Investing is a fundamental aspect of personal finance and wealth building, but it comes with inherent risks that every investor must understand. The potential for financial gain is often accompanied by the possibility of loss. Recognizing these risks is crucial for making informed decisions and developing effective investment strategies. This article will explore the various risks associated with investing, their implications, and how to manage them effectively.
Understanding investment risks involves acknowledging the uncertainty and potential financial loss associated with various investment decisions. Each type of investment carries its unique set of risks, influenced by market conditions, economic factors, and individual circumstances. By identifying these risks, investors can better prepare themselves to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape.
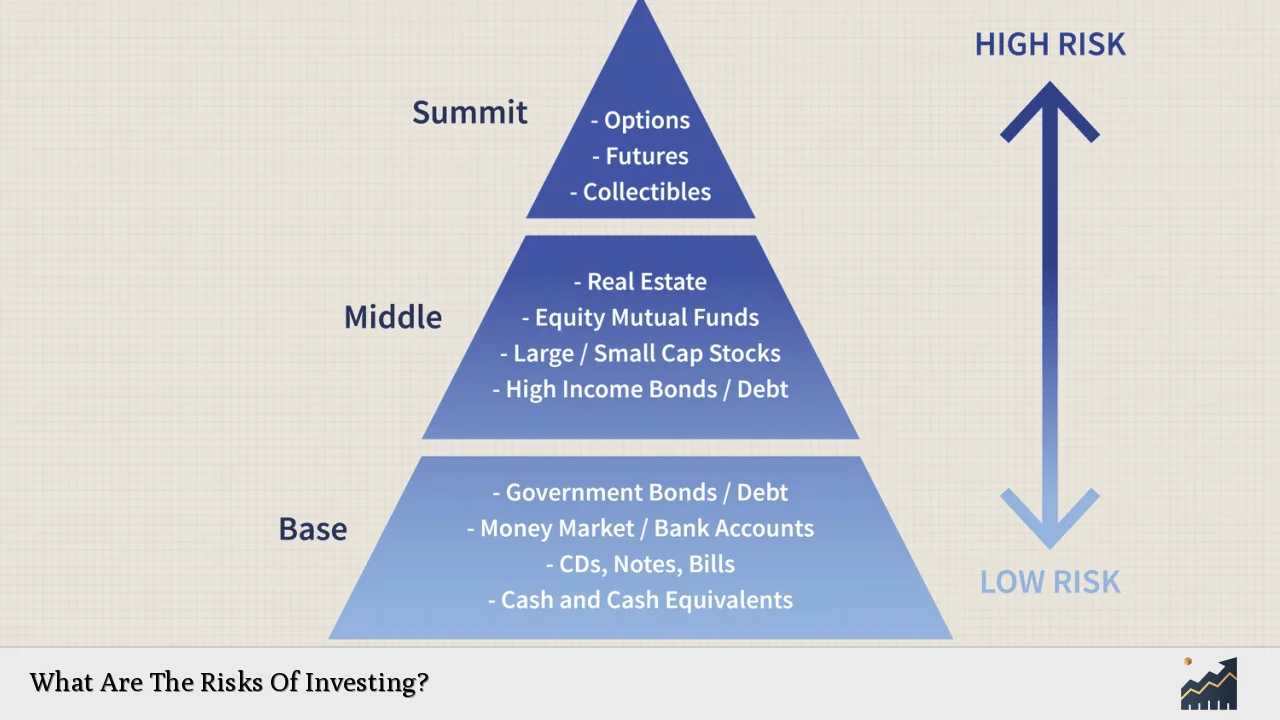
Investors must be aware that risk is not inherently negative; it is a necessary component of the investment process. Higher potential returns typically come with higher risks. Thus, understanding one’s risk tolerance is essential in aligning investment choices with personal financial goals.
| Type of Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Risk | Risk of losses due to market fluctuations. |
| Credit Risk | Risk of default by a borrower or issuer. |
| Liquidity Risk | Risk of not being able to sell an asset quickly. |
| Inflation Risk | Risk that inflation erodes purchasing power. |
| Concentration Risk | Risk from overexposure to a single investment. |
Market Risk
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, refers to the potential for losses due to overall market movements. This type of risk cannot be eliminated through diversification because it affects all investments across the board. Factors contributing to market risk include economic downturns, political instability, changes in interest rates, and natural disasters.
