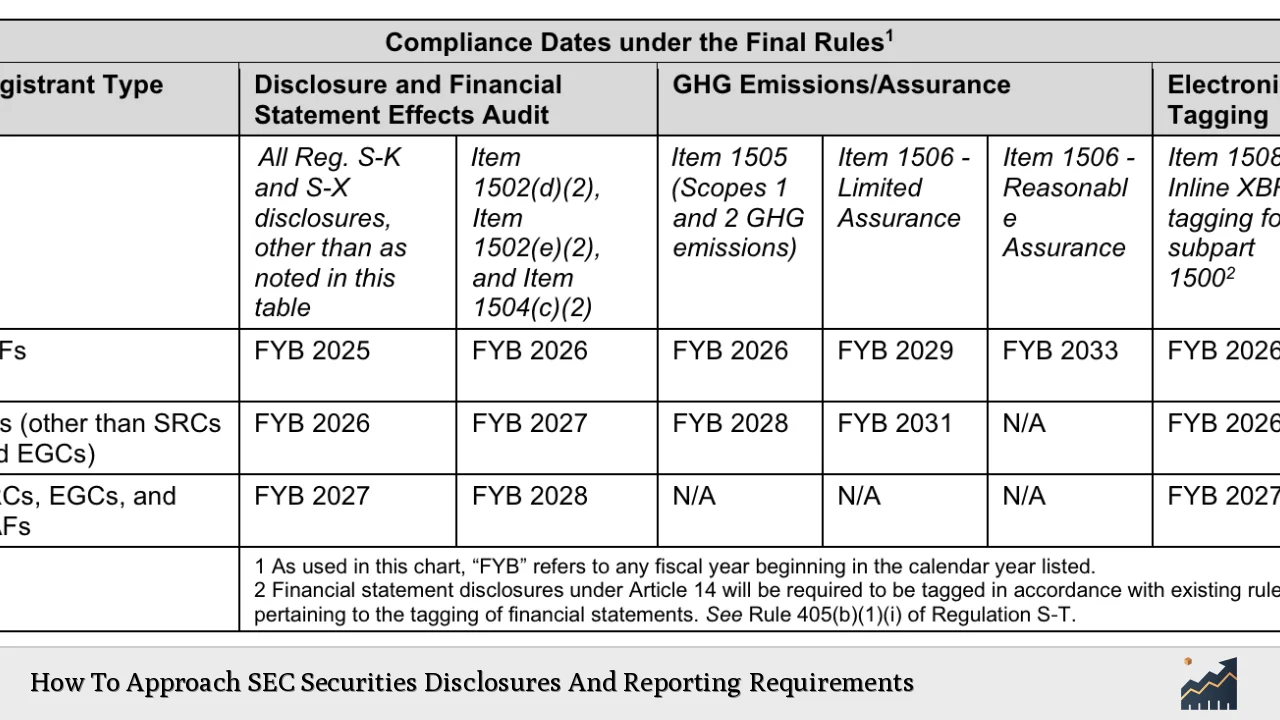
Navigating the complex landscape of SEC securities disclosures and reporting requirements is crucial for public companies and investors alike. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) mandates that companies provide transparent and comprehensive information about their financial health, operational risks, and management practices. This article delves into the intricacies of SEC reporting, highlighting market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Materiality | Information deemed significant enough to influence an investor’s decision-making process. |
| Form 10-K | Annual report providing a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance. |
| Form 10-Q | Quarterly report that includes unaudited financial statements and updates on company operations. |
| Form 8-K | Current report used to announce major events that shareholders should know about. |
| Climate Disclosure Rule | Recent regulations requiring companies to disclose climate-related risks affecting their operations. |
| Internal Controls | Processes implemented to ensure accuracy and reliability in financial reporting. |
| Cybersecurity Disclosures | Requirements for companies to disclose risks related to cybersecurity incidents. |
| Risk Management Frameworks | Structures that help companies identify, assess, and manage potential risks. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The SEC’s disclosure requirements have evolved significantly in response to changing market dynamics and investor expectations. Recent trends indicate a heightened focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, particularly with the introduction of the SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rule. This rule mandates that companies disclose material climate-related risks that could impact their financial condition or operational results.
