Investing in the Chinese stock market presents a unique opportunity for individual investors and finance professionals looking to diversify their portfolios. With China being the second-largest economy globally, its stock market offers a range of investment options, including A-shares, B-shares, and Hong Kong-listed stocks. This comprehensive guide will explore the current market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlook for investing in China’s stock market.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Market Size | China’s equity market is the second largest globally, with A-shares valued at over USD 8.5 trillion and B-shares around USD 3.4 trillion. |
| Investment Vehicles | Investors can access Chinese stocks through various methods, including direct purchases of shares, ETFs, and mutual funds. |
| Market Access | Foreign investors can access the A-share market through programs like QFII, RQFII, and Stock Connect. |
| Regulatory Environment | The Chinese government has recently relaxed restrictions for foreign investments in A-shares, making it easier for investors to participate. |
| Current Trends | The Chinese stock market has seen significant growth in 2024 due to government stimulus measures and a shift towards monetary easing. |
| Sector Opportunities | High-growth sectors include technology, consumer goods, and finance, which are attracting considerable investment interest. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The Chinese stock market has experienced remarkable volatility and growth in recent years. As of December 2024, the Shanghai Composite Index has surged by approximately 16.19% since the beginning of the year, reflecting a strong recovery following various economic challenges. This resurgence is attributed to a series of government interventions aimed at stimulating economic growth through fiscal policies and monetary easing.
Key Market Indices
- Shanghai Composite Index: Tracks all A-shares listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange.
- Shenzhen Component Index: Focuses on mid-cap stocks listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
- CSI 300 Index: Represents the top 300 stocks from both Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges.
The recent rally in these indices indicates a bullish sentiment among investors, driven by expectations of continued government support and economic recovery initiatives. Notable sectors leading this growth include technology and consumer goods, which have benefited from increased domestic consumption and innovation.
Implementation Strategies
Investors can choose from several strategies to gain exposure to China’s stock market:
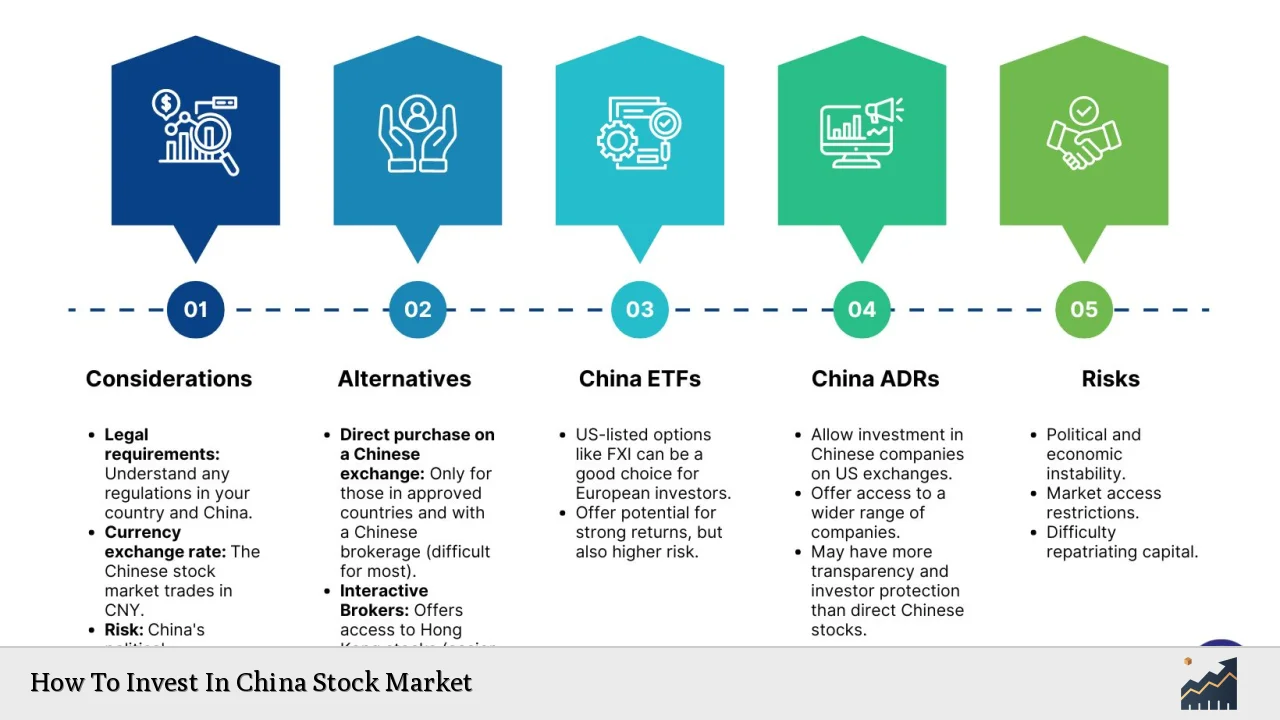
- Direct Investment: Purchasing A-shares directly through local brokerage accounts or via Stock Connect programs that link Hong Kong with mainland exchanges.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Investing in ETFs that track major indices like the CSI 300 or sector-specific funds focusing on technology or consumer goods. This method allows for diversified exposure with lower costs compared to direct stock purchases.
