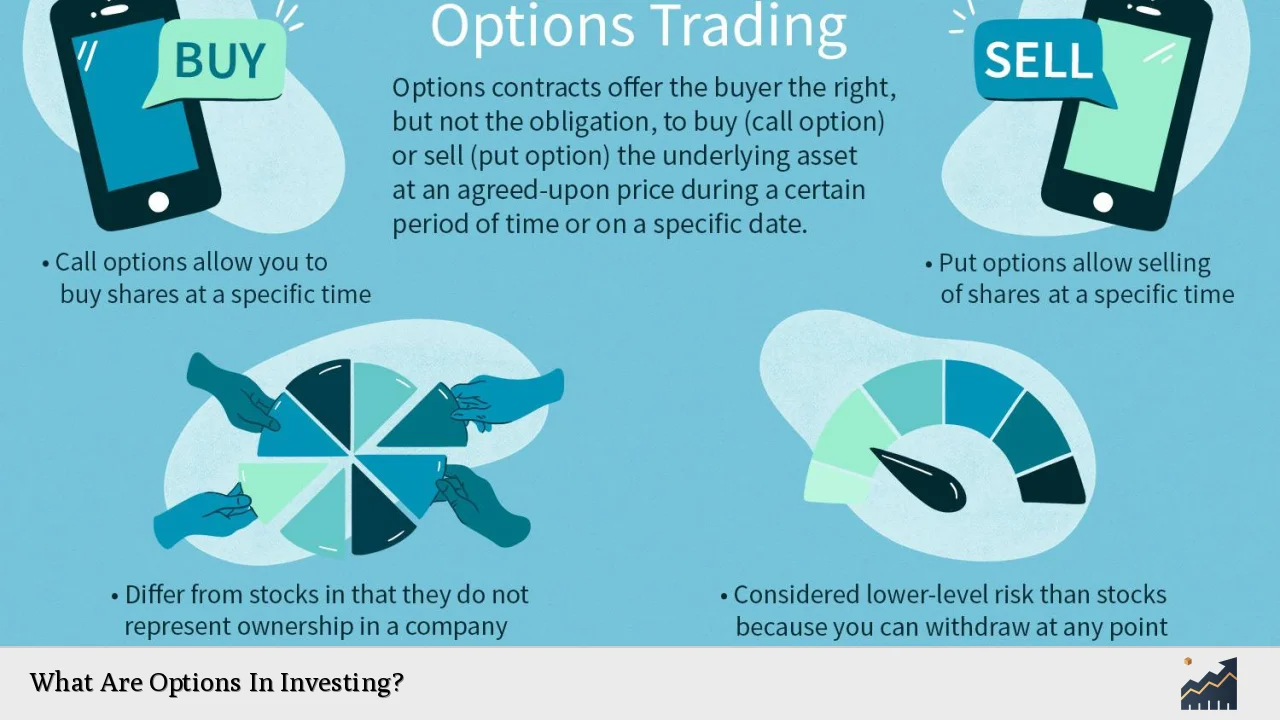
Options are financial derivatives that provide investors with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. This flexibility makes options a popular choice for both hedging and speculative strategies in the financial markets. Unlike traditional stock trading, where investors buy and sell shares directly, options trading allows for more complex strategies that can yield significant returns or protect against losses.
Options come primarily in two forms: call options and put options. A call option gives the holder the right to purchase an asset at a specified price (the strike price) before the option expires, while a put option gives the holder the right to sell an asset at the strike price within the same time frame. The appeal of options lies in their ability to leverage investments, allowing traders to control larger positions with a relatively small capital outlay.
| Type of Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Call Option | Right to buy an asset at a specified price before expiration. |
| Put Option | Right to sell an asset at a specified price before expiration. |
Types of Options
Options can be categorized into various types based on their characteristics and trading strategies. Understanding these types is crucial for effective options trading.
Call Options
Call options grant the holder the right to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price before or at expiration. Investors typically purchase call options when they anticipate that the price of the underlying asset will rise. If the asset’s market price exceeds the strike price before expiration, the call option becomes valuable, allowing investors to either exercise it or sell it for a profit.
