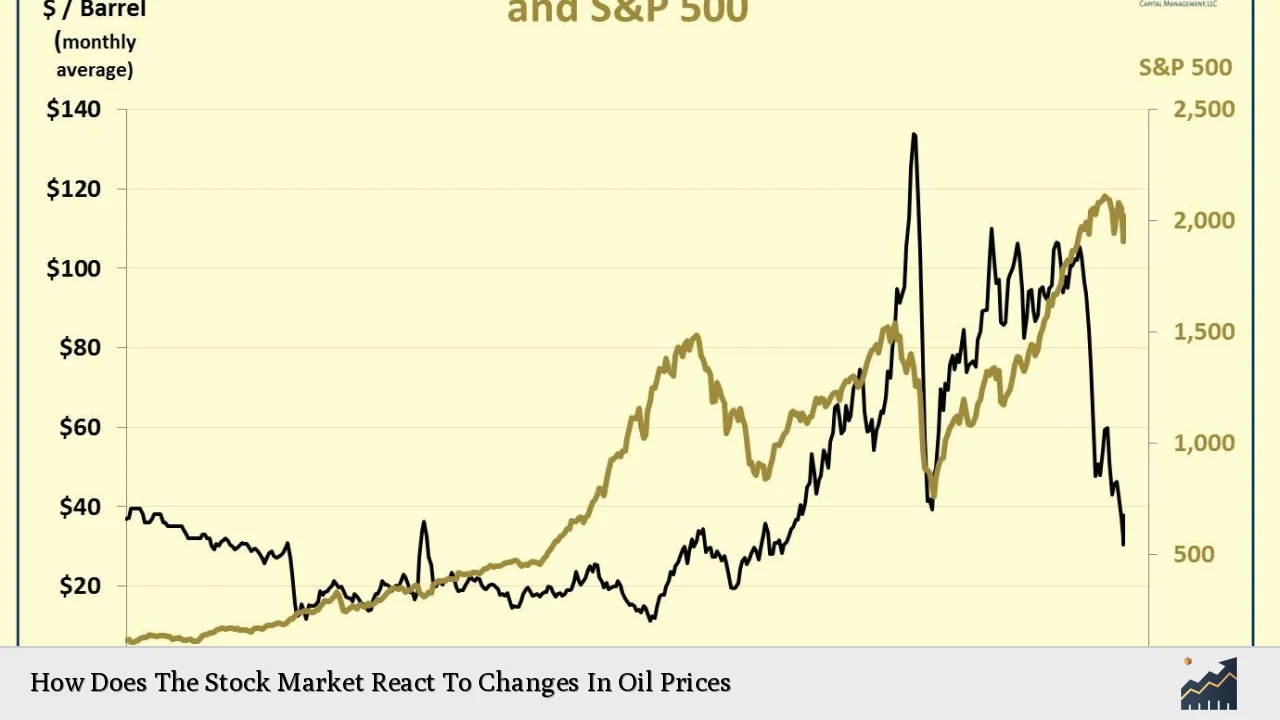
The relationship between oil prices and stock market performance has long intrigued investors and economists alike. Oil, as a critical input for many industries, influences production costs, consumer prices, and overall economic health. As such, fluctuations in oil prices can lead to significant shifts in investor sentiment and stock valuations. This article delves into the mechanisms through which oil price changes impact stock markets, analyzing current trends, implementation strategies for investors, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Oil Price Volatility | Oil prices are inherently volatile due to geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and changes in global demand. This volatility can lead to increased uncertainty in the stock market. |
| Sector Sensitivity | Sectors such as transportation and energy are particularly sensitive to oil price changes. Rising oil prices typically increase operational costs for these sectors, leading to lower profit margins and stock price declines. |
| Inflationary Pressures | Higher oil prices contribute to inflation, which can erode consumer purchasing power and dampen economic growth. This often results in negative sentiment in the stock market. |
| Correlation with Economic Indicators | Oil prices often correlate with broader economic indicators such as GDP growth rates and employment levels. A rise in oil prices may signal increased demand but can also indicate potential economic slowdowns if driven by supply constraints. |
| Geopolitical Risks | Geopolitical events affecting oil supply can lead to sharp price increases, creating volatility in the stock market as investors react to perceived risks. |
Market Analysis and Trends
Recent studies indicate that the correlation between oil prices and stock market performance is complex and varies over time. For instance, while some research suggests a positive correlation between rising oil prices and stock market gains—often attributed to increased revenues for energy companies—other studies highlight a more nuanced relationship where higher oil prices lead to increased production costs across various sectors.
