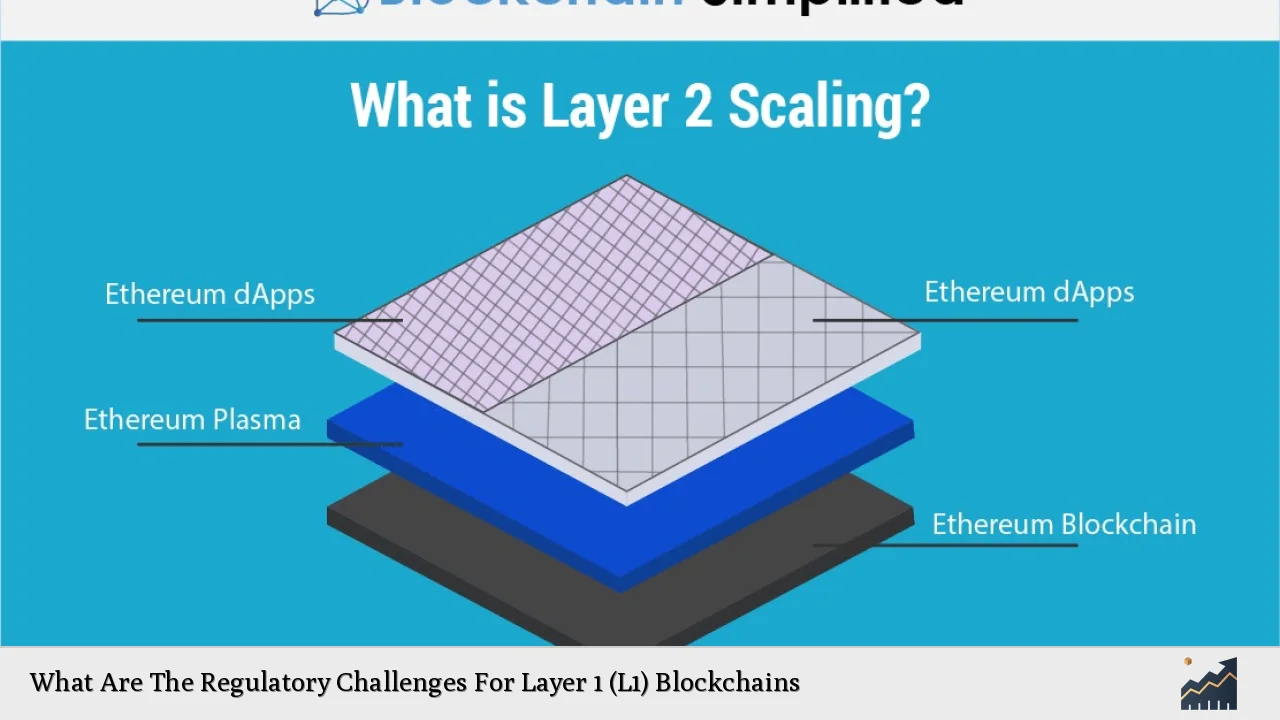
Layer 1 (L1) blockchains form the foundational layer of blockchain technology, responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the integrity of the network. With the increasing adoption of cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications, L1 blockchains face significant regulatory challenges that can impact their operation, growth, and overall market stability. This article delves into these challenges, providing a comprehensive analysis of the current landscape, implementation strategies, and future outlook.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Fragmentation | The lack of a unified regulatory framework across jurisdictions complicates compliance for L1 blockchains, leading to uncertainty and potential legal risks. |
| KYC/AML Compliance | Implementing Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols is essential but challenging due to the decentralized nature of L1 networks. |
| Consumer Protection | Regulatory bodies are increasingly focused on protecting consumers from fraud and market manipulation within the cryptocurrency space. |
| Taxation Issues | The classification of digital assets for tax purposes remains unclear, leading to compliance difficulties for L1 blockchain operators. |
| Technological Adaptation | As technology evolves, regulations must adapt, creating a lag that can hinder innovation and market growth. |
| Global Coordination | Effective regulation requires international cooperation to address cross-border issues related to cryptocurrency transactions. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The market for Layer 1 blockchains has seen explosive growth, with a collective market capitalization exceeding $2.8 trillion as of late 2024. This surge is attributed to significant price increases in major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which have risen by over 7,000% since January 2024. The growing interest in decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has further propelled the demand for L1 solutions.
