Calculating the yearly return on investment (ROI) is essential for investors looking to assess the performance of their investments. This metric allows individuals and businesses to determine how effectively their capital is being utilized. By understanding the ROI, investors can make informed decisions about where to allocate their resources for maximum benefit. The yearly ROI can be calculated in various ways, depending on the nature of the investment and the time frame involved.
The ROI is typically expressed as a percentage, representing the gain or loss generated relative to the initial investment cost. This percentage provides a straightforward way to compare different investments, regardless of their size or duration. Calculating the yearly return on investment also helps in understanding whether an investment meets personal or business financial goals.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Return on Investment (ROI) | A measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment. |
Understanding Return on Investment
Return on Investment (ROI) is a key financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by taking the net profit from an investment and dividing it by the initial cost of that investment. The result is then multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage. This calculation provides insight into how much profit was generated for each dollar invested.
Understanding ROI is crucial for investors because it allows them to compare the profitability of various investments. For example, if one investment has an ROI of 20% while another has an ROI of 15%, it would be prudent to choose the first investment, assuming all other factors are equal. However, it's important to consider that ROI does not account for the time value of money or risks associated with different investments.
When calculating ROI, it's essential to include all relevant costs associated with the investment. This includes not only the purchase price but also any additional expenses such as maintenance costs, taxes, and fees. By accurately accounting for all costs, investors can ensure they have a clear picture of their investment's performance.
Calculating Yearly Return on Investment
To calculate the yearly return on investment, follow these steps:
- Determine Initial Investment: Identify how much money was initially invested in the asset or project.
- Calculate Ending Value: Determine the current value of the investment at the end of the period you are evaluating.
- Calculate Net Profit: Subtract the initial investment from the ending value. This gives you the net profit or loss from your investment.
- Calculate ROI: Divide the net profit by the initial investment and multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
For example, if you invested $1,000 in a stock and its current value is $1,200 after one year, your net profit would be $200. The ROI would then be calculated as follows:
- Net Profit = Ending Value - Initial Investment = $1,200 - $1,000 = $200
- ROI = (Net Profit / Initial Investment) x 100 = ($200 / $1,000) x 100 = 20%
This indicates that your investment generated a 20% return over one year.
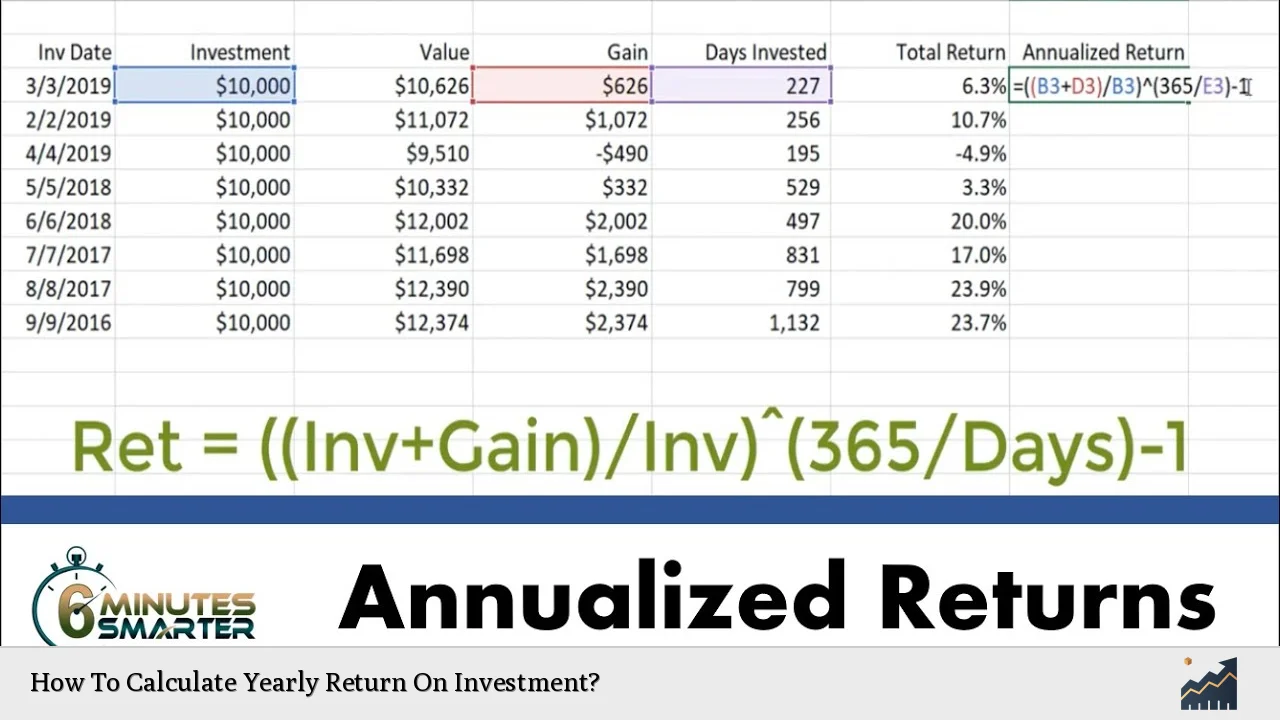
Annualizing Return on Investment
Annualizing ROI is particularly useful when comparing investments held over different periods. It allows investors to express returns on an annual basis, making comparisons more straightforward. There are two common methods for annualizing returns: Simple Annual ROI and Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR).
