Investment accounts are specialized financial accounts designed for individuals to buy, hold, and sell various investment assets such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other securities. Unlike traditional bank accounts, the value of assets in an investment account can fluctuate significantly based on market conditions. This potential for growth, along with the associated risks, makes investment accounts essential for achieving long-term financial goals such as retirement savings or wealth accumulation.
Investment accounts come in various forms, each serving different purposes and tax implications. Understanding these types is crucial for investors to select the most suitable account based on their financial objectives and investment strategies.
| Type of Investment Account | Description |
|---|---|
| Brokerage Account | Allows buying and selling of a wide range of securities. |
| Retirement Account | Tax-advantaged accounts specifically for retirement savings. |
Types of Investment Accounts
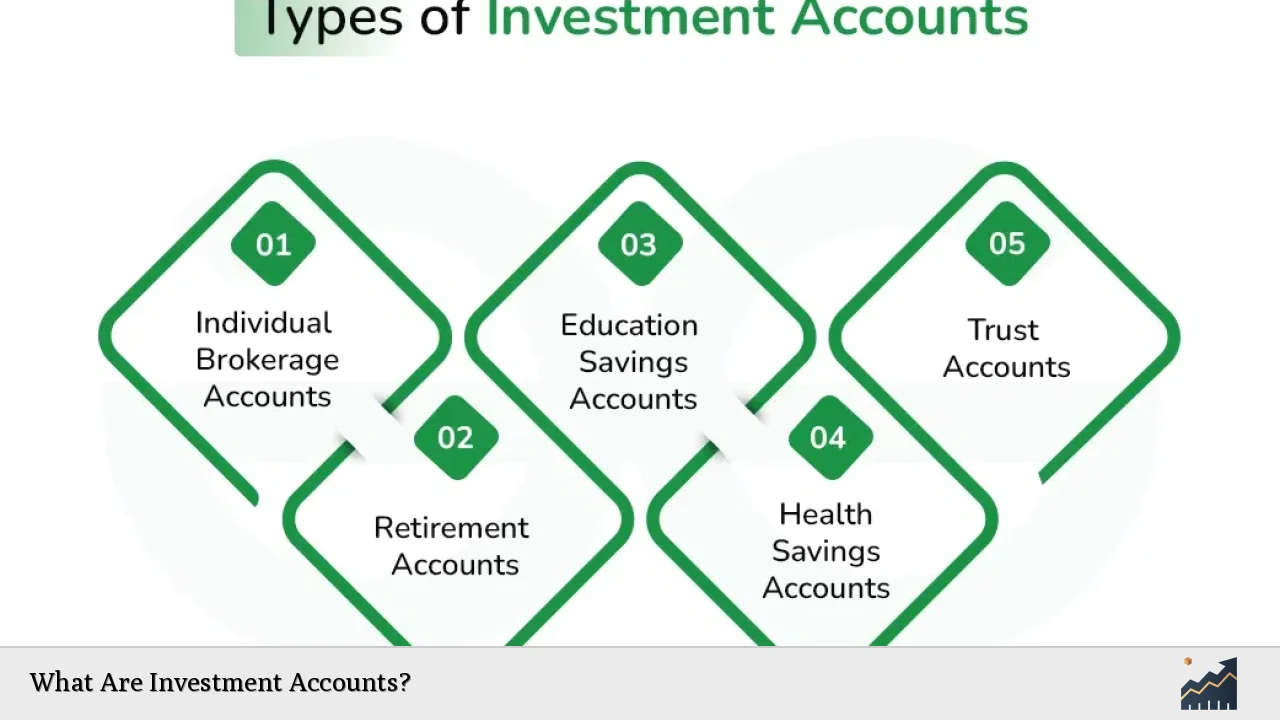
Investment accounts can be categorized into several types, each tailored to meet specific investment needs and goals. Understanding these categories helps investors make informed decisions about where to allocate their funds.
- Brokerage Accounts: These are the most common type of investment accounts that allow individuals to buy and sell a variety of securities including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. They can be either individual or joint accounts. Brokerage accounts are typically taxable, meaning any capital gains or dividends earned are subject to taxation in the year they are realized.