Put Options
In contrast, put options give holders the right to sell an underlying asset at a specified strike price before expiration. Investors buy put options when they expect that the asset’s price will decline. If the market price falls below the strike price, the put option gains value, enabling investors to either exercise it or sell it profitably.
American vs. European Options
Options can also be classified based on when they can be exercised:
- American Options: Can be exercised at any time before expiration.
- European Options: Can only be exercised on the expiration date.
This distinction affects trading strategies and potential profits.
How Options Work
Understanding how options work is vital for anyone looking to trade them effectively.
Option Premium
To acquire an option, investors must pay an option premium, which is the cost of purchasing the option contract. This premium varies based on several factors, including:
- The current price of the underlying asset
- The strike price
- The time remaining until expiration
- Market volatility
Exercising Options
When an option is exercised, it means that the holder has chosen to utilize their right to buy (for call options) or sell (for put options) the underlying asset at the strike price. If an investor holds a call option and decides to exercise it when the market price is higher than the strike price, they can purchase shares at a lower cost and potentially sell them for a profit.
Closing Positions
Investors can also choose not to exercise their options but instead close their positions by selling them in the market before expiration. This strategy allows traders to capitalize on changes in option premiums without needing to buy or sell the underlying assets directly.
Benefits of Trading Options
Options trading offers several advantages compared to traditional stock trading:
- Leverage: Options allow traders to control larger positions with less capital compared to buying stocks outright.
- Flexibility: Traders can implement various strategies depending on market conditions—whether bullish, bearish, or neutral.
- Risk Management: Options can serve as effective hedging tools, protecting existing investments from adverse market movements.
- Profit from Volatility: Traders can profit from fluctuations in asset prices, even if they do not have a directional bias.
Risks Associated with Options Trading
While options can provide substantial benefits, they also come with inherent risks that investors must understand:
- Limited Lifespan: Options have expiration dates, meaning their value can diminish rapidly as expiration approaches.
- Complexity: The variety of strategies and factors affecting options pricing can make them complicated for novice investors.
- Potential Losses: While buying options limits losses to the premium paid, selling options (writing) can expose investors to significant risks if not managed properly.
Strategies for Trading Options
Investors employ various strategies when trading options based on their market outlook and risk tolerance:
Long Call Strategy
In this strategy, an investor buys call options anticipating that the underlying stock will rise significantly. The maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for the option.
Long Put Strategy
Conversely, this strategy involves buying put options when an investor expects a decline in stock prices. Similar to long calls, maximum loss is confined to the premium paid.
Covered Call Strategy
This strategy involves holding a long position in an asset while selling call options against that position. It generates income through premiums but limits upside potential if stock prices rise significantly.
Protective Put Strategy
Investors use protective puts as insurance against declines in stock prices. By purchasing puts while holding shares, they can limit potential losses if prices fall.
How To Start Trading Options
Getting started with options trading involves several steps:
1. Open an Options Trading Account: Choose a brokerage that offers access to options trading and complete any necessary approvals.
2. Educate Yourself: Familiarize yourself with basic concepts and strategies related to options trading.
3. Develop a Trading Plan: Establish clear goals and risk management strategies before entering trades.
4. Start Trading: Begin with simple trades while gradually exploring more complex strategies as you gain experience.
FAQs About Options In Investing
- What are call and put options?
Call options give you the right to buy an asset; put options give you the right to sell it. - How do I profit from trading options?
You profit by exercising your option when favorable conditions arise or by selling your option for more than you paid. - What is an option premium?
The option premium is the cost you pay to acquire an option contract. - Can I lose money trading options?
Yes, especially if you buy options that expire worthless or if you write uncovered calls. - What are some common strategies for trading options?
Common strategies include long calls, long puts, covered calls, and protective puts.
By understanding these fundamental concepts of options investing—types of options available, how they work, benefits and risks associated with them—investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.