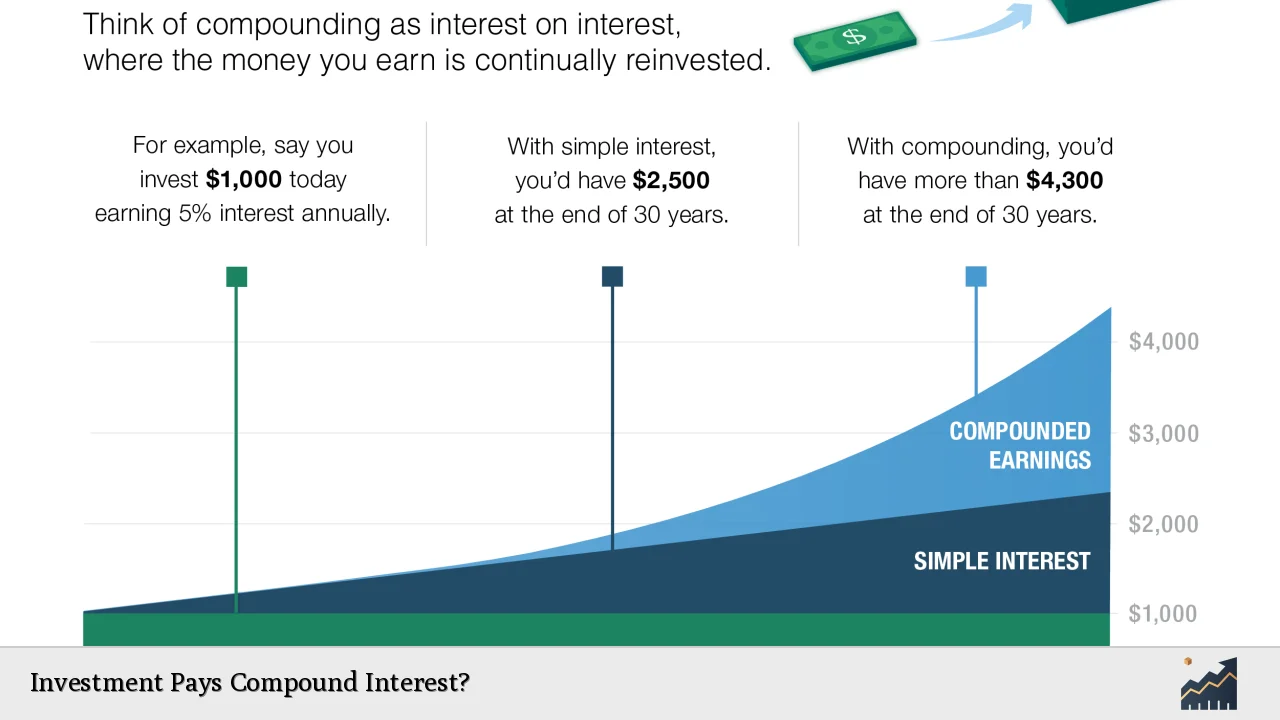
Compound interest is a powerful financial concept that allows your investments to grow exponentially over time. Unlike simple interest, which is calculated only on the principal amount, compound interest is calculated on the initial principal and also on the accumulated interest from previous periods. This means that over time, your interest earns additional interest, leading to a snowball effect that can significantly increase your wealth.
Investing in vehicles that pay compound interest can be a smart strategy for building long-term wealth. These investments can include savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), bonds, dividend stocks, and mutual funds. Each of these options has its own characteristics, risks, and potential returns, making it important to choose wisely based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
| Investment Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Savings Accounts | Low risk, low return; suitable for emergency funds. |
| Certificates of Deposit (CDs) | Fixed term; higher interest than savings accounts; penalties for early withdrawal. |
| Bonds | Debt securities; vary in risk; interest paid periodically. |
| Dividend Stocks | Equity investments; dividends can be reinvested for compounding. |
| Mutual Funds | Pools of investments; professionally managed; can include stocks and bonds. |
Understanding Compound Interest
Compound interest can be defined as the process where the interest earned on an investment is reinvested to generate additional earnings over time. This concept is often referred to as “interest on interest,” and it plays a crucial role in wealth accumulation. The longer you leave your money invested, the more pronounced the effects of compounding will be.
The power of compound interest becomes apparent when you consider how it operates over extended periods. For instance, if you invest a sum of money at a fixed interest rate, the amount you earn each year will increase as the principal grows. This means that even small initial investments can lead to substantial wealth over time if left to compound.
