Selecting the right smart contract platform is a critical decision for developers, startups, and enterprises looking to leverage blockchain technology. With numerous platforms available, each offering unique features, functionalities, and ecosystems, understanding the nuances of these options is essential for aligning them with project goals. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key factors to consider when choosing a smart contract platform, supported by current market trends and insights.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Market Growth | The global smart contract platforms market is projected to grow from approximately USD 1.21 billion in 2023 to around USD 218.59 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 78.12%. |
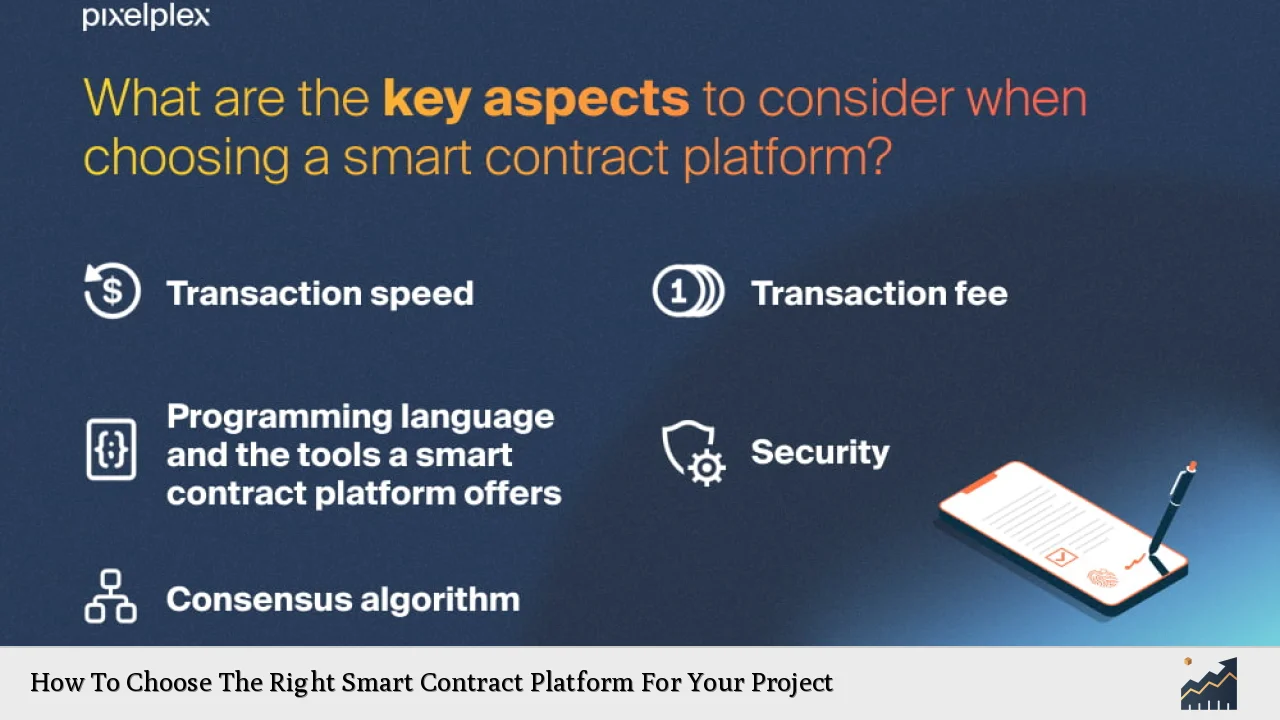
| Transaction Speed | Platforms like Solana boast transaction speeds exceeding 3,000 transactions per second (TPS), making them suitable for high-demand applications. |
| Security Features | Smart contracts must include robust security measures to protect against vulnerabilities; platforms are increasingly focusing on auditing and compliance. |
| Programming Languages | Common languages like Solidity facilitate easier development; however, proprietary languages may require additional learning. |
| Community Support | A larger developer community often translates to more resources, support, and faster troubleshooting capabilities. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to evolving regulations is crucial for maintaining legitimacy and avoiding legal pitfalls in various jurisdictions. |
| Integration Capabilities | The ability to integrate with existing systems and other blockchain networks can enhance functionality and user experience. |
| Cost Considerations | Transaction fees and overall cost of deployment can significantly impact project budgets; lower fees may enhance user adoption. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The smart contract market is experiencing rapid growth driven by increased adoption across various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. According to recent reports, the market is expected to reach USD 230.2 million in 2024 with a robust CAGR of 23.80%, potentially escalating to USD 1,946.78 million by 2034. This growth is fueled by the rising demand for decentralized applications (dApps) and the automation of processes through blockchain technology.