Current Market Trends
- Increased Transparency: Investors demand more transparency regarding corporate governance and risk management practices.
- Focus on ESG: Companies are increasingly required to disclose their sustainability efforts and how they manage climate-related risks.
- Digital Reporting: The SEC encourages digital formats for disclosures, improving accessibility and efficiency in reporting.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Enhanced scrutiny from regulators aims to ensure compliance with evolving disclosure standards.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively navigate SEC securities disclosures, companies must adopt structured implementation strategies:
- Establish a Disclosure Committee: Form a team responsible for overseeing compliance with SEC regulations.
- Develop a Reporting Calendar: Create a timeline for filing deadlines to ensure timely submissions of required reports.
- Enhance Internal Controls: Implement robust internal controls to maintain the accuracy of financial reporting. This includes regular audits and reviews of financial data.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage software solutions designed for financial reporting to streamline data collection and reporting processes.
- Training and Awareness: Educate staff on disclosure requirements to foster a culture of compliance within the organization.
Risk Considerations
Understanding the risks associated with SEC disclosures is vital for effective management:
- Legal Risks: Non-compliance with SEC regulations can lead to significant penalties, including fines and legal action.
- Reputational Risks: Inaccurate or misleading disclosures can damage a company’s reputation among investors and stakeholders.
- Operational Risks: Companies must be prepared for potential disruptions in their operations that could impact their ability to meet disclosure requirements.
- Market Risks: Fluctuations in market conditions can affect the materiality of certain disclosures, necessitating timely updates.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory framework governing SEC disclosures is multifaceted:
- Securities Act of 1933: Requires registration of securities offerings and mandates comprehensive disclosure of relevant information.
- Securities Exchange Act of 1934: Governs ongoing reporting obligations for publicly traded companies, including Forms 10-K, 10-Q, and 8-K.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Introduced stringent requirements for financial reporting accuracy and internal control assessments.
- Dodd-Frank Act: Enhanced transparency in financial markets through additional reporting requirements related to executive compensation and risk management practices.
Future Outlook
The future of SEC securities disclosures will likely be shaped by ongoing regulatory changes and market demands:
- Continued Emphasis on ESG Disclosures: As sustainability becomes increasingly important, companies will need to enhance their ESG reporting practices.
- Technological Integration: Advances in technology will continue to transform how companies approach financial reporting, with an emphasis on automation and data analytics.
- Global Standards Alignment: Companies operating internationally may face pressures to align U.S. disclosure practices with global standards set by organizations such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Increased Investor Engagement: Companies may need to engage more actively with investors regarding their disclosure practices and risk management strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions About How To Approach SEC Securities Disclosures And Reporting Requirements
- What are the main forms required by the SEC?
The primary forms include Form 10-K (annual report), Form 10-Q (quarterly report), and Form 8-K (current report for significant events). - How often do companies need to file reports?
Companies must file Form 10-K annually, Form 10-Q quarterly (for the first three quarters), and Form 8-K as needed when significant events occur. - What is materiality in SEC disclosures?
Materiality refers to information that could influence an investor’s decision-making process; it must be disclosed if it meets this threshold. - What are the consequences of non-compliance?
Consequences can include fines, legal actions, loss of investor trust, and reputational damage. - How does the Climate Disclosure Rule affect reporting?
This rule requires companies to disclose climate-related risks affecting their operations, including transition plans and scenario analyses. - What role do internal controls play in SEC compliance?
Internal controls ensure the accuracy of financial data reported to the SEC, helping prevent errors or fraud. - Are there specific guidelines for cybersecurity disclosures?
The SEC requires companies to disclose risks related to cybersecurity incidents that could materially affect their business operations. - How can technology assist in meeting SEC requirements?
Technology can streamline data collection, enhance accuracy in reporting, automate compliance processes, and facilitate better collaboration among teams.
By understanding these elements thoroughly, individual investors and finance professionals can better navigate the complexities of SEC securities disclosures while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.