Investors must understand that market risk can lead to significant fluctuations in the value of their portfolios. For instance, during economic recessions, stock prices may plummet across various sectors, impacting even well-performing companies.
To manage market risk effectively, investors should consider diversifying their portfolios across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and economic indicators can help investors make timely decisions that mitigate potential losses.
Credit Risk
Credit risk arises when an issuer or borrower fails to meet their financial obligations. This risk is particularly relevant for bondholders who rely on regular interest payments from issuers. If a company or government defaults on its debt, investors may lose part or all of their invested capital.
To assess credit risk, investors should review the credit ratings assigned to bonds or other debt instruments by reputable agencies. A higher credit rating indicates a lower likelihood of default. Investors can also diversify their fixed-income investments by including bonds from various issuers and sectors to spread out credit exposure.
It’s important for investors to conduct thorough due diligence before investing in any debt instruments. Understanding the financial health and stability of issuers can significantly reduce exposure to credit risk.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the challenge of quickly buying or selling an asset without causing a significant impact on its price. This risk is particularly pertinent in markets where assets may not have a ready buyer or seller at any given time.
For example, real estate investments often entail liquidity risk since selling property can take time and may require price concessions. Similarly, certain types of stocks or bonds may have low trading volumes, making them difficult to sell quickly without incurring losses.
Investors can manage liquidity risk by maintaining a portion of their portfolio in liquid assets such as cash or publicly traded securities that are easily convertible into cash. Additionally, understanding the liquidity profile of each investment before committing funds can help avoid situations where quick access to capital is needed.
Inflation Risk
Inflation risk represents the danger that rising prices will erode the purchasing power of money over time. When inflation outpaces investment returns, investors find that their real returns are diminished.
For instance, if an investor holds cash or fixed-income securities with low-interest rates during periods of high inflation, they may effectively lose money in terms of purchasing power.
To combat inflation risk, investors should consider assets that historically outpace inflation over the long term, such as equities or real estate. Additionally, inflation-protected securities (like TIPS) can provide a hedge against rising prices.
Concentration Risk
Concentration risk occurs when an investor has a significant portion of their portfolio invested in a single asset or sector. This lack of diversification can lead to substantial losses if that particular investment performs poorly.
For example, if an investor heavily invests in one stock or industry—such as technology—and that sector experiences a downturn, the investor could face significant financial hardship.
To mitigate concentration risk, diversification is key. Investors should spread their investments across various sectors and asset classes to reduce exposure to any single investment’s performance. Regular portfolio reviews can also help ensure that no single investment dominates the portfolio.
Managing Investment Risks
Effectively managing investment risks requires a proactive approach involving several strategies:
- Diversification: Spread investments across different asset classes and sectors.
- Research: Conduct thorough research on potential investments.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess your risk tolerance and adjust your portfolio accordingly.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with market trends and economic indicators.
- Professional Advice: Consider consulting with financial advisors for personalized guidance.
By employing these strategies, investors can better navigate the complexities associated with investing while minimizing potential losses.
FAQs About Risks Of Investing
- What are the main risks associated with investing?
The main risks include market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, inflation risk, and concentration risk. - How can I manage market risk?
Diversifying your portfolio across various asset classes can help mitigate market risk. - What is liquidity risk?
Liquidity risk refers to the difficulty in quickly buying or selling an asset without affecting its price significantly. - Why is credit risk important?
Credit risk is important because it affects the likelihood of receiving promised payments from borrowers. - How does inflation impact investments?
Inflation erodes purchasing power; if investments do not outpace inflation rates, real returns diminish.
Understanding these risks is essential for anyone looking to invest wisely. By being aware of potential pitfalls and employing effective management strategies, investors can enhance their chances of achieving their financial goals while minimizing adverse outcomes associated with investing.