Key trends influencing the market include:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: The merging of AI with smart contracts is enhancing their capabilities in execution and management.
- Layer 2 Solutions: These solutions are addressing scalability issues by allowing off-chain processing while maintaining security.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: As smart contracts gain traction, regulatory bodies are developing frameworks to ensure compliance and protect users.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The rise of DeFi platforms illustrates the growing reliance on smart contracts for financial services without traditional intermediaries.
Implementation Strategies
When implementing a smart contract solution, consider the following strategies:
- Define Clear Objectives: Understand your project requirements—whether you need complex logic or simple automation—and align them with platform capabilities.
- Select the Right Tools: Evaluate available development tools, libraries, and frameworks that can simplify the coding process and enhance functionality.
- Conduct Thorough Testing: Implement rigorous testing protocols to identify vulnerabilities before deployment. Utilize platforms that offer integrated testing environments.
- Plan for Scalability: Choose a platform that can handle future growth in user demand without compromising performance.
- Establish Compliance Protocols: Stay updated on regulatory changes in your region and ensure your smart contracts adhere to applicable laws.
Risk Considerations
Investing in smart contracts comes with inherent risks that must be managed effectively:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts can be susceptible to bugs or exploits if not properly coded or audited. Regular security audits are essential.
- Regulatory Risks: Non-compliance with local laws can lead to fines or project shutdowns. It’s crucial to monitor regulatory developments continuously.
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency landscape is highly volatile; projects may face funding challenges if market conditions change unexpectedly.
- Technology Risks: Rapid advancements in technology can render certain platforms obsolete. Continuous evaluation of emerging technologies is necessary.
Regulatory Aspects
Navigating the regulatory landscape is vital for any smart contract project:
- Understanding Jurisdictional Regulations: Different countries have varying regulations regarding blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. Familiarize yourself with local laws governing smart contracts.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR when handling user data within smart contracts.
- Licensing Requirements: Some jurisdictions may require specific licenses for operating blockchain-based services; ensure all necessary licenses are obtained before launching your project.
Future Outlook
The future of smart contract platforms appears promising as they continue to evolve alongside technological advancements:
- Enhanced Interoperability: Future platforms will likely focus on improving interoperability between different blockchains, allowing seamless integration and communication.
- Greater Adoption Across Industries: As organizations recognize the benefits of automation and transparency offered by smart contracts, adoption rates are expected to increase significantly across various sectors.
- Focus on User Experience: Platforms will prioritize user-friendly interfaces and tools that make it easier for non-developers to create and manage smart contracts.
- Sustainability Initiatives: With growing concerns about energy consumption in blockchain operations, future developments may focus on creating more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms.
Frequently Asked Questions About How To Choose The Right Smart Contract Platform For Your Project
- What factors should I consider when choosing a smart contract platform?
Consider transaction speed, security features, programming languages supported, community support, cost implications, and regulatory compliance. - How important is community support for a smart contract platform?
A strong community can provide valuable resources, troubleshooting support, and shared knowledge that can significantly enhance your development experience. - What are Layer 2 solutions?
Layer 2 solutions are secondary frameworks built on top of existing blockchains that improve scalability by processing transactions off-chain while maintaining security. - How do I ensure my smart contract is secure?
Conduct thorough audits using reputable firms, implement best coding practices, and continuously monitor for vulnerabilities post-deployment. - Are there specific programming languages I should learn?
The most common language for Ethereum-based platforms is Solidity; however, familiarize yourself with any proprietary languages used by other platforms you may consider. - What role do regulations play in smart contracts?
Regulations dictate how smart contracts can be implemented legally; staying compliant helps avoid legal issues that could jeopardize your project. - Can I integrate AI with my smart contracts?
Yes, integrating AI can enhance the functionality of smart contracts by automating decision-making processes based on real-time data analysis. - What should I do if market conditions change after launching my project?
Be prepared to pivot your strategy based on market feedback; continuous engagement with your user base will help adapt your offerings effectively.
This comprehensive guide provides an overview of critical aspects involved in choosing the right smart contract platform. By considering market trends, implementation strategies, risk factors, regulatory requirements, and future outlooks, stakeholders can make informed decisions that align their projects with industry standards and expectations.