
Implementation Strategies
FTX employed several strategies intended to protect user funds and enhance platform security:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This feature was mandatory for all transactions, adding an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a secondary device.
- Cold Wallet Storage: While FTX claimed to utilize cold wallets for storing digital assets, reports indicated that a significant amount remained in hot wallets, which are more vulnerable to attacks.
- Withdrawal Locks: To prevent unauthorized withdrawals, FTX implemented withdrawal locks that activated upon changes to account settings. This measure was meant to deter fraud but was insufficient against systemic vulnerabilities.
- API Key Whitelisting: Users could specify IP addresses allowed to access their accounts via API keys, enhancing control over account access.
- Monitoring and Compliance: FTX partnered with Chainalysis for transaction monitoring, aiming to detect suspicious activities in real-time.
Despite these measures, critical failures in execution led to substantial losses. The absence of a dedicated cybersecurity team and reliance on outdated technology significantly undermined these strategies.
Risk Considerations
The collapse of FTX highlighted several key risks associated with its operational framework:
- Cybersecurity Risks: The lack of a dedicated cybersecurity team resulted in inadequate monitoring and response capabilities. Critical vulnerabilities included outdated software and poorly managed access controls.
- Asset Management Risks: A heavy reliance on hot wallets left the majority of customer assets exposed. Reports indicated that private keys were stored insecurely, increasing the likelihood of theft or unauthorized access.
- Operational Risks: The absence of structured governance and risk management policies contributed to mismanagement of customer funds and operational chaos leading up to the bankruptcy filing.
These risks not only affected FTX but also had broader implications for investor confidence in cryptocurrency exchanges as a whole.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrency exchanges has become increasingly stringent following high-profile failures like that of FTX. Key regulatory considerations include:
- Customer Protection Rules: Regulatory bodies are now emphasizing the need for custodians to segregate customer funds from company assets. This is crucial in preventing misuse or misappropriation of funds.
- Compliance Requirements: Exchanges are expected to meet minimum capital requirements and maintain rigorous reporting standards. This includes regular audits and transparency regarding operational practices.
- Enhanced Oversight: Regulatory agencies are actively working towards developing comprehensive frameworks that address the unique challenges posed by digital asset markets. This includes collaboration between international regulators to ensure cohesive oversight.
The fallout from FTX’s collapse serves as a catalyst for regulatory reform aimed at enhancing consumer protection and restoring trust in the cryptocurrency market.
Future Outlook
The future of cryptocurrency exchanges will likely be shaped by lessons learned from the FTX debacle:
- Increased Investment in Security: Exchanges will need to prioritize cybersecurity measures by employing dedicated teams and adopting best practices for asset management.
- Regulatory Compliance as Competitive Advantage: Platforms that proactively comply with evolving regulations will likely gain investor trust and market share over those that do not prioritize compliance.
- Focus on Transparency: Investors will demand greater transparency regarding how exchanges manage their assets and handle customer funds. Clear communication about security protocols will be essential for rebuilding confidence in the sector.
As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to mature, it is imperative that exchanges learn from past mistakes and implement robust frameworks that prioritize security and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Security Measures Implemented By FTX Holdings
- What were the main security features used by FTX?
FTX implemented two-factor authentication (2FA), withdrawal locks, API key whitelisting, and partnered with Chainalysis for transaction monitoring. - Why did FTX fail despite having security measures?
The failure stemmed from inadequate execution of these measures, including reliance on hot wallets and lack of a dedicated cybersecurity team. - What lessons can other exchanges learn from FTX’s collapse?
Exchanges should prioritize cybersecurity investments, ensure regulatory compliance, and maintain transparency with users about asset management practices. - How did regulatory bodies respond after FTX’s bankruptcy?
Regulatory bodies have increased scrutiny on cryptocurrency exchanges, emphasizing customer protection rules and enhanced oversight mechanisms. - What is cold storage, and why is it important?
Cold storage refers to keeping cryptocurrencies offline to protect them from hacking attempts; it is crucial for securing large amounts of digital assets. - Are there any ongoing legal consequences for FTX?
The founders face multiple legal challenges including fraud charges; ongoing investigations continue into the financial practices at FTX. - How can investors protect themselves when using exchanges?
Investors should choose exchanges with strong security protocols, enable 2FA, monitor account activity regularly, and understand withdrawal policies. - What impact did FTX’s collapse have on the cryptocurrency market?
The collapse led to decreased investor confidence across the market and prompted calls for stricter regulations within the cryptocurrency sector.
This comprehensive analysis highlights both the implemented security measures at FTX Holdings and the critical failures that led to its downfall. By understanding these elements, investors can better navigate the evolving landscape of cryptocurrency trading while advocating for stronger protections within this dynamic market.