Return on Investment (ROI) is a critical financial metric that helps investors and businesses evaluate the efficiency and profitability of their investments. It provides a straightforward way to assess how much profit is generated from an investment relative to its cost. Understanding ROI is essential for making informed financial decisions, whether in business ventures, marketing campaigns, or personal investments.
Calculating ROI involves comparing the net profit from an investment to the initial cost of that investment. This calculation can help stakeholders determine which investments are yielding the best returns and guide future investment strategies. By analyzing ROI, businesses can optimize their resource allocation and ensure they are investing in the most profitable opportunities.
The concept of ROI is widely used across various industries, including finance, marketing, and project management. It enables stakeholders to quantify the effectiveness of their investments and make data-driven decisions. In this article, we will explore how to calculate ROI, its significance, and various factors that can influence it.
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A measure of profitability that evaluates the efficiency of an investment. |
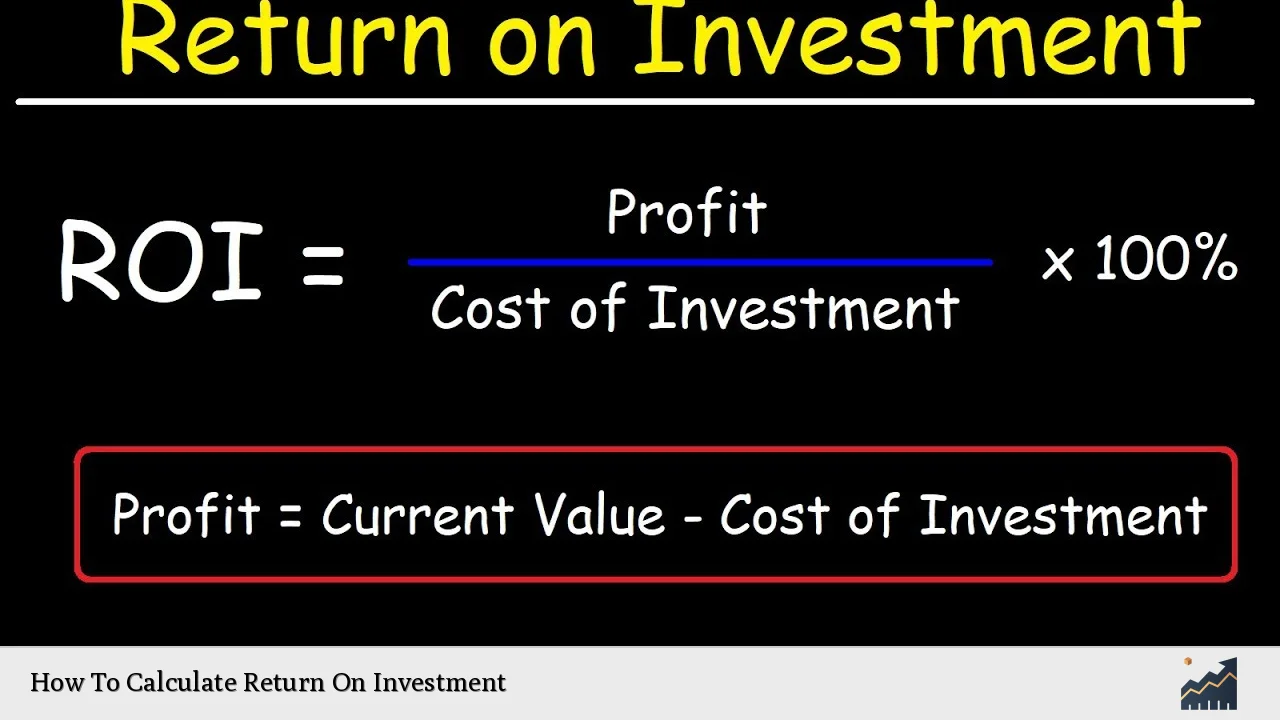
| Formula | ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100 |
| Importance | Helps in assessing the profitability of investments and guiding financial decisions. |
Understanding ROI
ROI is a versatile metric that can be applied in various contexts. At its core, it measures the gain or loss generated relative to the amount invested. The formula for calculating ROI is simple: it divides the net profit from an investment by its cost, then multiplies the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. This percentage indicates how much return was earned for every dollar invested.
For example, if an investor spends $1,000 on a project and makes a profit of $200, the ROI would be calculated as follows:
- Net Profit = $200
- Cost of Investment = $1,000
Using the formula:
$$
ROI = \left(\frac{200}{1000}\right) \times 100 = 20\%
$$
This means that for every dollar invested, there was a return of 20 cents.
