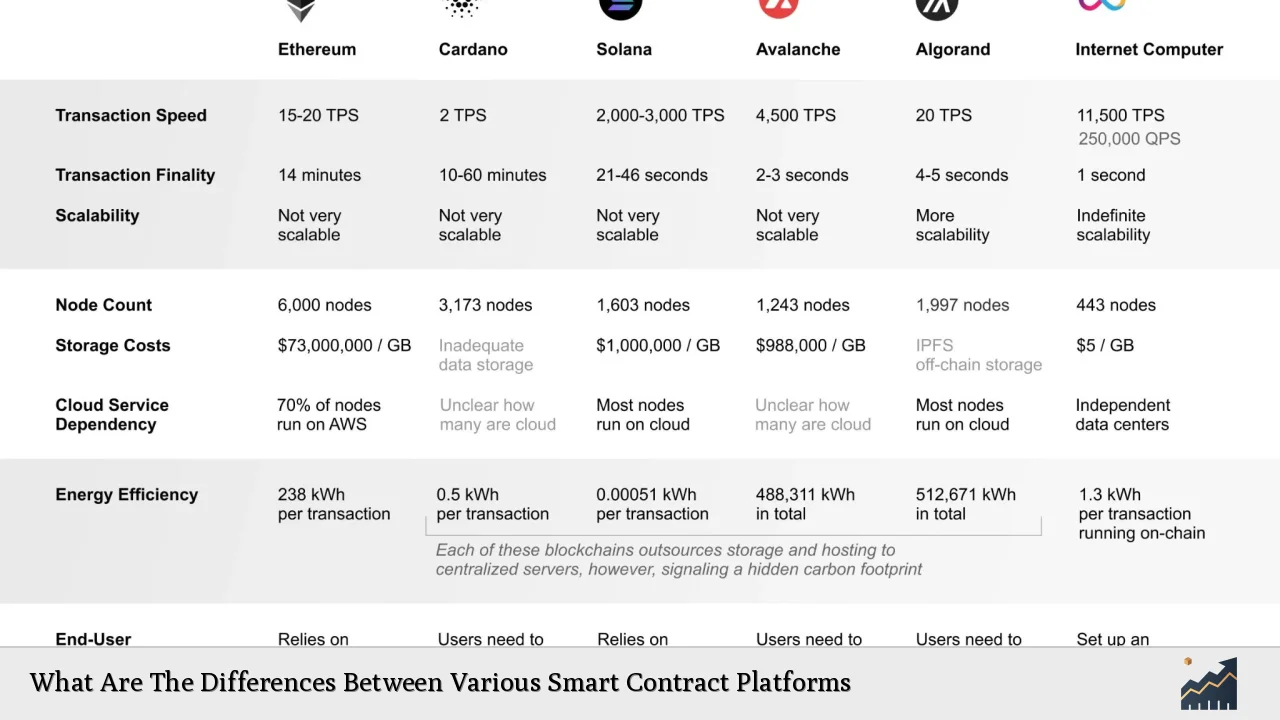
Smart contracts have revolutionized the way agreements are executed in the digital age, allowing for automated, self-executing contracts that operate on blockchain technology. This innovation has led to the emergence of several smart contract platforms, each with unique features, benefits, and limitations. Understanding these differences is crucial for investors and developers looking to leverage blockchain technology effectively. This article delves into the key smart contract platforms, their functionalities, and how they compare in terms of scalability, transaction costs, security, and ecosystem support.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Ethereum | The first and most widely used smart contract platform, known for its robust ecosystem and extensive developer community. It supports a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps) but suffers from high gas fees and scalability issues. |
| Solana | A high-performance platform that utilizes a unique Proof of History (PoH) consensus mechanism to achieve fast transaction speeds (up to 65,000 transactions per second) at low costs. It is gaining popularity for applications requiring high throughput. |
| Polkadot | Designed for interoperability between different blockchains, Polkadot allows various blockchains to communicate and share information securely. Its architecture supports multiple parallel blockchains (parachains), enhancing scalability. |
| Cardano | A platform focused on security and sustainability through a research-driven approach. It uses a unique proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Ouroboros but has faced criticism for slower development compared to competitors. |
| Binance Smart Chain (BSC) | A platform that offers lower transaction costs and faster confirmation times compared to Ethereum. However, it has faced scrutiny over centralization concerns due to its association with Binance. |
| Polygon | A Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that enhances its performance by reducing congestion and transaction fees while maintaining compatibility with Ethereum’s ecosystem. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The smart contract market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and legal services. According to recent reports, the global smart contracts market is projected to reach approximately $8.7 billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.4% from 2024.