To maximize the benefits of compound interest, it is essential to start investing early and consistently contribute to your investments. The earlier you begin investing, the more time your money has to grow through compounding.
Types of Investments That Pay Compound Interest
Several investment options allow you to benefit from compound interest. Here are some popular choices:
- Savings Accounts: These accounts typically offer lower interest rates but are very safe. They are ideal for emergency funds or short-term savings goals.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts and require you to lock in your money for a specified term. They are low-risk investments but may incur penalties for early withdrawals.
- Bonds: Bonds are loans made to governments or corporations in exchange for periodic interest payments. While they offer fixed income, their value can fluctuate based on market conditions.
- Dividend Stocks: Investing in stocks that pay dividends allows you to earn income while also benefiting from potential capital appreciation. Reinvesting dividends can significantly enhance your returns through compounding.
- Mutual Funds: These funds pool money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks and bonds. Many mutual funds offer reinvestment options for dividends and capital gains.
How Compound Interest Works in Different Investments
Understanding how compound interest works in various investment vehicles can help you make informed decisions about where to allocate your funds.
Savings Accounts
Savings accounts provide a straightforward way to earn compound interest. Banks typically compound interest daily or monthly, which means that even small amounts can grow over time. However, the returns are generally modest compared to other investment options.
Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
CDs usually offer higher rates than savings accounts because they require you to commit your funds for a fixed period. The longer the term, the higher the interest rate tends to be. Interest on CDs is compounded at regular intervals (monthly or annually), enhancing overall returns.
Bonds
Bonds pay periodic interest, which can also be reinvested for compounding benefits. While investing in bonds generally carries less risk than stocks, it is crucial to consider factors such as credit quality and market conditions when selecting bonds.
Dividend Stocks
Dividend stocks not only provide income through dividends but also have the potential for capital appreciation. By reinvesting dividends through a Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP), investors can purchase additional shares without incurring transaction fees, further enhancing compounding effects.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds allow investors to diversify their portfolios while benefiting from professional management. Many mutual funds automatically reinvest dividends and capital gains distributions, making them an effective vehicle for harnessing compound interest.
Importance of Reinvesting Earnings
One of the most critical aspects of maximizing compound interest is reinvesting earnings. Whether it’s through dividends from stocks or interest from bonds and CDs, reinvesting allows your investments to grow at an accelerated pace.
When you reinvest earnings instead of cashing them out, you’re effectively increasing your principal amount. This larger principal will then earn more in future periods due to compounding, leading to exponential growth over time.
Investors should also be mindful of tax implications when reinvesting earnings. In some cases, taxes may reduce the effective compounding rate if not managed properly.
Strategies for Maximizing Compound Interest
To take full advantage of compound interest in your investment strategy, consider these effective approaches:
- Start Early: The earlier you begin investing, the more time your money has to grow through compounding.
- Be Consistent: Regular contributions can significantly enhance compounding effects over time.
- Reinvest Earnings: Always consider reinvesting any earnings from dividends or interest payments back into your investments.
- Diversify Investments: A diverse portfolio can help balance risk while taking advantage of different compounding opportunities across asset classes.
- Avoid Early Withdrawals: Keeping your money invested allows it to continue growing without interruption from withdrawals or spending.
Risks Associated with Compound Interest Investments
While compound interest has many benefits, it’s essential to recognize potential risks involved with different investment types:
- Market Risk: Stocks and mutual funds are subject to market fluctuations that can affect their value.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in prevailing interest rates can impact bond prices and CD yields.
- Inflation Risk: If investment returns do not outpace inflation rates, purchasing power may decrease over time.
- Liquidity Risk: Some investments may tie up funds for extended periods (e.g., CDs), making it difficult to access cash when needed without penalties.
FAQs About Investment Pays Compound Interest
- What is compound interest?
Compound interest is calculated on the initial principal as well as on the accumulated interest from previous periods. - How does compound interest benefit investors?
It allows investments to grow exponentially over time by earning “interest on interest.” - Which investments typically offer compound interest?
Savings accounts, CDs, bonds, dividend stocks, and mutual funds often provide opportunities for compound growth. - Is it better to reinvest earnings?
Yes, reinvesting earnings maximizes growth potential by increasing the principal amount subject to compounding. - What risks should I consider with compound-interest investments?
Market risk, inflation risk, liquidity risk, and changes in interest rates are important considerations when investing.
By understanding how different investments work with compound interest and implementing effective strategies, individuals can significantly enhance their wealth-building efforts over time. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to optimize an existing portfolio, leveraging the power of compound interest is key to achieving long-term financial success.