Simple Annual ROI
Simple Annual ROI assumes that returns will remain consistent each year. To calculate this:
- Total Return: Calculate total return over multiple years.
- Divide by Years Held: Divide this total return by the number of years held.
For instance, if an investment returned 30% over three years, the Simple Annual ROI would be:
- Simple Annual ROI = Total Return / Number of Years = 30% / 3 = 10%
This method provides a quick estimate but does not account for compounding effects.
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
CAGR provides a more accurate measure by accounting for compounding over time. To calculate CAGR:
- Ending Value: Determine ending value after several years.
- Beginning Value: Identify initial investment amount.
- Number of Years: Count how many years the investment was held.
The formula for CAGR is:
$$
CAGR = \left( \frac{\text{Ending Value}}{\text{Beginning Value}} \right)^{\frac{1}{n}} - 1
$$
Where $$ n $$ represents the number of years held. For example, if you invested $1,000 and it grew to $1,500 over five years:
- CAGR = $$\left( \frac{1500}{1000} \right)^{\frac{1}{5}} - 1$$
Calculating this gives you a CAGR of approximately 8.45%. This means that your investment grew at an average rate of about 8.45% per year over five years.
Factors Affecting Yearly Return on Investment
Several factors can influence your yearly return on investment:
- Market Conditions: Economic trends and market fluctuations can significantly impact asset values.
- Investment Type: Different assets have varying risk levels and potential returns; stocks may yield higher returns than bonds but come with greater risk.
- Time Horizon: The length of time you hold an investment can affect its overall return due to compounding interest.
- Fees and Expenses: Management fees and transaction costs can reduce your net returns.
Understanding these factors helps investors make informed decisions about where to allocate their resources for optimal returns.
Importance of Yearly Return on Investment
Calculating yearly return on investment is crucial for several reasons:
- Performance Measurement: It provides a clear indicator of how well an investment is performing relative to others or against benchmarks.
- Informed Decision-Making: Investors can use ROI calculations to decide whether to hold or sell an asset based on its performance.
- Goal Setting: Knowing your expected ROI helps in setting realistic financial goals and expectations for future investments.
By regularly calculating and analyzing yearly ROIs, investors can adjust their strategies as needed to align with changing market conditions or personal financial goals.
FAQs About How To Calculate Yearly Return On Investment
- What is a good yearly return on investment?
A good yearly return on investment typically ranges from 7% to 10%, depending on market conditions. - How often should I calculate my ROI?
It’s advisable to calculate your ROI at least annually or when significant changes occur in your investments. - Can I calculate ROI for multiple investments?
Yes, you can calculate ROI for each individual investment and compare them side-by-side. - What are some limitations of using ROI?
ROI does not account for time value of money or risks associated with different investments. - How does inflation affect my ROI?
Inflation can erode purchasing power; thus, real returns should be considered when evaluating overall profitability.
Calculating yearly return on investment is essential for effective financial management and strategic planning in both personal and business contexts. By understanding how to accurately compute and analyze this metric, investors can enhance their decision-making processes and work towards achieving their financial objectives effectively.