Navigating the stock market can be daunting, especially for new investors who encounter a plethora of specialized terms and jargon. Understanding these terms is crucial for making informed investment decisions and effectively communicating within the financial community. This guide aims to demystify stock market jargon, providing clear definitions and insights into their implications for investors.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Bear Market | A market condition characterized by declining prices, typically defined as a drop of 20% or more from recent highs. It reflects widespread pessimism and can lead to reduced investor confidence. |
| Bull Market | Conversely, a bull market indicates rising prices and investor optimism, often associated with strong economic growth and positive corporate earnings. |
| Dividend | A portion of a company's earnings distributed to shareholders, often seen as a sign of financial health. Dividends can provide a steady income stream for investors. |
| Market Order | An order to buy or sell a stock at the current market price, ensuring immediate execution but not guaranteeing the price. |
| Limit Order | A request to buy or sell a stock at a specified price or better, allowing investors to control the price they pay or receive. |
| Liquidity | The ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price. High liquidity is generally favorable as it allows for quick transactions. |
| Volatility | A statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security. High volatility indicates higher risk but also potential for higher returns. |
| Margin Call | A demand by a broker for an investor to deposit more funds into their margin account when the account value falls below the required level, highlighting the risks associated with leveraged trading. |
| Earnings Per Share (EPS) | A company's profit divided by its number of outstanding shares, serving as an indicator of profitability and financial health. |
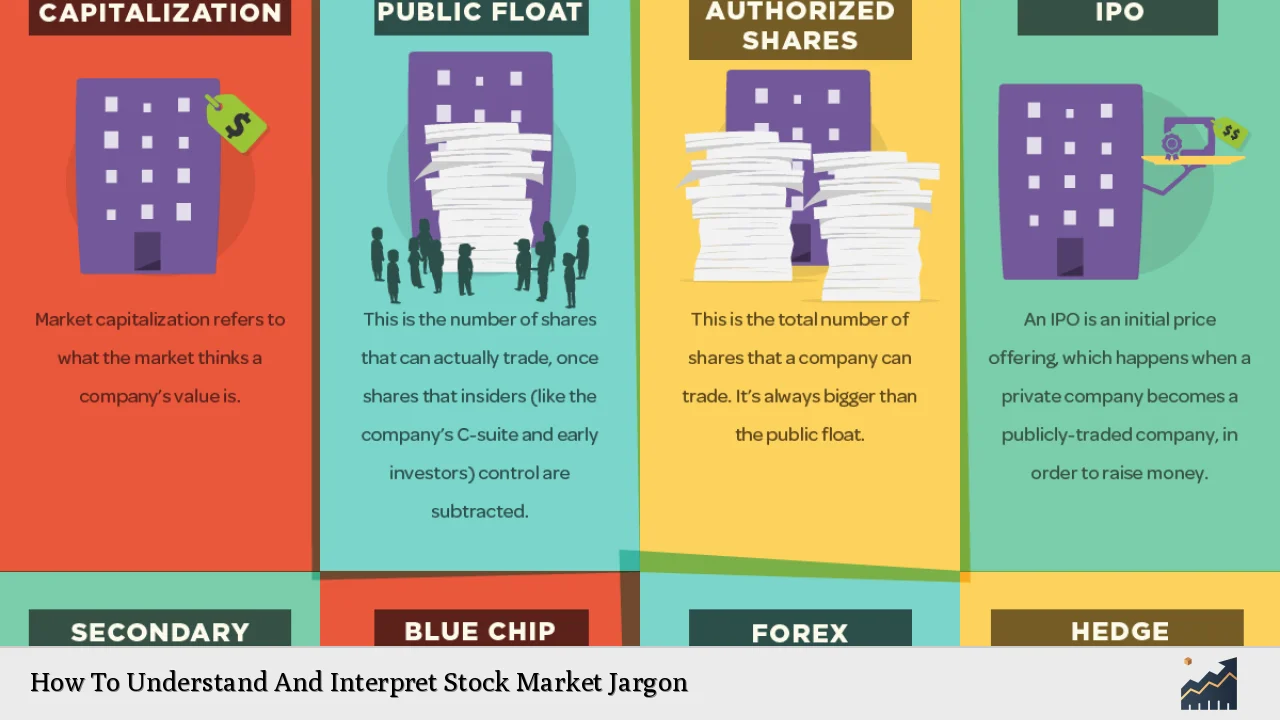
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | The process through which a private company offers shares to the public for the first time, often used to raise capital for expansion. |
| Stop Loss Order | An order placed to sell a stock when it reaches a certain price, designed to limit an investor's loss on a position. |
Market Analysis and Trends
Understanding stock market jargon is essential in analyzing current market trends. For instance, terms like "bull market" and "bear market" are not just descriptive but also indicative of broader economic conditions. As of December 2024, the Dow Jones Industrial Average has experienced fluctuations, marking its longest losing streak since 2020. This trend reflects investor sentiment and economic indicators such as inflation rates and corporate earnings.
