The U.S. stock market plays a pivotal role in the global financial landscape, influencing international markets through various channels such as trade, investment flows, and economic policies. As the largest and most liquid equity market, the U.S. not only attracts substantial foreign investments but also serves as a benchmark for global market performance. This interconnectedness means that fluctuations in U.S. stock indices can have far-reaching effects on economies and markets worldwide.
The influence of the U.S. stock market on international markets can be attributed to several key concepts, which are summarized in the table below.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
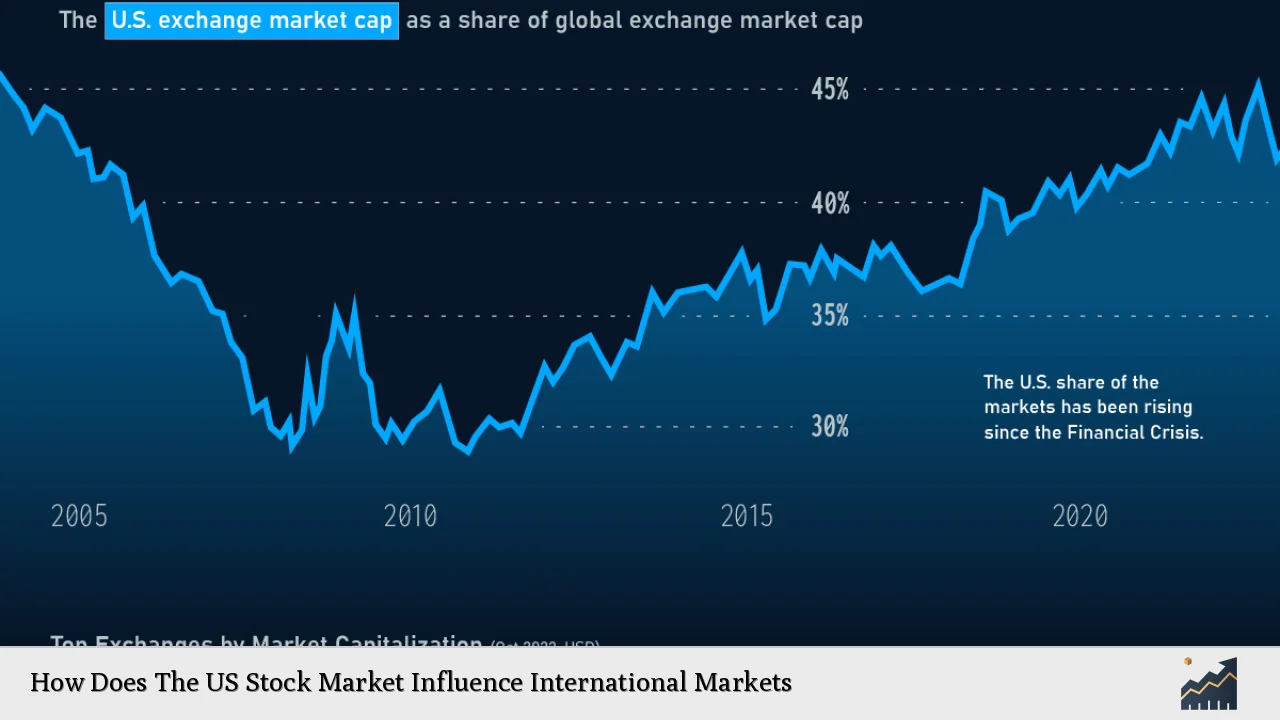
| Market Size and Liquidity | The U.S. stock market accounts for approximately 60% of the MSCI All Country World Index, making it a dominant player in global finance. Its liquidity attracts international investors, impacting their investment decisions. |
| Monetary Policy Transmission | U.S. Federal Reserve policies influence global interest rates and capital flows. Changes in U.S. interest rates can lead to capital outflows from emerging markets, affecting their currencies and economic stability. |
| Cross-Listing Effects | Many international companies list on U.S. exchanges, which enhances their visibility and access to capital. However, their stock performance is often correlated with U.S. market trends. |
| Investor Sentiment | The performance of major U.S. indices like the S&P 500 serves as a barometer for global investor sentiment, impacting risk appetite across international markets. |
| Trade Relationships | The strength of the U.S. economy influences global trade dynamics, affecting exports from other countries and their respective stock markets. |
| Global Economic Linkages | Economic developments in the U.S., such as GDP growth or recession, have significant implications for global economic health, impacting investment strategies worldwide. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The current state of the U.S. stock market reflects a complex interplay of economic indicators, investor behavior, and geopolitical events. As of December 2024, the S&P 500 has experienced a remarkable increase of approximately 27% since the beginning of the year, reaching record highs driven by strong corporate earnings and favorable economic data. This bullish sentiment has led to increased investment in both domestic and international equities.