- Retirement Accounts: These include accounts like Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and employer-sponsored plans such as 401(k)s. They offer tax advantages that encourage long-term saving for retirement. Contributions to traditional IRAs may be tax-deductible, while Roth IRAs allow for tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- Education Savings Accounts: Such as 529 plans, these accounts are specifically designed to save for educational expenses. They offer tax-free growth and withdrawals when used for qualified education expenses.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): These are tax-advantaged accounts that allow individuals to save for medical expenses. Contributions are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
- Custodial Accounts: Established for minors under the Uniform Transfers to Minors Act (UTMA) or Uniform Gifts to Minors Act (UGMA), these accounts allow adults to manage investments on behalf of a child until they reach adulthood.
Each type of account has unique rules regarding contributions, withdrawals, and taxation. Therefore, understanding these differences is important for optimizing investment strategies.
Key Features of Investment Accounts
Investment accounts come with various features that cater to different investor needs. Here are some key features that distinguish them:
- Liquidity: Most investment accounts provide high liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell assets quickly. However, certain retirement accounts may impose penalties for early withdrawals.
- Tax Implications: Investment accounts have different tax treatments based on their type. For example, capital gains from brokerage accounts are taxed annually, while retirement accounts may offer tax deferral or tax-free growth.
- Investment Choices: Depending on the account type, investors can choose from a wide range of assets including stocks, bonds, ETFs (exchange-traded funds), and mutual funds.
- Fees: Many investment accounts charge fees related to transactions, account maintenance, or management services. Understanding these costs is essential as they can impact overall returns.
- Account Management: Some investment accounts offer professional management services where financial advisors make investment decisions on behalf of the investor.
These features highlight the importance of selecting the right type of investment account that aligns with an individual’s financial goals and risk tolerance.
How to Open an Investment Account
Opening an investment account involves several steps that ensure investors select the right account type and provider based on their needs:
1. Determine Your Goals: Identify your financial objectives such as saving for retirement, education expenses, or building wealth through investments.
2. Choose the Right Account Type: Based on your goals, decide whether you need a brokerage account, retirement account, or another type of investment account.
3. Select a Brokerage Firm or Financial Institution: Research different firms based on fees, services offered, and user reviews. Look for a reputable firm that aligns with your investment strategy.
4. Complete the Application Process: Fill out the necessary application forms provided by the brokerage firm. This may include providing personal information such as Social Security number and employment details.
5. Fund Your Account: Transfer money into your new account through bank transfer or check deposit. Ensure you meet any minimum funding requirements set by the brokerage.
6. Start Investing: Once your account is funded, begin researching potential investments that align with your strategy and risk tolerance.
Following these steps will help ensure a smooth process when opening an investment account while maximizing your potential for achieving financial goals.
Managing Your Investment Account
Effective management of an investment account is crucial for achieving desired financial outcomes. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of your investments regularly to assess performance against market trends and personal goals. This helps identify when adjustments may be necessary.
- Diversification: Spread investments across various asset classes to reduce risk exposure. A diversified portfolio can help mitigate losses during market downturns.
- Rebalancing: Periodically review your portfolio allocation and rebalance it as needed to maintain your desired risk level and asset distribution.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market news and economic indicators that could affect your investments. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions about buying or selling assets.
- Consult Professionals if Needed: If managing an investment account becomes overwhelming or complex, consider seeking advice from financial advisors who can provide tailored strategies based on your situation.
By implementing these management strategies effectively, investors can enhance their chances of achieving their financial objectives over time.
Risks Associated with Investment Accounts
Investing inherently involves risks that can affect the value of assets held in investment accounts. Understanding these risks is essential for making informed decisions:
- Market Risk: The value of investments can fluctuate due to changes in market conditions or economic factors affecting specific sectors or industries.
- Credit Risk: This risk pertains to bonds where issuers may default on payments leading to potential losses for bondholders.
- Liquidity Risk: Some investments may not be easily sold without incurring significant losses if there is low demand in the market at the time of sale.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can impact bond prices inversely; rising rates typically lead to falling bond prices which can affect overall portfolio value.
Awareness of these risks allows investors to develop strategies that align with their risk tolerance while also taking advantage of potential returns over time.
FAQs About Investment Accounts
- What is an investment account?
An investment account is a financial account used to buy and hold securities such as stocks and bonds. - What types of investment accounts exist?
Common types include brokerage accounts, retirement accounts like IRAs, education savings accounts, and health savings accounts. - How do I open an investment account?
You need to determine your goals, choose an account type, select a brokerage firm, complete an application process, fund your account, and start investing. - What are the risks associated with investment accounts?
Risks include market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and interest rate risk which can affect asset values. - How should I manage my investment account?
Regularly monitor performance, diversify investments, rebalance your portfolio as needed, stay informed about market trends, and consult professionals if necessary.