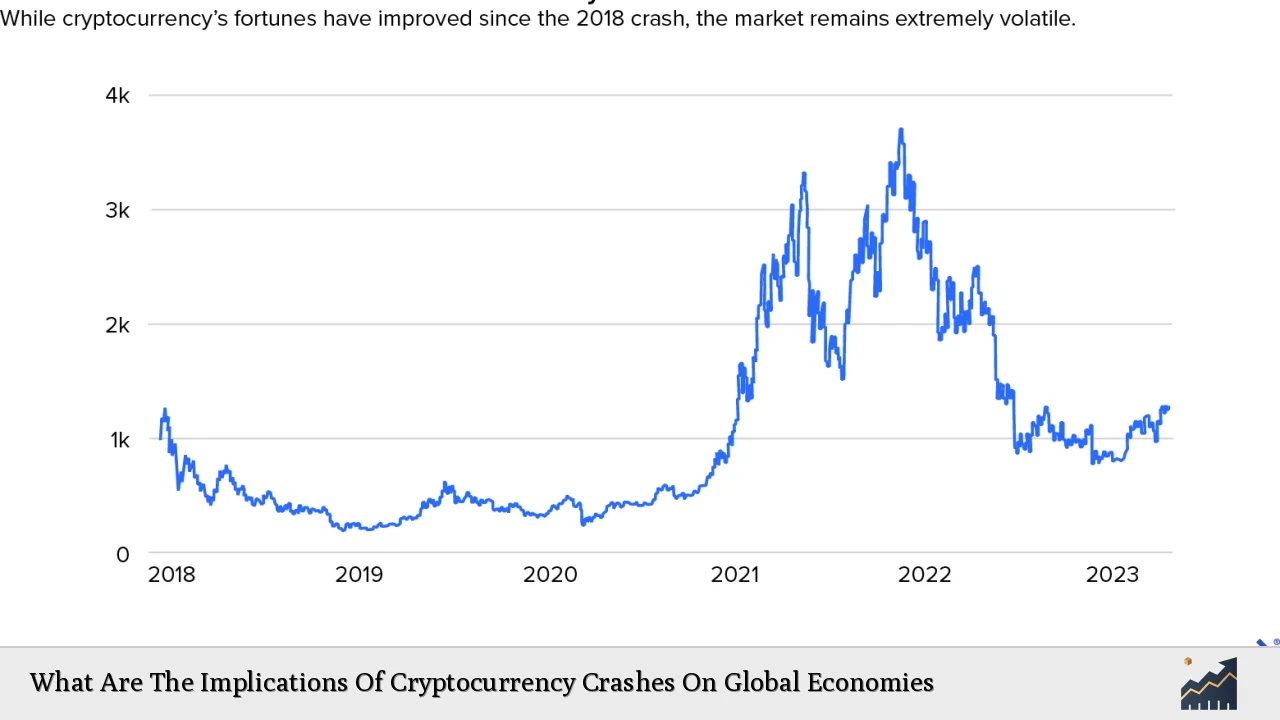
The cryptocurrency market has experienced significant fluctuations, with notable crashes that have raised concerns about their implications for global economies. As cryptocurrencies gained popularity, reaching a peak market capitalization of nearly $3 trillion in late 2021, their subsequent crashes have led to a loss of approximately $2 trillion in value, prompting discussions about their potential impact on the broader financial landscape. This analysis explores the implications of these crashes, examining market trends, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Market Volatility | Cryptocurrencies are characterized by extreme price volatility, which can lead to rapid wealth erosion for investors and affect consumer confidence. |
| Investor Behavior | Crashes can trigger panic selling among investors, leading to further declines and a potential liquidity crisis in the market. |
| Psychological Effects | The perception of cryptocurrencies as safe-haven assets can be undermined, affecting overall market sentiment and investment strategies. |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | Significant crashes often lead to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies, which may impose stricter regulations that could stifle innovation. |
| Economic Interconnectedness | The growing interconnectedness between cryptocurrencies and traditional financial markets raises concerns about systemic risks and potential contagion effects. |
| Tax Revenue Implications | As cryptocurrencies gain traction, governments face challenges in tax collection, potentially leading to budget deficits and economic instability. |
| Future Adoption Trends | The aftermath of crashes may lead to more cautious adoption of cryptocurrencies by institutions and individuals, impacting long-term growth prospects. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The cryptocurrency market has evolved dramatically over the past few years. Following its peak in late 2021, the market faced a series of downturns influenced by various factors:
- Macroeconomic Factors: Rising interest rates and inflation have prompted investors to seek safer assets. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy adjustments have made traditional investments more appealing compared to the volatile cryptocurrency market.