Key Trends Influencing Global Markets
- Interest Rate Adjustments: The Federal Reserve’s approach to interest rates significantly influences global borrowing costs. Recent trends indicate a potential easing cycle that could bolster investment in riskier assets globally.
- Emerging Market Vulnerability: Countries like Argentina and Turkey have faced capital outflows as investors seek higher returns in the U.S., leading to currency depreciation and increased inflation pressures. Conversely, nations with sound fiscal policies have shown resilience against these trends.
- Technological Sector Growth: The rise of technology stocks has been a driving force behind U.S. market performance, with sectors like artificial intelligence attracting significant investment interest globally.
Implementation Strategies
Investors seeking to navigate the interconnectedness of U.S. and international markets should consider several strategies:
- Diversification: Maintaining a diversified portfolio that includes both U.S. and international equities can mitigate risks associated with overexposure to any single market.
- Monitoring Economic Indicators: Keeping an eye on key economic indicators such as U.S. GDP growth rates, unemployment figures, and inflation data can provide insights into potential market movements.
- Understanding Currency Risks: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact returns on international investments; therefore, employing hedging strategies may be beneficial.
Risk Considerations
Investing in international markets carries inherent risks influenced by U.S. market dynamics:
- Market Volatility: Global markets often react sharply to changes in U.S. monetary policy or economic data releases, leading to increased volatility.
- Geopolitical Risks: Events such as trade disputes or political instability can disproportionately affect emerging markets that are heavily reliant on foreign investment.
- Liquidity Risks: On days when the U.S. market is closed, trading volumes in international markets may decrease significantly, leading to wider bid-ask spreads and reduced liquidity.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory environment surrounding both domestic and international markets is critical for maintaining investor confidence:
- SEC Regulations: The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees U.S. securities markets, ensuring transparency and protecting investors from fraud. These regulations also influence how foreign companies operate within U.S. markets.
- International Compliance Standards: Companies listed on U.S. exchanges must adhere to stringent reporting requirements that promote accountability and transparency across borders.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, several factors will shape the relationship between the U.S. stock market and international markets:
- Sustained Economic Growth: Continued growth in the U.S. economy is expected to bolster global demand for goods and services, positively impacting emerging markets.
- Interest Rate Trends: As central banks around the world respond to economic conditions, shifts in interest rate policies will likely remain a focal point for investors globally.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing innovations within sectors such as technology and healthcare will drive growth opportunities not just in the U.S., but across global markets as well.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Does The US Stock Market Influence International Markets
- What is the primary way the US stock market influences other countries?
The US stock market influences other countries primarily through its size and liquidity, which attract global investments and set benchmarks for performance. - How do US interest rate changes affect emerging markets?
Changes in US interest rates can lead to capital outflows from emerging markets as investors seek higher returns domestically, causing currency depreciation and inflation issues. - Why do many foreign companies list on US exchanges?
Foreign companies list on US exchanges to gain access to larger pools of capital, enhance visibility among investors, and benefit from higher liquidity. - What impact does US economic data have on global investor sentiment?
The performance of major US indices often serves as a barometer for global investor sentiment; strong US economic data typically boosts confidence across international markets. - How do geopolitical events affect US stock market influence?
Geopolitical events can create uncertainty that affects investor behavior globally; this often leads to increased volatility in both US and international markets. - What are some risks associated with investing internationally?
Risks include currency fluctuations, geopolitical instability, regulatory differences, and varying levels of market liquidity compared to domestic investments. - How can investors hedge against currency risk?
Investors can hedge against currency risk by using financial instruments such as options or futures contracts or by diversifying their investments across different currencies. - What role does technology play in shaping future market trends?
Technological advancements are expected to drive growth opportunities globally by fostering innovation across industries such as healthcare and artificial intelligence.
In conclusion, understanding how the U.S. stock market influences international markets is essential for individual investors and finance professionals alike. By recognizing these dynamics—ranging from monetary policy impacts to cross-listing effects—investors can better navigate their strategies in an increasingly interconnected financial world.