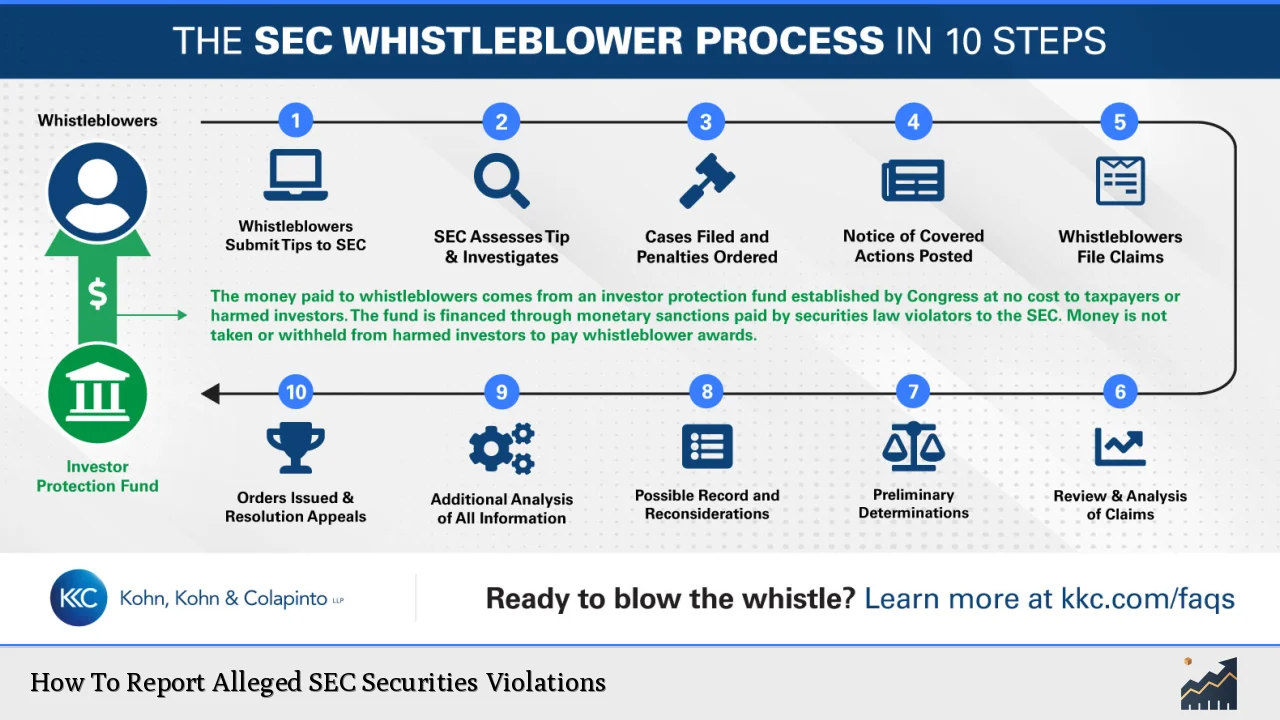
Reporting alleged violations of securities laws is a crucial process for maintaining the integrity of financial markets. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) provides mechanisms for individuals to report suspected misconduct, including fraud, insider trading, and market manipulation. This guide outlines the steps to effectively report these violations, the regulatory framework surrounding them, and the potential implications for both whistleblowers and the financial markets.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| SEC Reporting Mechanisms | The SEC offers various channels for reporting violations, including an online Tips, Complaints, and Referrals (TCR) form that allows for anonymous submissions. |
| Types of Violations | Common violations include Ponzi schemes, insider trading, market manipulation, and fraudulent financial reporting. |
| Whistleblower Protections | The SEC Whistleblower Program provides incentives and protections for individuals who report violations, including monetary rewards ranging from 10% to 30% of collected sanctions. |
| Regulatory Response | The SEC investigates reported violations and can impose significant penalties on wrongdoers, contributing to investor protection and market integrity. |
| Future Trends | As financial markets evolve, the SEC is likely to enhance its focus on emerging threats such as cybersecurity risks and cryptocurrency-related fraud. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The landscape of securities regulation is constantly evolving. In fiscal year 2024, the SEC filed 583 enforcement actions, resulting in over $8.2 billion in financial remedies—the highest amount recorded in its history. This reflects a robust approach to enforcement despite a 26% decline in total actions compared to the previous year. Notably, there was an increase in self-reporting by firms, indicating a shift towards a culture of compliance within the industry.
