Investing in venture capital (VC) funds can be an exciting opportunity for individuals looking to diversify their investment portfolios and engage with innovative startups. Venture capital funds primarily invest in early-stage companies with high growth potential, providing them with the necessary capital to scale their operations. This investment strategy is characterized by high risk and potentially high returns, making it essential for investors to understand the dynamics of the venture capital landscape before committing their resources.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Venture Capital Definition | Venture capital involves investing in startups and small businesses with high growth potential in exchange for equity, typically during early stages of development. |
| Investment Structure | VC funds are structured as limited partnerships where general partners manage the fund and make investment decisions, while limited partners provide capital but have no active role. |
| Risk and Return Profile | The venture capital model is inherently risky; approximately 65% of investments may not return capital, while successful investments can yield substantial returns, often concentrated in a few “home run” companies. |
| Market Trends | The global venture capital market is projected to grow from $309.54 billion in 2024 to $435.56 billion by 2031, driven by increasing startup activity and innovation across sectors. |
| Investment Strategies | Successful VC funds often employ strategies like diversification across industries or stages of development, as well as specialization in particular sectors to leverage expertise. |
| Regulatory Considerations | Investors must be aware of regulations governing VC investments, including compliance with SEC guidelines and understanding the legal structure of funds. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The venture capital landscape has undergone significant transformation in recent years. The global VC market size is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5% from 2024 to 2031, reaching around $435.56 billion by 2031. This growth is fueled by an increase in the number of startups seeking funding, particularly in technology-driven sectors such as artificial intelligence (AI), healthcare, and renewable energy.
Current Market Statistics
- Global Market Size: Estimated at $309.54 billion in 2024.
- Projected Growth: Expected to reach $435.56 billion by 2031.
- Regional Insights:
- North America dominates with over 40% of global revenue.
- Asia-Pacific shows the fastest growth at a CAGR of 7% from 2024 to 2031.
Investment Dynamics
The venture capital market is characterized by its focus on high-risk, high-reward investments. The average deal size has increased significantly, particularly for seed and early-stage investments. In Q2 2024 alone, global VC funding reached $94 billion across approximately 4,500 deals, marking a recovery from previous downturns. Notably, sectors like AI have attracted substantial investment due to their transformative potential.
Implementation Strategies
Investing in a venture capital fund requires careful planning and strategy formulation. Here are key steps for individual investors:
Understanding Fund Structures
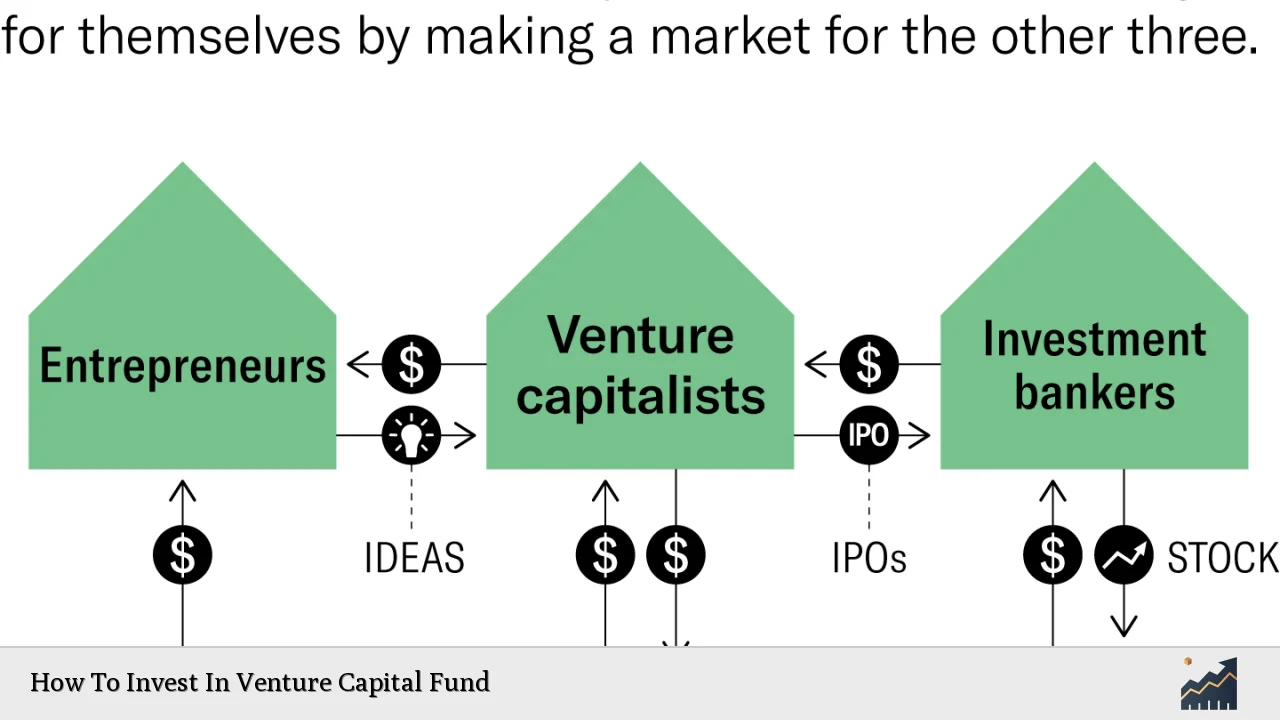
- Limited Partnerships: Most VC funds operate as limited partnerships where general partners (GPs) manage the fund and make investment decisions while limited partners (LPs) contribute capital without involvement in day-to-day operations.
