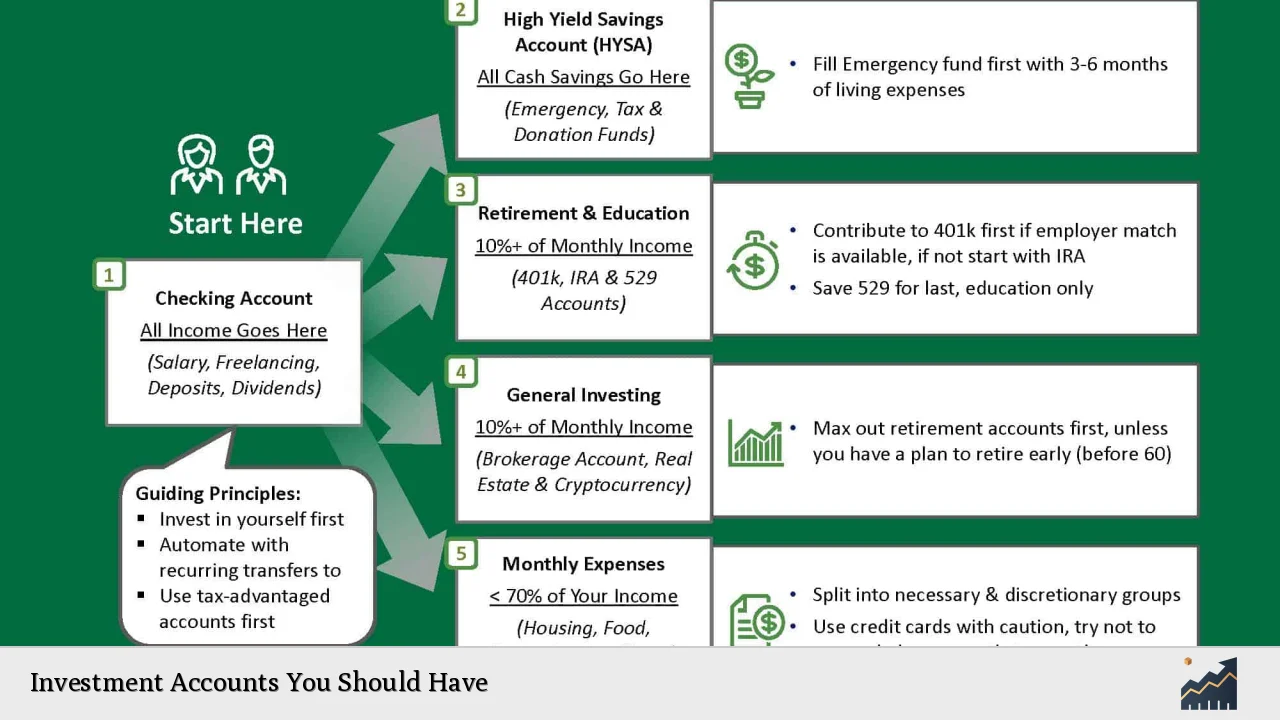
Choosing the right investment accounts is crucial for achieving your financial goals. Different accounts serve various purposes, from retirement savings to education funding. Understanding the types of investment accounts available can help you make informed decisions that align with your financial objectives.
Investment accounts can be broadly categorized into three main types: tax-deferred retirement accounts, brokerage accounts, and education savings accounts. Each type has unique features, benefits, and limitations that cater to different investment strategies and goals. Selecting the right combination of these accounts can optimize your investment potential and tax efficiency.
| Account Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Tax-Deferred Retirement Accounts | Accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s that allow you to save for retirement with tax benefits. |
| Brokerage Accounts | Flexible accounts for buying and selling various investments like stocks and bonds. |
| Education Savings Accounts | Accounts designed to save for educational expenses, such as 529 plans. |
Tax-Deferred Retirement Accounts
Tax-deferred retirement accounts are essential for anyone looking to save for retirement while minimizing their tax burden. These accounts allow your investments to grow without being taxed until you withdraw the funds, typically during retirement when your income may be lower.
Types of Retirement Accounts
- Traditional IRA: Contributions are tax-deductible, and taxes are paid upon withdrawal during retirement. This account is suitable for individuals who expect to be in a lower tax bracket when they retire.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning withdrawals during retirement are tax-free. This account is ideal for younger investors who expect their income—and tax rate—to increase over time.