Current Trends
- Interoperability: As businesses seek to integrate multiple blockchain solutions, platforms like Polkadot that facilitate cross-chain communication are gaining traction.
- Layer 2 Solutions: Solutions like Polygon are becoming critical in addressing Ethereum’s scalability issues by enabling faster transactions at lower costs.
- AI Integration: The rise of AI-powered smart contracts is set to enhance automation and decision-making capabilities within decentralized applications.
- Regulatory Compliance: With increasing scrutiny from regulators worldwide, platforms that can embed compliance measures directly into their smart contracts will likely see higher adoption rates.
Implementation Strategies
When selecting a smart contract platform, developers should consider several factors:
- Scalability: Platforms like Solana and Polkadot offer superior scalability compared to Ethereum.
- Cost Efficiency: Binance Smart Chain and Polygon provide lower transaction fees than Ethereum.
- Ecosystem Support: Ethereum remains the leader due to its extensive community and resources available for developers.
- Security Features: Platforms must implement robust security measures to protect against vulnerabilities inherent in smart contract code.
Risk Considerations
Investing in or developing on smart contract platforms involves several risks:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs or flaws in the code can lead to significant financial losses. Regular audits are essential.
- Regulatory Risks: The evolving legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies can impact the viability of certain platforms.
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile; investments in tokens associated with these platforms can be risky.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory environment for smart contracts varies significantly across jurisdictions:
- In some regions like Arizona and Tennessee in the U.S., laws explicitly recognize smart contracts as legally binding.
- The European Union is working towards comprehensive regulations that could affect how smart contracts operate across member states.
Developers must ensure their smart contracts comply with local laws regarding data protection (e.g., GDPR) and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
Future Outlook
The future of smart contract platforms looks promising as technology evolves:
- Increased Adoption: As more businesses recognize the efficiency gains from using smart contracts, adoption will likely accelerate.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations such as hybrid smart contracts combining on-chain and off-chain components may emerge.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: Ongoing improvements in security practices will be crucial as threats evolve.
Investors should remain vigilant about emerging trends and regulatory developments that may impact their strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions About Smart Contract Platforms
- What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing agreement where the terms are directly written into code on a blockchain. - How do different platforms compare in terms of transaction speed?
Solana offers up to 65,000 transactions per second, while Ethereum handles around 15 TPS under current conditions. - Are smart contracts legally binding?
The legal status varies by jurisdiction; some regions recognize them as legally binding while others do not. - What are the main risks associated with using smart contracts?
Main risks include coding vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainties, and market volatility. - How can I choose the right platform for my project?
Consider factors like scalability needs, transaction costs, ecosystem support, and security features. - What role does interoperability play in smart contracts?
Interoperability allows different blockchains to communicate effectively, enhancing functionality across platforms. - What future trends should I watch in the smart contract space?
Look for advancements in AI integration, regulatory developments, and improvements in security protocols. - Can I modify a deployed smart contract?
Once deployed on most blockchains, a smart contract cannot be changed; however, mechanisms like “pause” functions can allow temporary halts or modifications under specific conditions.
This comprehensive analysis highlights the key differences between various smart contract platforms while providing insights into current market trends and future directions. Investors and developers must stay informed about these dynamics to make strategic decisions in this rapidly evolving landscape.