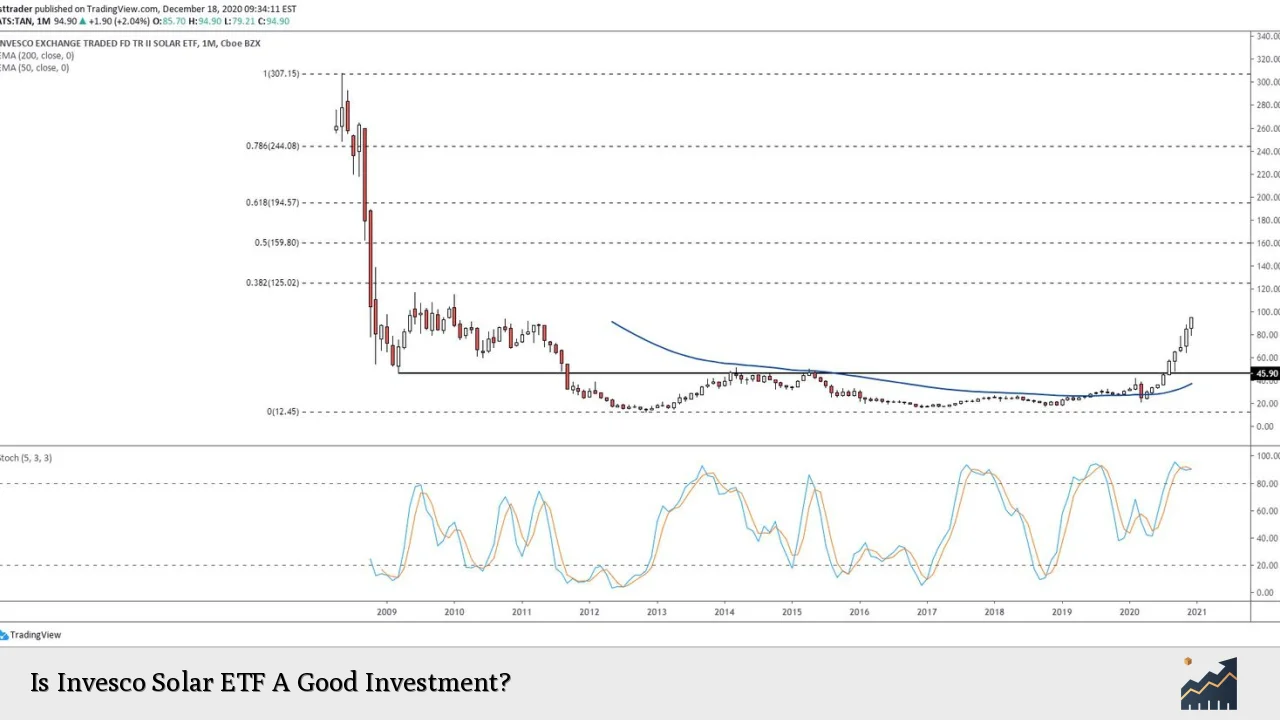
The Invesco Solar ETF (TAN) offers investors exposure to the solar energy sector, tracking the MAC Global Solar Energy Index. As renewable energy continues to gain traction globally, the ETF’s performance can be influenced by a variety of factors including market trends, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. This analysis delves into the current market landscape, implementation strategies, risks, regulatory aspects, and future outlook for TAN, helping investors determine whether it represents a sound investment opportunity.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Market Performance | TAN has underperformed compared to the S&P 500 over the past decade, with an annualized return of approximately 1.7% versus 11.8% for the S&P 500. |
| Expense Ratio | The fund has an expense ratio of 0.69%, which is moderate for an ETF but can impact long-term returns. |
| Market Volatility | The solar sector is subject to high volatility due to fluctuating demand, supply chain issues, and regulatory changes. |
| Top Holdings | TAN’s portfolio is heavily weighted towards U.S. companies like Enphase Energy and First Solar, which may provide some insulation from global supply issues. |
| Government Policies | Supportive policies such as tariffs on imports and incentives from the Inflation Reduction Act are crucial for U.S. solar companies. |
| Future Outlook | The outlook for TAN is mixed; while there are growth opportunities in renewable energy, oversupply and economic conditions could pose challenges. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The solar energy market has seen significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy sources and technological advancements that have reduced costs. However, the Invesco Solar ETF has struggled to keep pace with broader market indices:
- Underperformance: Over the last ten years, TAN has returned about 1.7% annually compared to over 11% for the S&P 500. Year-to-date performance shows a decline of approximately 32.9%, reflecting ongoing challenges in the sector.