- 401(k): Offered by employers, this account allows employees to contribute a portion of their salary before taxes. Many employers match contributions up to a certain percentage, effectively providing free money towards your retirement.
- SEP IRA: Designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners, this account allows higher contribution limits than traditional IRAs, making it a great option for those with fluctuating incomes.
Benefits of Retirement Accounts
Investing in tax-deferred retirement accounts provides several advantages:
- Tax Savings: Contributions may lower your taxable income in the year you make them.
- Compound Growth: Your investments grow without the drag of annual taxes, potentially increasing your overall returns.
- Employer Matches: Many employers offer matching contributions in 401(k) plans, which can significantly boost your retirement savings.
Having a mix of these accounts can provide flexibility and maximize your savings over time.
Brokerage Accounts
Brokerage accounts offer a flexible way to invest in various assets such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and ETFs. Unlike retirement accounts, brokerage accounts do not have contribution limits or restrictions on withdrawals, making them suitable for both short-term trading and long-term investing.
Types of Brokerage Accounts
- Standard Brokerage Account: This account allows you to buy and sell a wide range of investments without restrictions on the amount you can contribute or withdraw.
- Margin Account: This type allows you to borrow money from the broker to purchase more securities than you could with just your cash balance. While this can amplify gains, it also increases risk.
Benefits of Brokerage Accounts
Investing through brokerage accounts comes with several benefits:
- Liquidity: You can access your funds at any time without penalties, making it easier to respond to market changes or personal financial needs.
- Diverse Investment Options: You can invest in various asset classes, allowing for a diversified portfolio tailored to your risk tolerance.
- Flexibility: There are no restrictions on how much you can invest or when you can withdraw funds.
Brokerage accounts are ideal for investors looking for flexibility and control over their investment choices while managing their financial goals actively.
Education Savings Accounts
Education savings accounts are specifically designed to help families save for future educational expenses. These accounts offer tax advantages that can significantly reduce the cost of higher education when used appropriately.
Types of Education Savings Accounts
- 529 Plans: These state-sponsored plans allow you to save money for education expenses while enjoying tax-free growth and withdrawals when used for qualified expenses like tuition and fees.
- Coverdell Education Savings Account (ESA): This account allows contributions up to $2,000 per year per beneficiary. Earnings grow tax-free if used for qualified education expenses before age 30.
Benefits of Education Savings Accounts
Investing in education savings accounts provides several advantages:
- Tax-Free Growth: Earnings grow without being taxed as long as withdrawals are used for qualified educational expenses.
- Flexibility in Use: Funds from 529 plans can be used at eligible institutions nationwide, including colleges, universities, vocational schools, and even K-12 expenses in some cases.
- State Tax Deductions: Many states offer tax deductions or credits for contributions made to 529 plans, providing additional incentives to save.
These accounts are vital for families planning for their children’s education costs while maximizing potential savings through tax benefits.
Choosing the Right Investment Accounts
When deciding which investment accounts to open, consider the following factors:
- Financial Goals: Identify what you’re saving for—retirement, education, or wealth accumulation—and choose accounts that align with those objectives.
- Time Horizon: Understand how long you plan to invest. Longer time horizons may benefit from more aggressive investments in stocks or mutual funds.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess how much risk you’re willing to take. Higher-risk investments may yield greater returns but come with increased volatility.
By evaluating these factors and understanding the different types of investment accounts available, you can create a diversified portfolio that meets your specific needs while maximizing growth potential.
FAQs About Investment Accounts
- What is a brokerage account?
A brokerage account is an investment account that allows individuals to buy and sell securities like stocks and bonds. - What is the difference between a traditional IRA and a Roth IRA?
A traditional IRA offers tax-deductible contributions but taxes withdrawals; a Roth IRA has no upfront tax deduction but allows tax-free withdrawals. - Can I have multiple investment accounts?
Yes, having multiple investment accounts can help diversify your investments and optimize tax benefits. - What are the benefits of using a 529 plan?
A 529 plan provides tax-free growth on investments when used for qualified educational expenses. - How do I choose the right investment account?
Consider your financial goals, time horizon, risk tolerance, and whether you need immediate access to funds when choosing an investment account.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of investment accounts available is essential for effective financial planning. By strategically selecting the right combination of tax-deferred retirement accounts, brokerage accounts, and education savings accounts based on your unique circumstances and goals, you can build a robust financial future that meets both short-term needs and long-term aspirations.