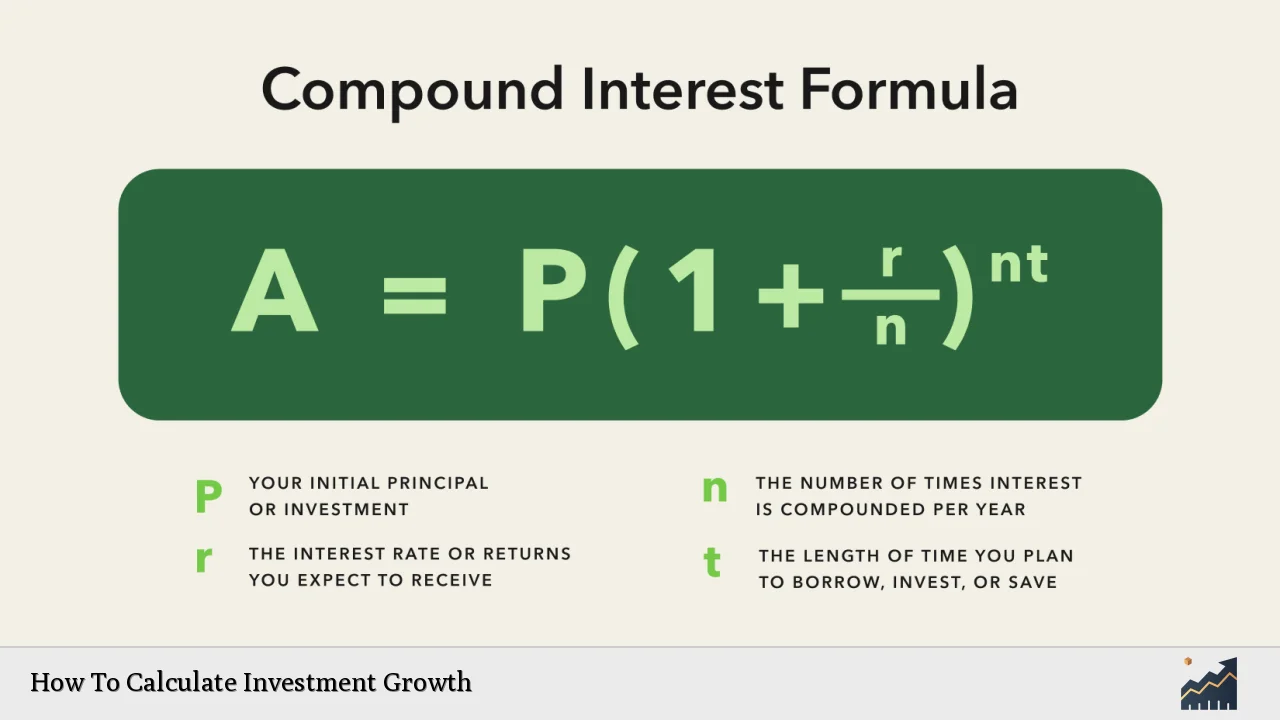
Calculating investment growth is essential for investors seeking to understand how their investments will perform over time. Investment growth refers to the increase in value of an investment over a specified period, influenced by factors such as initial investment amount, additional contributions, the rate of return, and the duration of the investment. By understanding these elements, investors can make informed decisions about their portfolios and financial goals.
Investment growth is primarily driven by compound interest, where the returns on an investment generate additional returns. This concept is crucial because it highlights the importance of time in investing; the longer an investment is held, the greater its potential growth due to compounding effects.
Investors can utilize various tools and methods to calculate their potential investment growth. These calculations can help assess whether an investment aligns with their financial objectives. Below is a table summarizing key components involved in calculating investment growth.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Investment | The starting amount of money invested. |
| Regular Contributions | Additional amounts invested over time. |
| Rate of Return | The percentage increase expected from the investment. |
| Investment Duration | The total time the money is invested. |
Understanding Investment Components
To effectively calculate investment growth, it is vital to understand the various components involved in the process. Each component plays a significant role in determining how much your investment will grow over time.