- Fund Lifecycle: A typical VC fund has a lifecycle of about 7-10 years. Initial fundraising is followed by an investment period (usually three to five years), after which the focus shifts to managing the portfolio and planning exits.
Selecting a Fund
When choosing a venture capital fund to invest in:
- Assess Track Record: Review the historical performance of the fund managers and their previous funds.
- Evaluate Investment Thesis: Understand the fund’s focus—whether it specializes in specific industries or stages of company development.
- Consider Fees: Be aware of management fees (typically around 2%) and carried interest (usually about 20% of profits).
Diversification vs. Specialization
Investors can choose between diversified funds that spread investments across various sectors or specialized funds focusing on specific industries where they may have more expertise or interest.
Risk Considerations
Investing in venture capital comes with inherent risks:
- High Failure Rate: Approximately 65% of venture deals do not return the invested capital. Thus, it is crucial for investors to be prepared for potential losses.
- Illiquidity: Venture capital investments are typically illiquid; investors may not see returns for several years until an exit event occurs (e.g., IPO or acquisition).
Mitigating Risks
- Follow-On Investments: Successful VC firms reserve a portion of their funds for follow-on investments in promising portfolio companies to maintain ownership stakes and support growth.
- Diversification Strategy: By investing across multiple sectors or stages, investors can mitigate risks associated with individual company failures.
Regulatory Aspects
Understanding regulatory frameworks is essential for any investor considering venture capital:
- SEC Regulations: In the U.S., VC funds must comply with Securities and Exchange Commission regulations regarding fundraising and reporting requirements.
- Limited Partnership Agreements (LPA): Investors should carefully review LPAs that outline their rights, obligations, fee structures, and exit strategies.
Future Outlook
The future of venture capital appears promising but will require adaptability:
- Emerging Sectors: Continued interest in AI, healthcare innovation, sustainability technologies, and fintech will drive future investments.
- Global Expansion: As markets mature globally, opportunities will arise outside traditional hubs like Silicon Valley, particularly in emerging economies where entrepreneurial ecosystems are developing rapidly.
Overall, individual investors looking to enter the venture capital space should conduct thorough research on potential funds, understand market dynamics, assess risk tolerance levels, and stay informed about regulatory changes that could impact their investments.
Frequently Asked Questions About How To Invest In Venture Capital Fund
- What is a venture capital fund?
A venture capital fund pools money from investors to invest in early-stage companies with high growth potential. - How do I invest in a venture capital fund?
You can invest by becoming a limited partner in an existing VC fund or through special-purpose vehicles (SPVs) that allow access to specific deals. - What are the risks associated with investing in VC?
The primary risks include high failure rates among startups, illiquidity of investments, and potential loss of principal. - What fees should I expect when investing?
Typical fees include management fees around 2% and carried interest around 20% on profits generated by the fund. - How long does it take to see returns from VC investments?
Returns typically materialize over several years following exit events such as IPOs or acquisitions. - What types of companies do VC funds invest in?
VC funds often target technology-driven startups across various sectors including healthcare, fintech, and consumer goods. - Can I invest directly in startups instead of through a fund?
Yes, individual investors can engage in angel investing or participate in crowdfunding platforms focused on startups. - How can I evaluate a venture capital fund before investing?
Review the fund’s track record, investment strategy, fee structure, and management team experience before making a decision.
Investing in venture capital can be rewarding but requires careful consideration of various factors including market trends, risk management strategies, regulatory compliance, and thorough due diligence on potential funds.