The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound and lasting impact on the dynamics of the stock market, reshaping investor behavior, altering market volatility, and influencing regulatory measures. As the world grappled with the health crisis, financial markets experienced unprecedented fluctuations characterized by rapid declines followed by volatile recoveries. This article explores the various dimensions of these changes, providing a comprehensive analysis of market trends, implementation strategies for investors, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks in the context of a post-pandemic world.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
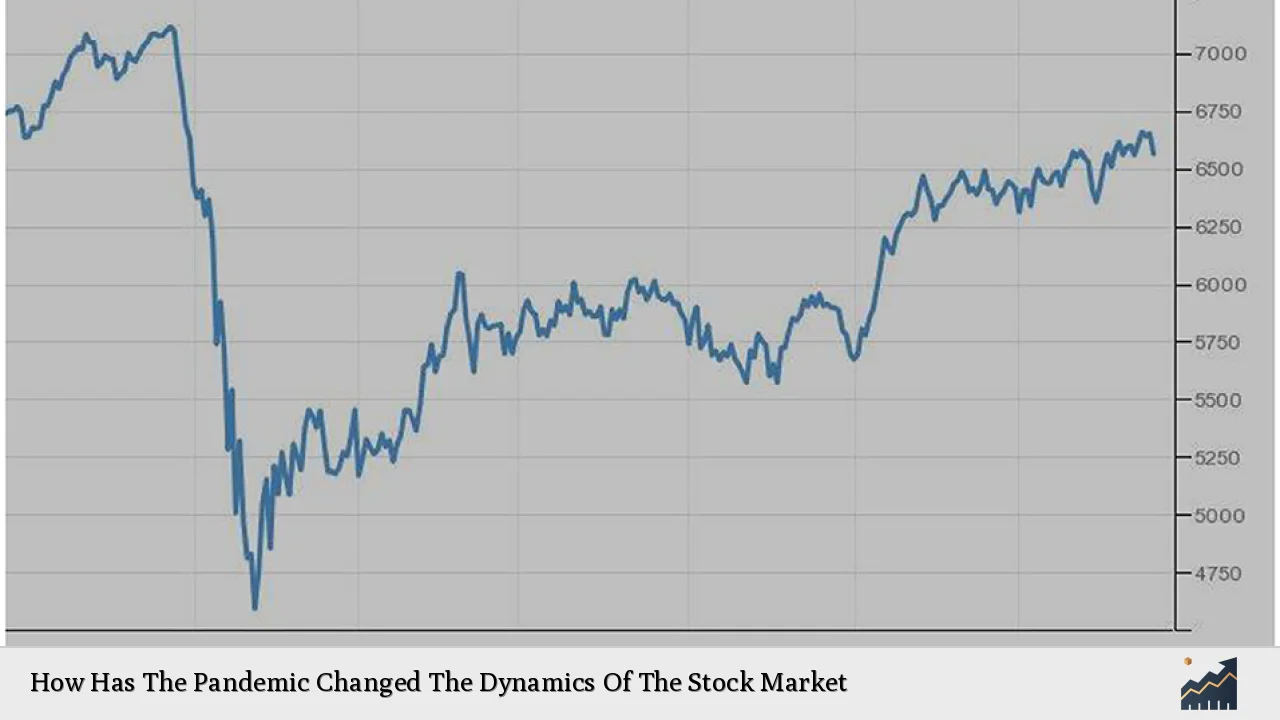
| Market Volatility | The pandemic led to extreme volatility in stock markets globally. For instance, the S&P 500 dropped by approximately 33% from February to March 2020 before rebounding sharply due to government interventions and monetary policy adjustments. |
| Investor Behavior | Investor sentiment shifted significantly, with increased fear and uncertainty leading to panic selling. However, as markets stabilized, a trend towards retail investing emerged, fueled by platforms like Robinhood. |
| Sector Performance | Certain sectors such as technology and healthcare outperformed during the pandemic due to increased demand for digital services and medical solutions, while travel and hospitality sectors suffered severe declines. |
| Government Intervention | Central banks worldwide implemented aggressive monetary policies, including interest rate cuts and quantitative easing measures, to stabilize economies and support financial markets. |
| Long-term Changes | The pandemic accelerated trends such as remote work and e-commerce, fundamentally altering business models and investment strategies across various sectors. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a series of events that reshaped market dynamics. Initially marked by sharp declines, stock indices around the world witnessed historic drops. For example:
- On March 12, 2020, the S&P 500 fell by nearly 10%, marking one of its worst single-day performances in history.