- Volatility Factors: The solar industry faces volatility due to various factors including changes in government policy, global supply chain disruptions, and fluctuating material costs. For instance, recent oversupply issues have led to price declines in solar modules by around 50% in 2023.
- Regulatory Environment: Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping market dynamics. The Inflation Reduction Act has provided support for domestic solar manufacturers through tax incentives and tariffs on imported products, which could benefit companies within TAN’s portfolio.
Implementation Strategies
Investing in TAN can be approached through several strategies:
- Long-Term Investment: Given its historical underperformance, investors looking for long-term growth may consider TAN as part of a diversified portfolio focused on renewable energy.
- Tactical Trading: Due to its volatility, TAN may present short-term trading opportunities for investors who can capitalize on price fluctuations.
- Sector Rotation: Investors might use TAN as a tactical allocation within a broader strategy that includes other sectors poised for growth as market conditions change.
Risk Considerations
Investing in TAN comes with inherent risks:
- Market Volatility: The solar sector is highly volatile; prices can swing dramatically based on supply-demand imbalances or shifts in investor sentiment.
- Concentration Risk: TAN’s portfolio is heavily weighted towards a few key holdings (like Enphase Energy and First Solar), which increases exposure to company-specific risks.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in government policies or tariffs can significantly impact profitability for companies within the ETF.
- Economic Sensitivity: The performance of TAN is sensitive to broader economic conditions; high interest rates or economic downturns could adversely affect investment returns.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape is crucial for TAN’s performance:
- Tariffs and Trade Policies: Tariffs on Chinese solar imports have been beneficial for U.S.-based companies within TAN’s portfolio but could lead to retaliatory measures affecting global trade dynamics.
- Incentives from Government Programs: The Inflation Reduction Act aims to bolster domestic production of solar technologies through tax credits and financial incentives, supporting companies within the ETF.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations globally may enhance demand for solar technologies but could also impose compliance costs on manufacturers.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Invesco Solar ETF is complex:
- Growth Potential: As global efforts towards sustainability increase, there is substantial potential for growth in the solar sector. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that global solar capacity will continue expanding rapidly.
- Risks of Oversupply: Despite growth potential, oversupply issues could persist if production outpaces demand. This scenario could lead to further price declines and negatively impact profitability across the sector.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in solar technology and energy storage solutions may enhance efficiency and reduce costs, potentially benefiting companies within TAN’s holdings.
In summary, while there are promising aspects regarding the future of solar energy and potential gains from investing in TAN, significant risks remain that could hinder performance. Investors should weigh these factors carefully when considering an investment in the Invesco Solar ETF.
Frequently Asked Questions About Is Invesco Solar ETF A Good Investment?
- What is Invesco Solar ETF (TAN)?
TAN is an exchange-traded fund that tracks the MAC Global Solar Energy Index, providing exposure to companies involved in solar energy production. - How has TAN performed historically?
TAN has underperformed relative to major indices like the S&P 500 over the past decade with low annualized returns. - What are the main risks associated with investing in TAN?
The main risks include market volatility, concentration risk due to heavy reliance on a few companies, and regulatory uncertainties. - Is now a good time to invest in TAN?
The decision depends on individual risk tolerance; current market conditions suggest caution due to ongoing volatility. - What are the top holdings in TAN?
The top holdings include Enphase Energy, First Solar, Sunrun, among others primarily based in the U.S. - What is the expense ratio of TAN?
TAN has an expense ratio of 0.69%, which is moderate compared to other ETFs. - How does government policy affect TAN?
Government policies regarding tariffs and incentives significantly influence profitability for companies within TAN’s portfolio. - What does the future hold for solar investments?
The future appears promising due to increasing demand for renewable energy but remains clouded by potential oversupply issues.
This comprehensive analysis provides insights into whether investing in Invesco Solar ETF aligns with your financial goals and risk appetite.