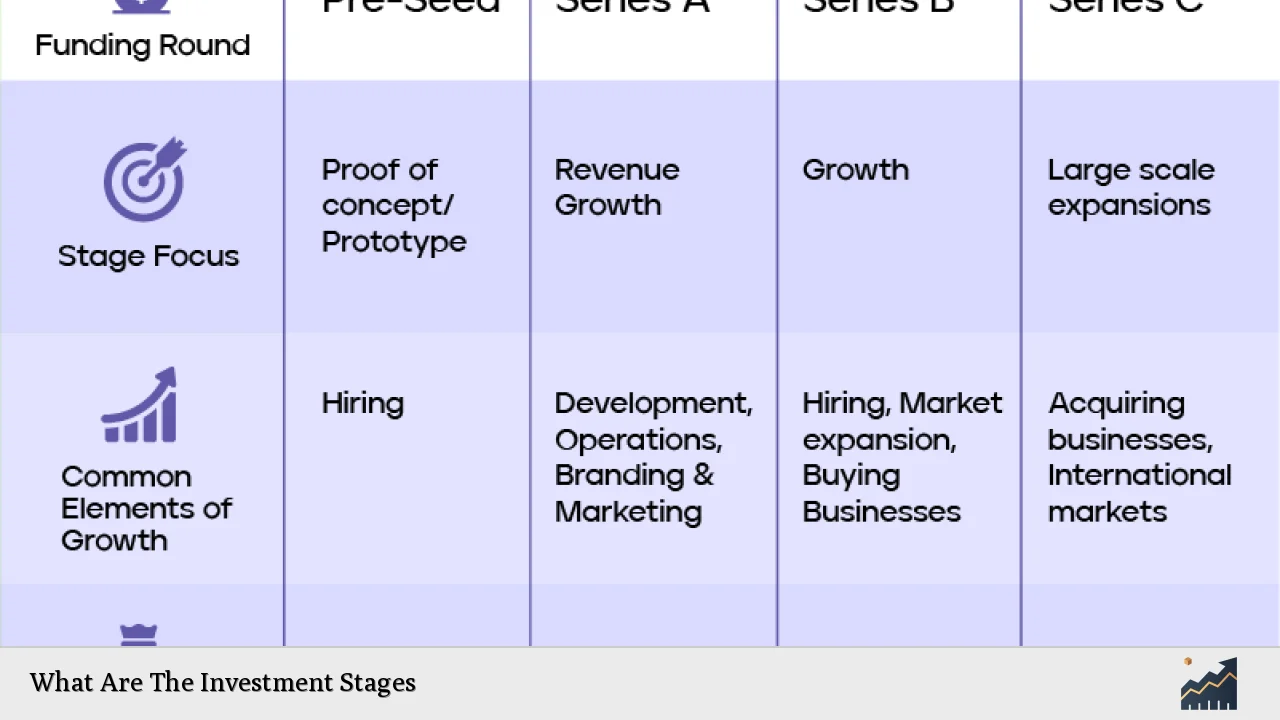
Understanding the various investment stages is crucial for entrepreneurs and investors alike. Each stage represents a different phase in the lifecycle of a business, particularly startups, and corresponds to specific funding needs, investor expectations, and business milestones. The journey typically begins with the initial concept of a business idea and progresses through several rounds of funding until the company reaches maturity or goes public.
Investment stages can be categorized into several key phases: pre-seed, seed, Series A, Series B, Series C, and beyond. Each stage serves a unique purpose and involves different types of investors, from friends and family to venture capitalists. Understanding these stages enables entrepreneurs to strategize effectively for funding and growth.
| Investment Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-Seed | Initial funding to develop an idea or prototype. |
| Seed | Funding to launch the business and gain initial traction. |
| Series A | Funding for scaling operations and refining products. |
| Series B | Funding to expand market reach and increase production. |
| Series C | Funding for further expansion, often globally. |
Pre-Seed Stage
The pre-seed stage is often considered the very beginning of a startup’s journey. At this point, entrepreneurs are focused on developing their initial ideas and assessing their viability. This stage typically involves minimal funding, often sourced from personal savings, friends, or family. Entrepreneurs may also seek small investments from angel investors who are willing to take risks on unproven concepts.