Current Market Statistics
- Dow Jones Industrial Average: Closed at 43,828.06 with a decline over several days.
- S&P 500: Finished at 6,051.09.
- Nasdaq Composite: Experienced significant volatility but showed resilience amidst broader market declines.
These statistics highlight the importance of understanding market conditions through jargon that describes these movements.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively navigate the stock market, investors should implement strategies that incorporate knowledge of key terms:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various sectors to mitigate risk.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: Investing a fixed amount regularly regardless of stock price fluctuations.
- Averaging Down: Buying additional shares as prices drop to lower the average cost per share.
By employing these strategies, investors can leverage their understanding of jargon to make informed decisions and manage their portfolios effectively.
Risk Considerations
Investing in stocks carries inherent risks that are often articulated through specific jargon:
- Volatility: Understanding that high volatility stocks can lead to significant gains or losses.
- Margin Trading: While it can amplify returns, it also increases risk; thus, understanding margin calls is critical.
- Liquidity Risk: Knowing how quickly you can exit positions without significant price impact is vital for managing risk.
Implementing robust risk management practices helps investors navigate these challenges while using appropriate terminology.
Regulatory Aspects
Regulatory bodies like the SEC play a crucial role in overseeing stock markets. Understanding terms related to regulation is important:
- Compliance: Investors must be aware of regulations governing trading practices.
- Reporting Requirements: Companies must adhere to strict reporting standards that affect stock valuations.
Recent regulatory changes emphasize transparency and investor protection, impacting how investors interpret market movements.
Future Outlook
The future of investing will likely see increased reliance on technology and data analysis. Emerging trends include:
- AI in Trading: Utilizing artificial intelligence for predictive analytics in trading strategies.
- Sustainable Investing: Growing interest in ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors influencing investment decisions.
Investors should stay informed about these trends and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions About How To Understand And Interpret Stock Market Jargon
- What is a bear market?
A bear market refers to a period when stock prices fall by 20% or more from recent highs, indicating widespread pessimism among investors. - What does liquidity mean in investing?
Liquidity measures how easily an asset can be bought or sold in the market without affecting its price. - How do dividends work?
Dividends are payments made by a company to its shareholders from its profits, providing income in addition to capital gains. - What is an IPO?
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is when a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time to raise capital. - What is volatility?
Volatility refers to the degree of variation in trading prices over time; high volatility means greater risk but also potential rewards. - What does averaging down mean?
Averaging down involves buying more shares of a declining stock to reduce the average cost per share. - What are margin calls?
A margin call occurs when an investor must deposit more funds into their margin account due to falling asset values. - Why is understanding stock market jargon important?
Understanding jargon helps investors make informed decisions, communicate effectively with other investors and analysts, and interpret market conditions accurately.
This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for individual investors and finance professionals alike. By mastering stock market jargon, one can enhance their investment acumen and navigate the complexities of financial markets with confidence.