- Correlation with Traditional Markets: Cryptocurrencies have become increasingly correlated with stock markets. For instance, during periods of economic uncertainty or stock market declines, cryptocurrencies tend to follow suit. This correlation undermines their previously touted status as a diversification tool.
- Regulatory Developments: Governments are grappling with how to regulate cryptocurrencies effectively. Increased regulatory scrutiny following major crashes (e.g., the collapse of FTX) has led to uncertainty in the market, causing investors to reassess their positions.
- Market Sentiment: The psychological impact of crashes can lead to diminished confidence in cryptocurrencies as legitimate investment vehicles. This sentiment shift can result in reduced participation from both retail and institutional investors.
Implementation Strategies
Investors and financial professionals must adopt strategic approaches to navigate the complex landscape shaped by cryptocurrency crashes:
- Diversification: Reducing exposure to cryptocurrencies by diversifying into traditional assets can mitigate risks associated with volatility.
- Risk Management: Implementing robust risk management practices is essential. This includes setting stop-loss orders and maintaining a balanced portfolio that aligns with individual risk tolerance levels.
- Education and Awareness: Staying informed about market trends and regulatory changes is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Investors should engage in continuous education regarding cryptocurrency fundamentals and market dynamics.
- Long-Term Perspective: While short-term volatility can be alarming, maintaining a long-term investment perspective may help investors weather temporary downturns.
Risk Considerations
The implications of cryptocurrency crashes extend beyond individual losses; they pose broader risks to economic stability:
- Systemic Risk: The interconnectedness between cryptocurrencies and traditional financial markets raises concerns about systemic risks. A significant crash could trigger a liquidity crisis affecting banks and financial institutions with exposure to crypto assets.
- Investor Protection: The lack of regulatory oversight in many jurisdictions leaves investors vulnerable. Crashes often expose weaknesses in investor protections, leading to calls for stronger regulatory frameworks.
- Tax Revenue Challenges: Governments may struggle with tax collection as more transactions occur outside traditional financial systems. This could lead to budget shortfalls and hinder public services.
Regulatory Aspects
Regulatory responses play a critical role in shaping the future of cryptocurrencies:
- Increased Scrutiny: Following major crashes, regulators are likely to impose stricter rules governing cryptocurrency exchanges and initial coin offerings (ICOs). This could stifle innovation but enhance investor protections.
- Global Coordination: The international nature of cryptocurrency markets necessitates coordinated regulatory efforts among countries. Disparate regulations can lead to regulatory arbitrage, where businesses exploit loopholes in less regulated jurisdictions.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): In response to the rise of cryptocurrencies, many central banks are exploring or implementing CBDCs. These digital currencies could provide a stable alternative while allowing governments greater control over monetary policy.
Future Outlook
The future of cryptocurrencies remains uncertain but holds potential for transformative impacts on global economies:
- Continued Growth: Despite recent downturns, analysts predict that the cryptocurrency market will continue to grow. The global cryptocurrency market is projected to expand by $34.5 billion from 2024 to 2028 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.64%.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations within blockchain technology may drive new applications beyond finance, including supply chain management and healthcare solutions.
- Institutional Adoption: As regulatory clarity improves, institutional adoption may increase significantly. Financial institutions are beginning to integrate crypto services into their offerings, indicating a shift toward mainstream acceptance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cryptocurrency Crashes On Global Economies
- What causes cryptocurrency crashes?
The primary causes include macroeconomic factors like rising interest rates, increased correlation with traditional markets, regulatory uncertainties, and speculative trading behaviors. - How do cryptocurrency crashes affect investor behavior?
Crashes often lead to panic selling among investors, resulting in further price declines and loss of confidence in the asset class. - Are cryptocurrencies too interconnected with traditional financial systems?
Yes, increasing interconnectedness raises concerns about systemic risks; a significant crash could impact broader financial stability. - What role do regulations play after a crash?
Regulations may tighten following crashes as governments seek to protect investors and stabilize markets; however, this could also hinder innovation. - Can cryptocurrency crashes impact tax revenues?
Yes, as transactions move outside traditional systems, governments may face challenges in tax collection, potentially leading to budget deficits. - What is the long-term outlook for cryptocurrencies?
The long-term outlook remains positive despite volatility; technological advancements and increasing institutional adoption could drive growth. - How should investors approach cryptocurrencies post-crash?
Investors should focus on diversification, risk management strategies, continuous education on market trends, and maintaining a long-term perspective. - What are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)?
CBDCs are digital currencies issued by central banks that aim to provide stable alternatives while enhancing governmental control over monetary policy.
The implications of cryptocurrency crashes on global economies are multifaceted. While they pose risks such as systemic instability and challenges for regulatory frameworks, they also present opportunities for innovation within financial systems. As the landscape evolves, stakeholders must navigate these complexities with informed strategies that prioritize risk management and adaptability.