Initial Investment refers to the amount of money you start with when making an investment. This figure sets the foundation for all future growth calculations.
Regular Contributions are any additional funds you plan to invest periodically, such as monthly or annually. These contributions can significantly enhance your total returns, especially if made consistently over a long period.
The Rate of Return represents the expected annual increase in your investment’s value. This rate can vary based on market conditions and the type of investments chosen. Understanding historical performance can help set realistic expectations for future returns.
Finally, Investment Duration is the length of time you plan to keep your money invested. The longer your money remains invested, the more opportunity it has to grow through compounding.
The Importance of Compounding
Compounding is a critical concept in investment growth calculations. It refers to earning interest on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest from previous periods. This process can lead to exponential growth over time, making it one of the most powerful tools for investors.
For example, if you invest a sum of money at a fixed rate of return, compounding allows your earnings to generate additional earnings. The effect of compounding becomes more pronounced as time passes; thus, starting early can lead to significantly higher returns compared to waiting until later in life to invest.
Investors should also consider how frequently their investments compound. Common compounding frequencies include annually, semi-annually, quarterly, or monthly. More frequent compounding results in greater overall returns because interest is calculated and added to the principal more often.
Calculating Future Value
To estimate future value (FV) from an investment, you need to consider all components discussed previously. The future value represents what your initial investment and any contributions will be worth at a specified point in time based on expected returns.
While specific formulas are typically used for this calculation, understanding that future value reflects how much your investments will grow helps frame your financial goals effectively.
For practical purposes, many investors use online calculators that simplify this process by allowing users to input their initial investment, regular contributions, expected rate of return, and duration. These tools provide quick estimates without requiring complex calculations.
Evaluating Investment Performance
Once you have calculated potential growth for your investments, evaluating performance becomes essential. This evaluation helps determine whether your investments are meeting expectations or if adjustments are necessary.
Performance evaluation involves comparing actual returns against initial projections. If an investment consistently underperforms compared to its expected rate of return, it may be wise to reassess its viability within your portfolio.
Additionally, consider factors like market conditions and economic indicators when evaluating performance. Understanding these external influences can provide insights into why certain investments may not be performing as anticipated.
Diversification Strategies
Diversification is another crucial aspect when calculating potential investment growth. By spreading investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate), investors can reduce risk while potentially enhancing returns.
A well-diversified portfolio minimizes exposure to any single asset’s volatility and increases the chances that some investments will perform well even when others do not. This strategy helps stabilize overall portfolio performance and contributes positively to long-term growth.
Investors should regularly review their asset allocation strategy and make adjustments as necessary based on changing market conditions or personal financial goals.
Monitoring Your Investments
Monitoring your investments regularly ensures that they align with your financial objectives and risk tolerance levels. Keeping track of performance allows you to make informed decisions about buying or selling assets as needed.
Consider setting up a schedule for reviewing your portfolio—monthly or quarterly reviews can help stay on top of market trends and performance metrics. This practice enables timely adjustments that can enhance overall investment growth.
In addition to monitoring performance metrics like return on investment (ROI), also pay attention to fees associated with managing your investments. High fees can erode returns over time; therefore, understanding cost structures is essential for maximizing growth potential.
FAQs About How To Calculate Investment Growth
- What is compound interest?
Compound interest is interest calculated on both the initial principal and accumulated interest from previous periods. - How does regular contribution affect my investment?
Regular contributions increase the total amount invested over time, enhancing potential returns through compounding. - What factors influence my rate of return?
Factors include market performance, type of assets held, economic conditions, and individual investment strategies. - Why is diversification important?
Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across different asset classes, enhancing stability and potential returns. - How often should I review my investments?
Regular reviews—monthly or quarterly—help ensure that your portfolio remains aligned with financial goals and market conditions.
By understanding how to calculate investment growth effectively through these components and strategies, investors can make informed decisions that lead toward achieving their financial objectives while minimizing risks associated with investing.