Investing in venture capital (VC) funds offers a unique opportunity to participate in the growth of innovative startups. These funds pool money from various investors to finance early-stage companies, aiming for high returns through equity stakes. While the potential rewards are significant, the risks associated with investing in VC funds are also considerable, as many startups fail to achieve profitability. Understanding how to navigate this investment landscape is crucial for anyone looking to diversify their portfolio and tap into the high-growth potential of emerging businesses.
To begin investing in VC funds, one must first grasp the fundamental concepts and structures of venture capital. This includes knowing the roles of general partners (GPs) who manage the funds and limited partners (LPs) who provide the capital. Additionally, it's essential to recognize the various types of VC funds, their investment strategies, and the typical fee structures involved.
The following table summarizes key aspects of venture capital investing:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| General Partners (GPs) | Managers of the fund responsible for investment decisions. |
| Limited Partners (LPs) | Investors who provide capital but do not manage the fund. |
| Investment Horizon | Typically 10-12 years for returns on investments. |
| Fee Structure | Commonly a "2-and-20" model: 2% management fee and 20% carry on profits. |
Understanding Venture Capital
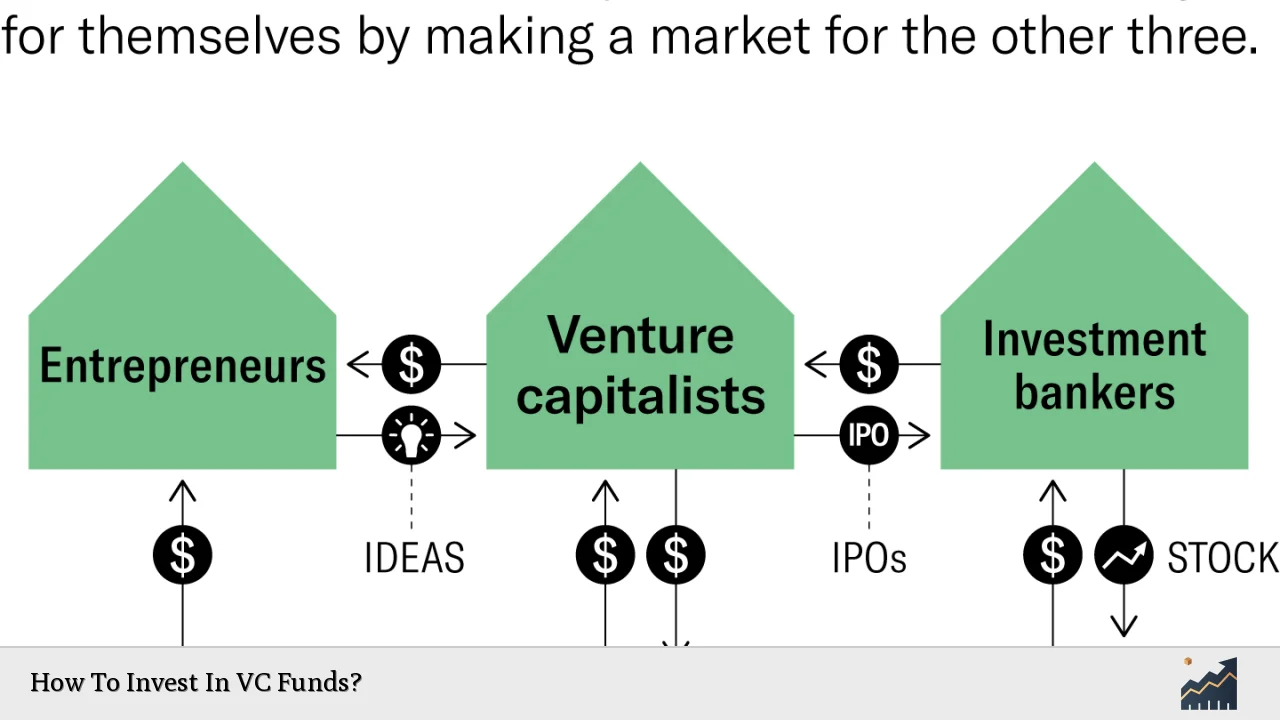
Venture capital is a form of private equity that focuses on investing in startups and small businesses with high growth potential. Unlike traditional investments in public companies, VC investments are made in private firms that often lack a proven track record. The aim is to provide these companies with the necessary capital to scale their operations and achieve significant market presence.