Recent trends show that:
- Increased Whistleblower Activity: The SEC received over 45,000 tips in FY 2024, with more than 24,000 coming from whistleblowers. This surge highlights growing awareness and willingness among individuals to report misconduct.
- Focus on Cybersecurity: With rising incidents of cyber fraud and data breaches affecting public companies, the SEC has intensified scrutiny over compliance with cybersecurity regulations.
- Cryptocurrency Regulation: As digital currencies gain popularity, the SEC is actively investigating potential frauds related to cryptocurrencies and initial coin offerings (ICOs).
Implementation Strategies
To report alleged securities violations effectively:
- Gather Evidence: Collect all relevant information before filing a complaint. This includes documentation of transactions, communications related to the alleged misconduct, and any other pertinent evidence.
- Choose Reporting Method: Utilize the SEC’s TCR form for anonymous reporting or consult with legal counsel for guidance on how to proceed while protecting your identity.
- Submit Your Report: Complete the TCR form online or contact the SEC’s Office of Investor Education and Advocacy if you need assistance.
- Follow Up: After submitting your report, you may not receive immediate feedback due to confidentiality protocols; however, you can inquire about the status of your complaint through official channels.
- Consider Legal Representation: Engaging with an attorney experienced in securities law can help navigate complex legal waters and enhance your chances of a successful outcome.
Risk Considerations
Reporting securities violations carries certain risks:
- Retaliation: Whistleblowers may face backlash from employers or colleagues. The SEC provides protections under its Whistleblower Program to mitigate these risks.
- Legal Implications: Misreporting or failing to provide accurate information can lead to legal repercussions for the whistleblower. It is crucial to ensure that all claims are substantiated with credible evidence.
- Market Repercussions: Reporting misconduct can impact stock prices and investor confidence in affected companies. While this may serve the greater good by promoting transparency, it can also lead to volatility in the short term.
Regulatory Aspects
The SEC plays a pivotal role in enforcing securities laws:
- Enforcement Actions: The agency has broad authority to investigate alleged violations and can pursue civil actions against offenders. In FY 2024 alone, it imposed penalties totaling billions of dollars.
- Whistleblower Incentives: The Dodd-Frank Act established the SEC Whistleblower Program to encourage reporting by offering financial rewards based on collected sanctions from successful enforcement actions.
- Investor Protection Initiatives: The SEC continuously updates its regulations to address new challenges in the financial landscape, ensuring that investors are protected from fraudulent activities.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead:
- Technological Advancements: As technology continues to reshape financial markets, regulatory bodies like the SEC will need to adapt their strategies to combat new forms of fraud related to fintech innovations.
- Enhanced Compliance Culture: Increasingly proactive compliance measures among firms suggest a shift towards self-regulation within the industry, potentially reducing reliance on external reporting mechanisms over time.
- Global Regulatory Coordination: With financial markets becoming more interconnected globally, collaboration between regulatory bodies across borders will be essential in addressing cross-border securities violations effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions About How To Report Alleged SEC Securities Violations
- What types of violations can I report?
You can report various violations such as insider trading, Ponzi schemes, market manipulation, accounting fraud, and misleading statements about securities. - How do I file a complaint with the SEC?
You can file a complaint using the SEC’s online Tips, Complaints & Referrals (TCR) form or contact their Office of Investor Education and Advocacy for assistance. - Can I remain anonymous when reporting?
Yes, you can submit your complaint anonymously through the TCR form; however, providing your identity may help facilitate investigations. - What protections do whistleblowers have?
The SEC provides protections against retaliation for whistleblowers under its Whistleblower Program; this includes confidentiality during investigations. - What rewards are available for whistleblowers?
Whistleblowers may receive monetary rewards ranging from 10% to 30% of any sanctions collected as a result of their information leading to successful enforcement actions. - How long does it take for the SEC to act on my report?
The timeline varies based on case complexity; however, significant cases may take months or even years before reaching resolution. - Is legal representation necessary when reporting?
While not required, having legal representation can be beneficial for navigating complex issues related to securities law and ensuring proper submission of your claim. - What happens after I file my complaint?
After filing your complaint, it will be reviewed by SEC staff who will determine whether further investigation is warranted based on the information provided.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower individual investors and finance professionals with knowledge about reporting alleged securities violations effectively while understanding their rights and responsibilities within this critical regulatory framework.