Managing your investments effectively is crucial for achieving your financial goals and securing your financial future. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the key principles of investment management can help you make informed decisions and optimize your portfolio’s performance. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps and strategies for managing your investments successfully.
Effective investment management involves a combination of strategic planning, risk assessment, diversification, and ongoing monitoring. By following these principles, you can create a robust investment strategy that aligns with your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
| Key Components | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Strategic Planning | Aligns investments with goals |
| Risk Assessment | Minimizes potential losses |
| Diversification | Spreads risk across assets |
| Ongoing Monitoring | Ensures portfolio optimization |
Define Your Investment Goals
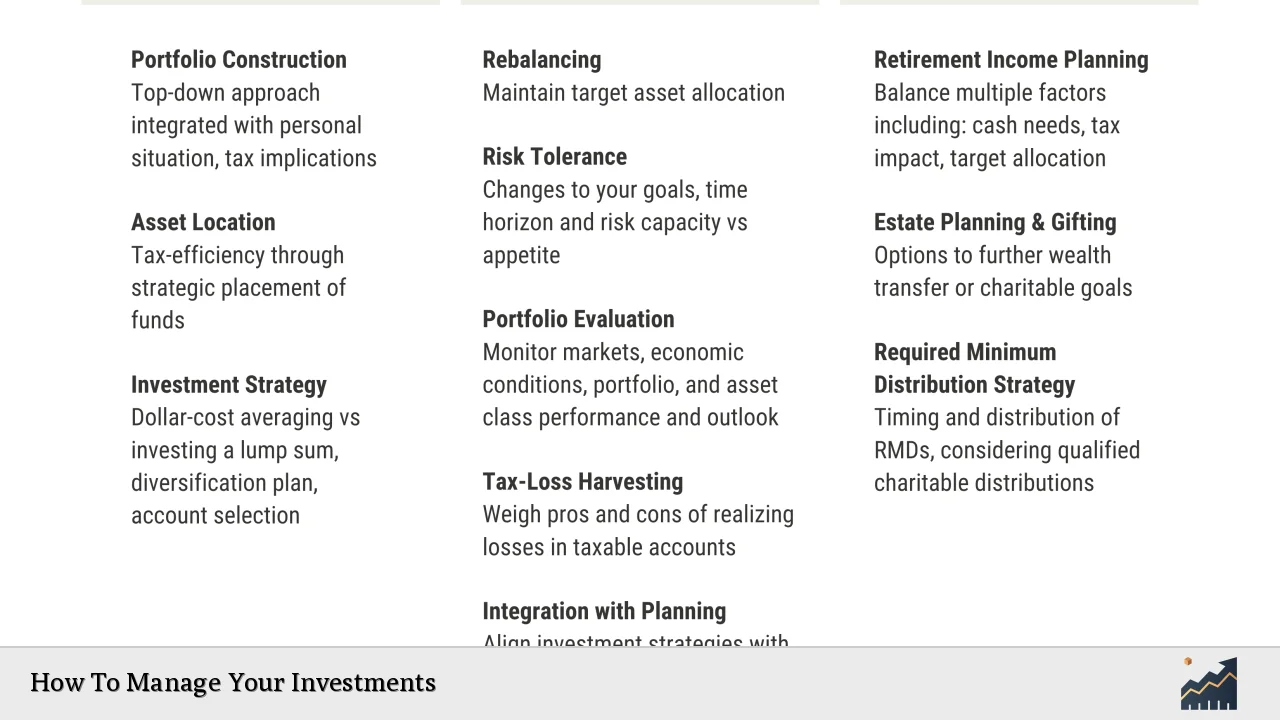
The first step in managing your investments is to clearly define your financial objectives. Your goals will serve as the foundation for your investment strategy and help guide your decision-making process. Consider both short-term and long-term goals, such as saving for a down payment on a house, funding your children’s education, or planning for retirement.
When setting your investment goals, it’s essential to make them SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This approach will help you create a clear roadmap for your investment journey and allow you to track your progress effectively.
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve
- Measurable: Set concrete targets to measure progress
- Achievable: Ensure your goals are realistic and attainable
- Relevant: Align your goals with your overall financial plan
- Time-bound: Set specific timeframes for achieving your objectives
By establishing well-defined goals, you can tailor your investment strategy to meet your unique needs and circumstances. This personalized approach will help you stay focused and motivated as you work towards your financial aspirations.