Understanding ROI is crucial because it allows investors to compare different investment opportunities easily. A higher ROI indicates a more profitable investment. However, it’s important to note that while ROI provides valuable insights into profitability, it does not account for factors such as time or risk involved in different investments.
Steps to Calculate ROI
Calculating ROI involves several key steps that ensure accuracy and relevance in your assessment. Here’s a breakdown of these steps:
- Define the Investment: Identify all costs associated with the investment. This includes initial capital outlay and any additional expenses incurred during the investment period.
- Determine Net Profit: Calculate the total revenue generated from the investment and subtract all associated costs. This gives you the net profit.
- Apply the Formula: Use the basic ROI formula to calculate your return on investment.
- Analyze Results: Interpret the ROI percentage to understand how well your investment performed compared to others.
- Consider Time Factors: While calculating ROI provides a snapshot of profitability, consider how long it took to achieve those returns. This can affect decision-making regarding future investments.
By following these steps meticulously, you can derive meaningful insights from your ROI calculations and make informed decisions about where to allocate resources effectively.
Factors Influencing ROI
Several factors can influence the calculation and interpretation of ROI. Understanding these factors is critical for accurate assessments:
- Investment Duration: The time frame over which an investment is held can significantly impact its overall return. Longer durations may yield different results compared to short-term investments due to market fluctuations.
- Market Conditions: Economic trends and market conditions can affect revenue generation and costs associated with investments. Changes in demand or supply can alter expected returns.
- Operational Efficiency: The efficiency with which a business operates can impact its profitability. Streamlined operations often lead to higher returns on investments.
- Risk Assessment: Higher-risk investments may offer higher potential returns but also come with increased chances of losses. Evaluating risk is essential when interpreting ROI figures.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing ROIs across different sectors or time periods can provide context for understanding performance. It helps investors gauge whether their returns are satisfactory relative to industry standards.
By considering these factors when calculating and analyzing ROI, investors can gain deeper insights into their financial performance and make more strategic decisions.
Common Mistakes in Calculating ROI
When calculating ROI, it’s easy to make mistakes that can lead to misleading conclusions. Here are some common pitfalls:
- Ignoring All Costs: Failing to account for all associated costs can inflate perceived profits. Ensure that both direct and indirect costs are included in your calculations.
- Overlooking Time Factors: Not considering how long it takes to achieve returns can skew results. Always factor in time when evaluating investments against each other.
- Misinterpreting Results: A high ROI does not always mean a good investment if associated risks are high or if market conditions are volatile. Look beyond numbers for comprehensive insights.
- Neglecting Contextual Comparisons: Comparing ROIs without considering industry benchmarks or market conditions may lead to erroneous conclusions about performance.
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can improve your accuracy when calculating and interpreting ROI, leading to better-informed financial decisions.
Real-Life Examples of Calculating ROI
Understanding how to calculate ROI becomes clearer through real-life examples across different contexts:
1. Real Estate Investment:
- Purchase Price: $200,000
- Renovation Costs: $50,000
- Selling Price after One Year: $300,000
- Net Profit = Selling Price – (Purchase Price + Renovation Costs) = $300,000 – ($200,000 + $50,000) = $50,000
- Cost of Investment = Purchase Price + Renovation Costs = $200,000 + $50,000 = $250,000
- ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100 = ($50,000 / $250,000) x 100 = 20%
2. Marketing Campaign:
- Total Marketing Spend: $10,000
- Revenue Generated from Campaign: $50,000
- Net Profit = Revenue Generated – Total Marketing Spend = $50,000 – $10,000 = $40,000
- Cost of Investment = Total Marketing Spend = $10,000
- ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100 = ($40,000 / $10,000) x 100 = 400%
These examples illustrate how different types of investments yield varying ROIs based on their unique contexts and associated costs.
FAQs About How To Calculate Return On Investment
- What does ROI stand for?
ROI stands for Return on Investment. - Why is calculating ROI important?
Calculating ROI helps assess the profitability and efficiency of an investment. - How do I interpret my ROI results?
A higher ROI indicates a more profitable investment; compare it with industry standards for context. - Can I calculate negative ROI?
Yes, negative ROI indicates a loss on an investment relative to its cost. - What factors should I consider when calculating ROI?
Consider all costs involved, time duration of the investment, market conditions, and operational efficiency.
By following these guidelines on calculating Return on Investment effectively and understanding its implications within various contexts—whether personal finance or business strategy—you will be better equipped to make informed decisions that enhance your financial outcomes.