The venture capital ecosystem consists of various players, including entrepreneurs seeking funding, investors looking for opportunities, and intermediaries such as investment banks. The process typically begins when a startup seeks funding through different rounds, including seed funding, Series A, B, C, etc. Each round signifies a stage of growth and funding requirement.
Investors should be aware that investing in VC funds carries inherent risks. Many startups fail to deliver returns, making it crucial for investors to diversify their portfolios across multiple startups or funds. This diversification helps mitigate risks associated with individual company failures.
Types of Venture Capital Funds
There are several types of VC funds that cater to different investment strategies and risk appetites:
- Seed Funds: Focus on very early-stage companies that are just starting out.
- Early-Stage Funds: Invest in companies that have developed a product but need additional funding to grow.
- Late-Stage Funds: Target more established companies that are nearing an exit event like an IPO or acquisition.
- Sector-Specific Funds: Concentrate on specific industries such as technology, healthcare, or clean energy.
Understanding these categories can help investors choose funds that align with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
How to Evaluate Venture Capital Funds
Evaluating a VC fund before investing is critical. Here are some factors to consider:
- Track Record: Examine the historical performance of the fund manager and their previous investments.
- Investment Thesis: Understand the fund’s strategy regarding which sectors or stages they focus on.
- Management Team: Assess the experience and expertise of the GPs managing the fund.
- Fee Structure: Be aware of management fees and carried interest; these can significantly impact net returns.
Investors should also consider conducting due diligence on the underlying portfolio companies within the fund. This includes understanding their business models, market potential, and competitive landscape.
The Investment Process
Investing in VC funds typically involves several steps:
1. Accreditation: Ensure you meet the criteria to be considered an accredited investor, as many VC funds require this status due to regulatory reasons.
2. Research Funds: Identify potential VC funds by researching their performance history, sector focus, and management team.
3. Review Offering Documents: Carefully read through private placement memoranda (PPMs) and other offering documents provided by the fund.
4. Meet with Fund Managers: Engage with GPs to ask questions about their strategy, performance expectations, and risk management practices.
5. Commit Capital: Once comfortable with your choice, commit your capital according to the fund's minimum investment requirements.
6. Monitor Investments: After investing, keep track of fund performance through periodic updates from GPs.
Risks Involved in Venture Capital Investing
While venture capital can yield high returns, it is not without risks:
- High Failure Rate: Many startups do not succeed; thus, investors should expect some losses.
- Illiquidity: VC investments are typically illiquid for several years until an exit occurs.
- Market Volatility: Economic downturns can impact startup valuations significantly.
Investors must be prepared for these risks and consider them when allocating capital towards venture capital investments.
Key Considerations Before Investing
Before diving into venture capital investing, consider these important aspects:
- Investment Goals: Define what you aim to achieve—high returns, diversification, or supporting innovation.
- Time Horizon: Be ready for a long-term commitment; venture capital investments generally take years to mature.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your comfort level with high-risk investments before committing significant capital.
By understanding these factors, investors can make informed decisions about entering the venture capital space.
FAQs About How To Invest In VC Funds
- What is a venture capital fund?
A venture capital fund pools money from investors to finance early-stage startups. - Who can invest in VC funds?
Typically, only accredited investors can invest due to regulatory requirements. - What is a common fee structure for VC funds?
The standard fee structure is often "2-and-20": a 2% management fee and 20% carry on profits. - How long does it take to see returns from VC investments?
Returns from VC investments usually materialize after several years during exit events. - What are the main risks associated with investing in VC funds?
The main risks include high failure rates among startups and illiquidity of investments.
In conclusion, investing in venture capital funds presents an exciting opportunity for those looking to engage with innovative startups while seeking substantial returns. By understanding how these funds operate and carefully evaluating options based on personal investment goals and risk tolerance, investors can navigate this complex landscape effectively.