During this phase, the primary goal is to create a minimum viable product (MVP) that demonstrates the potential of the business idea. Entrepreneurs must conduct thorough market research to validate their concepts and understand customer needs. The pre-seed stage is crucial for laying the groundwork for future investment rounds.
Investors at this stage are usually looking for promising ideas with strong potential rather than established businesses. They are often motivated by the possibility of high returns if the startup succeeds.
Seed Stage
Once a startup has developed its MVP and validated its concept, it enters the seed stage. This phase marks the transition from an idea to an actual business with some customer traction. Seed funding is primarily used to cover initial operational costs such as product development, marketing efforts, hiring employees, and conducting market research.
At this stage, entrepreneurs typically seek larger investments compared to the pre-seed phase. Funding can come from angel investors, venture capital firms specializing in early-stage investments, or crowdfunding platforms. Investors in this stage look for startups that have demonstrated some level of market validation and potential for growth.
The seed stage is critical as it sets the foundation for future growth. Startups aim to establish a solid customer base while refining their products based on feedback received during initial sales efforts.
Series A Funding
Following successful seed funding, startups progress to Series A funding. This stage represents a significant milestone in a startup’s lifecycle as it typically involves larger amounts of capital—often exceeding $10 million. Series A funding is primarily aimed at scaling operations and optimizing business models.
At this point, startups should have a clear product-market fit and be ready to expand their customer base significantly. Investors during this phase are usually venture capital firms that provide not only capital but also strategic guidance and industry connections.
Funds raised during Series A are often allocated towards enhancing product features, expanding marketing efforts, hiring key personnel, and improving operational efficiencies. This stage is crucial as it determines whether a startup can transition from a small operation into a more established player in its industry.
Series B Funding
The Series B funding round typically occurs when a startup has established itself in the market but seeks additional resources to grow further. At this stage, companies usually have a dedicated user base and consistent revenue streams. The primary focus during Series B is on expanding market reach, increasing production capacity, and enhancing overall operational capabilities.
Funding amounts in Series B can range from $7 million to $10 million or more. Investors at this stage include venture capital firms that specialize in later-stage investments, as well as private equity firms looking for high-growth opportunities.
Startups utilize Series B funds for various purposes such as entering new markets, launching new products, or improving customer service operations. This phase is critical for solidifying a startup’s position within its industry while preparing for potential future funding rounds.
Series C Funding
Once a startup has successfully navigated earlier rounds of funding, it may seek Series C funding. This phase is intended for companies that are well-established but looking to expand further—often into international markets or by acquiring other businesses.
Series C funding can involve substantial amounts of capital—often exceeding $20 million—and attracts not only venture capitalists but also institutional investors looking for lower-risk opportunities with established companies.
Funds raised during this round are typically used for scaling operations significantly, developing new products or services, or making strategic acquisitions that enhance competitive advantage. The goal at this stage is not just growth but achieving profitability while positioning the company favorably for an eventual public offering (IPO).
Subsequent Rounds: Series D and Beyond
After Series C, some startups may pursue additional rounds such as Series D or even Series E funding if they have not yet achieved their goals or if new opportunities arise that require immediate investment before an IPO. These later rounds often indicate that a company is either addressing performance issues or seizing lucrative growth opportunities.
Investors in these stages expect detailed plans on how funds will be utilized effectively to achieve specific milestones before considering an IPO or acquisition strategy.
Conclusion
Navigating through these investment stages requires careful planning and execution by entrepreneurs seeking to grow their startups successfully. Each phase presents unique challenges and opportunities that must be addressed strategically to attract the right investors and secure necessary funding.
By understanding these stages—pre-seed through Series C (and beyond)—entrepreneurs can better prepare themselves for each step of their journey toward building a successful business capable of thriving in competitive markets.
FAQs About Investment Stages
- What is the pre-seed stage?
The pre-seed stage is where entrepreneurs develop their initial ideas and seek minimal funding from personal networks. - How much funding do startups typically raise during seed rounds?
Seed funding amounts can range from $500k to $5 million depending on the startup’s needs. - What happens during Series A funding?
During Series A funding, startups aim to scale operations significantly with investments often exceeding $10 million. - What is the purpose of Series B funding?
Series B funding focuses on expanding market reach and increasing production capacity for established startups. - Why might a startup pursue Series D funding?
A startup may pursue Series D funding if it needs additional resources to address performance issues or capitalize on new opportunities.