Investing in stocks has become a cornerstone of wealth building in modern finance, but for Muslim investors, the question of whether stock market participation aligns with Islamic principles is crucial. The concept of halal investing, which adheres to Shariah law, has gained significant traction in recent years, with the global Islamic finance industry projected to reach $6.67 trillion by 2027. This growth reflects the increasing demand for financial products that comply with Islamic ethical standards while still offering competitive returns.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
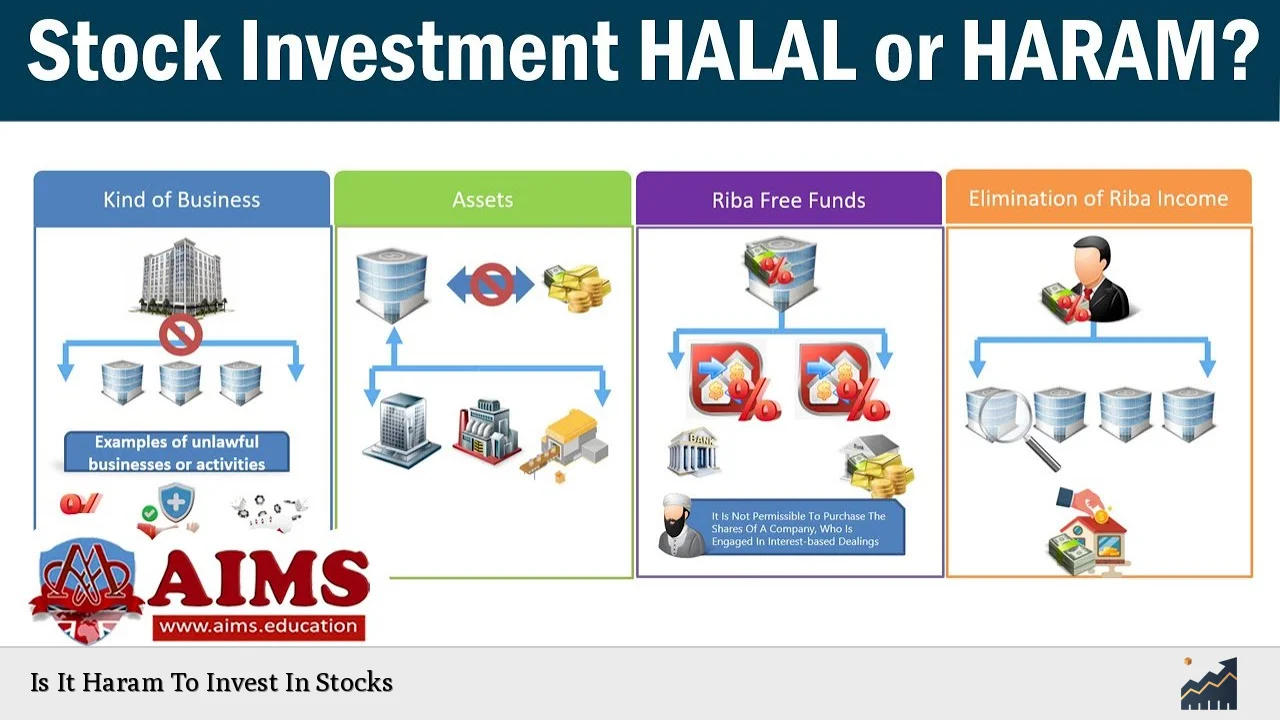
| Shariah Compliance | Stocks must adhere to Islamic principles, avoiding industries like alcohol, gambling, and interest-based finance |
| Screening Process | Companies are evaluated based on their business activities and financial ratios to ensure halal status |
| 5% Rule | Tolerance for impermissible income, which must not exceed 5% of total revenue |
| Purification | Process of donating impermissible portions of gains to charity |
Market Analysis and Trends
The Islamic finance market has shown remarkable resilience and growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 10% expected between 2024 and 2029. This expansion is not limited to Muslim-majority countries; it’s gaining traction globally as an ethical alternative to conventional finance.
Islamic banking dominates the sector, accounting for the largest share of Shariah-compliant assets. However, Islamic equity investments, including stocks, are rapidly growing. The total net income reported by Islamic financial institutions worldwide increased from $10.5 billion in 2020 to $32 billion in 2021, indicating a strong recovery and growth trajectory.
The sukuk (Islamic bonds) market has also seen significant development, with sustainable and green sukuk issuances reaching nearly $4 billion in Q1 2024, a 17% increase from the previous year. This trend aligns with the global shift towards sustainable and ethical investing, making Islamic finance increasingly attractive to both Muslim and non-Muslim investors seeking socially responsible investment options.