- Mutual Funds: Engaging with professionally managed funds that specialize in Chinese equities can provide insights from local analysts who understand the market nuances.
- B-Shares: These are shares of Chinese companies listed on domestic exchanges but denominated in foreign currencies. They are accessible to foreign investors but typically represent a smaller pool compared to A-shares.
Steps to Invest
- Research Investment Options: Analyze various ETFs or mutual funds that focus on Chinese equities.
- Open a Brokerage Account: Choose a brokerage that provides access to Chinese markets or international ETFs.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Consider mixing investments across sectors to mitigate risks associated with volatility.
- Monitor Economic Indicators: Stay updated on China’s economic policies, inflation rates, and other macroeconomic indicators that could affect your investments.
Risk Considerations
Investing in the Chinese stock market comes with inherent risks:
- Market Volatility: The Chinese market is known for its rapid fluctuations influenced by government policies and global economic conditions.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in regulations can significantly impact foreign investment opportunities. Recent reforms have made it easier for foreign investors to access A-shares but ongoing policy shifts must be monitored closely.
- Economic Factors: Economic slowdowns or geopolitical tensions can adversely affect market performance. For instance, trade relations with major economies like the U.S. may influence investor sentiment.
- Currency Risk: Fluctuations in the Renminbi (RMB) against other currencies can affect returns for foreign investors.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory environment surrounding foreign investment in China has evolved significantly:
- QFII/RQFII Programs: These programs allow qualified foreign institutional investors to invest directly in China’s A-share markets under specific quotas.
- Stock Connect Programs: This initiative enables international investors to trade A-shares via Hong Kong brokers without needing a local account.
- Recent Reforms: As of December 2024, new measures have reduced minimum shareholding thresholds and lock-up periods for foreign investments in A-shares. These changes aim to attract more diverse capital into China’s markets.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, several factors will shape the trajectory of investments in China’s stock market:
- Continued Government Support: Analysts expect ongoing fiscal stimulus and monetary easing from Beijing as part of their strategy to bolster economic growth post-pandemic.
- Sector Growth Potential: Emerging industries such as green technology, digital economy sectors, and healthcare are anticipated to drive future growth as China shifts towards innovation-driven development.
- Global Economic Conditions: The performance of China’s stock market will also depend on global economic trends and how they interact with domestic policies. Investors should keep an eye on central bank actions worldwide that may influence capital flows into China.
Frequently Asked Questions About How To Invest In China Stock Market
- What are A-shares?
A-shares are shares of Chinese companies listed on mainland exchanges (Shanghai and Shenzhen) that are primarily available to domestic investors but can be accessed by foreign investors through specific programs. - How can I invest in Chinese stocks from abroad?
You can invest through international brokerage accounts that offer access to B-shares or ETFs focused on Chinese equities. - What are the risks of investing in China?
The primary risks include market volatility, regulatory changes, currency fluctuations, and potential geopolitical tensions affecting investor confidence. - Are there any restrictions for foreign investors?
While recent reforms have eased access to A-shares for foreign investors, there are still regulations governing investment quotas and shareholding limits. - What sectors should I focus on when investing in China?
Sectors such as technology, consumer goods, healthcare, and renewable energy are currently seen as high-growth areas within China’s economy. - How do I choose an ETF for investing in China?
Look for ETFs that track major indices like the CSI 300 or those focusing on specific sectors you are interested in while considering management fees and performance history. - What is the outlook for China’s stock market?
The outlook remains positive due to government support measures aimed at stimulating growth; however, ongoing monitoring of economic indicators is essential. - Should I consult a financial advisor before investing?
Yes, consulting a financial advisor familiar with international investments can help tailor your strategy based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Investing in China’s stock market requires careful consideration of various factors including regulatory environments, market trends, sector opportunities, and potential risks. By staying informed and adopting a strategic approach, individual investors can navigate this complex yet rewarding landscape effectively.