Assess Your Risk Tolerance
Understanding your risk tolerance is crucial for developing an investment strategy that you can stick to in the long run. Risk tolerance refers to your ability and willingness to endure fluctuations in the value of your investments. Factors that influence risk tolerance include:
- Age and investment timeline
- Financial situation and income stability
- Personal comfort level with market volatility
- Overall financial goals and objectives
To assess your risk tolerance, consider taking a risk assessment questionnaire or consulting with a financial advisor. This evaluation will help you determine the appropriate balance between risk and potential returns in your investment portfolio.
Risk-Return Trade-off
It’s important to understand the relationship between risk and potential returns. Generally, investments with higher potential returns come with higher levels of risk. Conversely, lower-risk investments typically offer more modest returns. Finding the right balance is key to managing your investments effectively.
| Risk Level | Potential Returns |
|---|---|
| Low | Lower, more stable |
| Moderate | Balanced growth potential |
| High | Higher, more volatile |
Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification is a fundamental principle of investment management that helps reduce risk by spreading your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions. By diversifying your portfolio, you can potentially minimize the impact of poor performance in any single investment on your overall returns.
Key strategies for diversifying your portfolio include:
- Investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents
- Allocating assets across different market sectors and industries
- Including both domestic and international investments
- Considering alternative investments like real estate or commodities
- Using mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) for broad market exposure
Remember that diversification doesn’t guarantee profits or protect against losses, but it can help manage risk and potentially improve your long-term investment outcomes.
Develop an Asset Allocation Strategy
Asset allocation is the process of dividing your investment portfolio among different asset categories, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. Your asset allocation strategy should be based on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline.
A well-designed asset allocation strategy can help you:
- Balance risk and reward in your portfolio
- Maintain a consistent approach to investing
- Adjust your investments as your goals or circumstances change
Consider using the following guidelines when developing your asset allocation strategy:
- Stocks: Higher growth potential, higher risk
- Bonds: Lower risk, income generation
- Cash and equivalents: Liquidity and stability
As you age or your financial situation changes, you may need to adjust your asset allocation to maintain an appropriate balance of risk and potential returns.
Implement a Regular Rebalancing Schedule
Rebalancing is the process of realigning your portfolio’s asset allocation to its original target percentages. Over time, market fluctuations can cause your portfolio to drift from its intended allocation, potentially exposing you to more or less risk than you’re comfortable with.
Implementing a regular rebalancing schedule helps maintain your desired asset allocation and can potentially improve your long-term investment returns. Consider rebalancing your portfolio:
- On a set schedule (e.g., annually or semi-annually)
- When your asset allocation drifts beyond a predetermined threshold
- In response to significant life events or changes in your financial situation
Rebalancing may involve selling investments that have performed well and buying those that have underperformed, which can help you maintain a disciplined approach to investing.
Monitor and Review Your Investments Regularly
Ongoing monitoring and review of your investments are essential for ensuring that your portfolio remains aligned with your goals and risk tolerance. Regular reviews allow you to:
- Assess the performance of individual investments
- Identify underperforming assets that may need to be replaced
- Evaluate the overall health of your portfolio
- Make necessary adjustments to your investment strategy
Set a schedule for reviewing your investments, such as quarterly or semi-annually. During these reviews, consider the following factors:
- Performance relative to benchmarks and your goals
- Changes in your personal financial situation or goals
- Market conditions and economic trends
- Fees and expenses associated with your investments
By staying informed and proactive in managing your investments, you can make timely decisions and keep your portfolio on track to meet your financial objectives.
Consider Professional Advice
While many investors choose to manage their investments independently, seeking professional advice can be beneficial, especially for complex financial situations or large portfolios. A financial advisor can provide valuable insights, help you develop a comprehensive investment strategy, and offer guidance on navigating market volatility.
When considering professional advice, look for:
- Credentials and qualifications (e.g., CFP, CFA)
- Experience and track record
- Fee structure and transparency
- Alignment with your investment philosophy and goals
Remember that even if you work with a financial advisor, it’s important to stay informed and involved in the management of your investments.
FAQs About How To Manage Your Investments
- How often should I review my investment portfolio?
It’s generally recommended to review your portfolio at least annually or semi-annually, and more frequently if there are significant market changes or life events. - What’s the ideal asset allocation for my age?
A common rule of thumb is to subtract your age from 100 to determine the percentage of stocks in your portfolio, with the remainder in bonds and cash. - How can I minimize taxes on my investments?
Consider tax-efficient investment strategies such as using tax-advantaged accounts, holding investments long-term, and harvesting tax losses when appropriate. - Should I invest in individual stocks or mutual funds?
For most investors, a diversified portfolio of low-cost index funds or ETFs provides broad market exposure with lower risk than individual stock picking. - How much should I be saving for retirement?
Aim to save at least 15% of your income for retirement, including any employer contributions. Adjust this percentage based on your age and retirement goals.