Implementation Strategies
For Muslim investors looking to participate in the stock market while adhering to Islamic principles, several strategies can be employed:
Shariah-Compliant Stock Screening
Investors can use specialized platforms or indices that screen stocks based on Shariah compliance. These tools evaluate companies on two main criteria:
- Business activities: Excluding companies involved in prohibited industries such as alcohol, gambling, and conventional financial services.
- Financial ratios: Assessing debt levels, interest income, and cash holdings to ensure they fall within acceptable limits.
Islamic ETFs and Mutual Funds
For those who prefer a more hands-off approach, Islamic Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and mutual funds offer pre-screened portfolios of Shariah-compliant stocks. These funds are managed by experts who ensure ongoing compliance with Islamic principles.
Direct Stock Investment
Investors can also directly purchase stocks of companies that have been verified as Shariah-compliant. This approach requires more research and due diligence but allows for greater control over the investment portfolio.
Purification Process
Even when investing in Shariah-compliant stocks, a small portion of income may come from non-compliant sources. Islamic investors are expected to “purify” their earnings by donating this portion to charity, typically calculated as a percentage of dividends received.
Risk Considerations
While investing in Shariah-compliant stocks can align with Islamic principles, it’s important to consider the associated risks:
Market Volatility: Like all stock investments, Islamic stocks are subject to market fluctuations and economic conditions.
Limited Diversification: The exclusion of certain industries may lead to a more concentrated portfolio, potentially increasing risk.
Compliance Changes: Companies may fall out of Shariah compliance, requiring investors to reassess and potentially divest.
Performance Tracking: Islamic indices may underperform or outperform conventional indices, depending on market conditions and sector performance.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulation of Islamic finance varies globally, with some countries having dedicated frameworks for Shariah-compliant investments. Key regulatory considerations include:
Shariah Governance: Many jurisdictions require Islamic financial institutions to have Shariah supervisory boards to ensure compliance.
Disclosure Requirements: Companies and funds may need to disclose their Shariah compliance status and screening methodologies.
International Standards: Organizations like the Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI) and the Islamic Financial Services Board (IFSB) provide guidelines and standards for Islamic finance practices.
Future Outlook
The future of Islamic stock investing looks promising, driven by several factors:
Technological Advancements: Fintech innovations are making it easier to screen and trade Shariah-compliant stocks, increasing accessibility for retail investors.
Growing Awareness: As understanding of Islamic finance principles increases globally, more investors may seek out these ethical investment options.
Sustainable Finance Synergies: The alignment between Islamic finance principles and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria is likely to attract a broader investor base.
Product Innovation: The development of new Islamic financial products, such as Shariah-compliant REITs and green sukuk, will provide more diverse investment opportunities.
Regulatory Harmonization: Efforts to standardize Islamic finance regulations across different jurisdictions could facilitate cross-border investments and improve market efficiency.
As the Islamic finance industry continues to evolve, it’s clear that stock investing can be halal when approached with careful consideration of Shariah principles. The growing ecosystem of Shariah-compliant investment options, coupled with increasing market sophistication, provides Muslim investors with ample opportunities to participate in the stock market while adhering to their religious beliefs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Is It Haram To Invest In Stocks
- Can Muslims invest in any stock on the market?
No, Muslims should only invest in stocks that are Shariah-compliant, meaning they adhere to Islamic principles in their business activities and financial practices. - How can I determine if a stock is halal?
You can use specialized Islamic finance screening tools, consult Shariah-compliant indices, or seek advice from Islamic financial advisors who evaluate stocks based on business activities and financial ratios. - What industries are typically excluded from halal stock investing?
Industries commonly excluded include alcohol, gambling, pork-related products, conventional financial services, weapons, and adult entertainment. - Is it permissible to invest in companies with some level of interest-based debt?
Most scholars allow investing in companies with a limited amount of interest-based debt, typically not exceeding 33% of the company’s market capitalization or total assets. - What is the concept of purification in Islamic stock investing?
Purification involves calculating and donating the portion of investment returns that may have come from non-compliant sources to charity, ensuring the overall investment remains halal. - Are dividends from stocks considered halal?
Dividends from Shariah-compliant stocks are generally considered halal. However, investors should ensure the company maintains its compliance status and purify any portions from non-compliant activities. - Can short-selling stocks be considered halal?
Most Islamic scholars consider short-selling to be haram as it involves selling something you don’t own and can be seen as excessive speculation.