- By late March 2020, many indices had lost over a third of their value compared to pre-pandemic levels.
As governments implemented lockdowns and restrictions, economic activity plummeted. However, as fiscal stimulus measures were rolled out and vaccination campaigns began in late 2020 and early 2021, markets began to recover. By December 2021, the S&P 500 had regained its losses and reached new highs.
Key Trends Observed:
- Increased Volatility: The pandemic introduced unprecedented volatility into financial markets. The VIX index (a measure of market volatility) spiked to levels not seen since the 2008 financial crisis.
- Rise of Retail Investors: With traditional investment avenues disrupted, many individuals turned to stock trading as a means of income generation. Platforms like Robinhood saw massive increases in user sign-ups.
- Sector Rotation: There was a notable shift in sector performance. Technology stocks surged due to increased reliance on digital solutions while energy stocks lagged due to reduced demand.
Implementation Strategies
Investors must adapt their strategies to navigate the new landscape shaped by the pandemic. Here are some effective approaches:
- Diversification: Investors should diversify their portfolios across various sectors to mitigate risks associated with sector-specific downturns.
- Focus on Growth Stocks: Given the acceleration of digital transformation during the pandemic, growth stocks in technology and healthcare sectors may offer substantial long-term returns.
- Utilizing ETFs: Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) provide an efficient way for investors to gain exposure to multiple sectors without having to pick individual stocks.
- Monitoring Economic Indicators: Keeping an eye on key economic indicators such as unemployment rates, consumer spending data, and inflation rates can provide insights into market trends and potential investment opportunities.
Risk Considerations
While opportunities abound in the current market environment, investors must remain vigilant regarding potential risks:
- Market Volatility: The stock market remains susceptible to sudden swings due to geopolitical tensions or economic data releases.
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: As central banks begin tapering stimulus measures or adjusting interest rates in response to inflationary pressures, markets could react negatively.
- Regulatory Changes: Increased scrutiny on technology companies regarding data privacy and monopolistic practices could impact stock valuations.
Regulatory Aspects
The pandemic has also prompted regulatory bodies to reassess their frameworks:
- Increased Oversight: Regulatory agencies like the SEC have intensified scrutiny over market practices amid concerns about volatility driven by retail trading platforms.
- Market Circuit Breakers: The implementation of circuit breakers has been crucial in managing extreme volatility during trading sessions.
- Focus on Transparency: There is an ongoing push for greater transparency in financial markets, especially concerning how companies communicate risks associated with their operations during crises.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, several factors will likely shape the future dynamics of the stock market:
- Continued Recovery: As economies recover from the pandemic's effects, analysts predict gradual growth in corporate earnings which could support higher stock valuations.
- Technological Advancements: The ongoing digital transformation will likely continue driving growth in technology sectors while traditional industries adapt to new business models.
- Inflation Concerns: Persistent inflation could lead central banks to tighten monetary policy sooner than anticipated, impacting market liquidity and valuations.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Has The Pandemic Changed The Dynamics Of The Stock Market
- What were the immediate effects of COVID-19 on stock markets?
The immediate effects included significant declines in major indices due to panic selling triggered by uncertainty surrounding the pandemic. - How did government interventions influence stock market recovery?
Government interventions such as fiscal stimulus packages and monetary easing helped stabilize markets by providing liquidity and supporting consumer spending. - What sectors performed well during the pandemic?
Sectors like technology and healthcare saw substantial gains due to increased demand for digital services and medical solutions. - What risks should investors be aware of post-pandemic?
Investors should be cautious about market volatility, interest rate changes, and regulatory shifts that could impact specific sectors. - How has investor behavior changed since the pandemic?
There has been a notable increase in retail investing as individuals seek alternative income sources amid economic uncertainty. - What long-term changes can we expect in stock market dynamics?
The pandemic has accelerated trends such as remote work and e-commerce adoption which will likely continue influencing investment strategies. - Are there any new regulations affecting investors?
Yes, increased scrutiny on trading platforms and calls for greater transparency are shaping new regulatory frameworks. - What is the outlook for stock markets moving forward?
The outlook remains cautiously optimistic with expectations for gradual recovery supported by economic growth but tempered by potential inflationary pressures.
The COVID-19 pandemic has irrevocably altered the landscape of global financial markets. Understanding these changes is crucial for investors aiming to navigate this new environment effectively. By employing strategic investment approaches while remaining aware of evolving risks and regulatory frameworks, investors can position themselves for success in a post-pandemic world.