However, this rapid growth comes with heightened scrutiny from regulators worldwide. Governments are increasingly concerned about the potential for fraud, money laundering, and other illicit activities facilitated by these technologies. As a result, regulatory bodies are beginning to impose stricter compliance requirements on L1 blockchain operators.
Implementation Strategies
To navigate the complex regulatory environment, L1 blockchain projects must adopt comprehensive compliance strategies that include:
- Robust KYC/AML Protocols: Implementing effective KYC measures helps verify user identities and mitigate risks associated with financial crimes.
- Legal Consultation: Engaging legal experts familiar with blockchain regulations can provide insights into jurisdiction-specific requirements.
- Regular Audits: Conducting periodic audits ensures adherence to compliance standards and helps identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Collaboration with Regulators: Establishing open lines of communication with regulatory bodies can facilitate smoother compliance processes and foster trust.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing advanced technologies such as AI for monitoring transactions can enhance compliance efforts by identifying suspicious activities in real-time.
Risk Considerations
Investors and stakeholders in L1 blockchains should be aware of several key risks:
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in regulations or enforcement actions can significantly impact the viability of blockchain projects.
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is notoriously volatile, posing risks to investors’ capital.
- Technological Risks: Security vulnerabilities in blockchain protocols can lead to hacks or data breaches.
- Reputational Risks: Non-compliance with regulations can damage an organization’s reputation and lead to loss of consumer trust.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape for Layer 1 blockchains is characterized by fragmentation and uncertainty. Key challenges include:
- Lack of Clarity: Many jurisdictions have yet to establish clear guidelines regarding the classification of digital assets (e.g., securities vs. commodities), complicating compliance efforts.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Regulators are increasingly focused on safeguarding consumers from fraud and misrepresentation in the crypto space.
- Cross-Border Transactions: The global nature of cryptocurrencies necessitates international cooperation among regulators to address issues related to cross-border transactions effectively.
- Evolving Regulations: As blockchain technology evolves, so too must regulations. This creates a dynamic environment where compliance requirements may change rapidly.
Future Outlook
The future of Layer 1 blockchains will likely be shaped by ongoing regulatory developments. Key trends to watch include:
- Increased Regulation: Expect more jurisdictions to implement comprehensive regulations governing cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies.
- Innovation in Compliance Solutions: The demand for effective compliance tools will drive innovation within the industry, leading to new technologies that streamline KYC/AML processes.
- Global Standards Development: Efforts toward establishing global standards for blockchain regulation may emerge as governments recognize the need for coordinated approaches.
- Market Maturation: As regulatory frameworks become clearer, the cryptocurrency market may mature, attracting more institutional investors seeking compliant investment opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions About Regulatory Challenges For Layer 1 Blockchains
- What are Layer 1 blockchains?
Layer 1 blockchains are foundational networks that handle core functionalities such as transaction processing and security without relying on secondary layers. - Why is regulation important for Layer 1 blockchains?
Regulation is crucial for ensuring consumer protection, preventing illicit activities, and fostering trust among users and investors. - What are KYC and AML?
KYC (Know Your Customer) refers to processes that verify user identities, while AML (Anti-Money Laundering) involves measures designed to prevent money laundering activities. - How do regulatory challenges affect investment?
Uncertainty in regulations can deter investment due to perceived risks associated with non-compliance or sudden changes in legal frameworks. - What role do international regulations play?
International regulations are essential for addressing cross-border issues related to cryptocurrency transactions and ensuring consistent standards globally. - How can L1 projects prepare for regulatory changes?
L1 projects should stay informed about regulatory developments, engage legal counsel, and implement robust compliance measures proactively. - What impact does technology have on regulation?
The rapid evolution of technology often outpaces regulatory frameworks, creating challenges as regulators strive to keep pace with innovations. - Will regulations stifle innovation in blockchain?
While some argue that stringent regulations may hinder innovation, others believe that clear guidelines can foster a safer environment conducive to growth.
In conclusion, Layer 1 blockchains face a myriad of regulatory challenges that require careful navigation. By implementing robust compliance strategies and staying informed about evolving regulations, stakeholders can mitigate risks while capitalizing on the opportunities presented by this transformative technology.