Current Market Statistics
As of December 2024, Brent crude futures are trading around $74 per barrel, while West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is at approximately $71 per barrel. These prices reflect recent fluctuations driven by geopolitical tensions and supply chain issues stemming from sanctions on Russian oil and concerns over Iranian supply disruptions.
Historical Context
Historically, significant oil price shocks have led to substantial stock market downturns. For example, during the 1973 Oil Crisis, major global markets experienced severe declines due to skyrocketing oil prices. More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic saw dramatic shifts in both oil demand and stock market performance as economies grappled with lockdowns and reduced consumption.
Implementation Strategies
Investors can adopt various strategies to navigate the relationship between oil prices and stock market performance:
- Sector Diversification: Investing in sectors less sensitive to oil price fluctuations can mitigate risks. For instance, technology or healthcare sectors may offer more stability compared to energy or transportation sectors.
- Use of ETFs: Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) focused on energy stocks or commodities can provide exposure while diversifying risk across multiple companies.
- Monitoring Economic Indicators: Keeping an eye on inflation rates, GDP growth, and geopolitical developments can help investors anticipate potential impacts on both oil prices and stock performance.
- Hedging Strategies: Investors might consider using options or futures contracts on oil to hedge against potential losses from rising oil prices affecting their portfolios.
Risk Considerations
While investing with an understanding of the relationship between oil prices and the stock market can be beneficial, several risks must be considered:
- Market Volatility: Sudden spikes or drops in oil prices can lead to increased volatility in the stock market, making it challenging for investors to make informed decisions.
- Sector-Specific Risks: Companies heavily reliant on oil may face significant financial pressures during periods of high oil prices due to increased operational costs.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Political instability in key oil-producing regions can lead to unpredictable swings in both oil prices and associated stock valuations.
Regulatory Aspects
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the energy sector's impact on financial markets. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) monitors disclosures related to energy companies' financial health and their exposure to commodity price fluctuations. Additionally, international regulations regarding emissions and environmental standards are increasingly influencing how companies operate within this sector.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, several factors will likely shape the interaction between oil prices and the stock market:
- Transition to Renewable Energy: As global economies shift towards renewable energy sources, traditional fossil fuel markets may experience declining demand over time. This transition could alter how sensitive stock markets are to fluctuations in oil prices.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in extraction technologies (e.g., fracking) have made previously inaccessible reserves viable, potentially stabilizing supply levels despite geopolitical tensions.
- Global Economic Recovery: The pace of recovery from economic downturns will significantly influence demand for oil. A robust recovery could lead to higher demand—and consequently higher prices—while a sluggish recovery might dampen both demand for oil and overall market performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Does The Stock Market React To Changes In Oil Prices
- How do rising oil prices affect consumer spending?
Rising oil prices typically increase transportation costs, which can lead to higher consumer goods prices. This often results in reduced discretionary spending as consumers allocate more of their budgets toward essential goods. - Which sectors are most affected by changes in oil prices?
The transportation sector is heavily impacted due to its reliance on fuel; similarly, industries like manufacturing that depend on logistics are also affected by rising fuel costs. - Can falling oil prices positively impact the stock market?
Yes, falling oil prices can lower production costs for many companies, potentially boosting profit margins and leading to higher stock valuations across various sectors. - What role does geopolitical risk play in this relationship?
Geopolitical risks can create uncertainty that affects both oil supply and investor sentiment. Events such as conflicts or sanctions can lead to sudden spikes in oil prices that negatively impact stock markets. - How should investors adjust their portfolios based on changing oil prices?
Investors may consider diversifying their portfolios by including sectors less sensitive to oil price fluctuations or using hedging strategies to manage risk. - Are there any indicators that predict changes in this relationship?
Certain economic indicators such as inflation rates, employment data, and global demand trends can provide insights into how changes in oil prices may affect the broader stock market. - What is the long-term outlook for stocks related to fossil fuels?
The long-term outlook is uncertain as global economies transition towards renewable energy sources; however, fossil fuel stocks may continue to experience volatility influenced by regulatory changes and market dynamics. - How do analysts forecast the impact of oil price changes on stocks?
Analysts often use historical data correlations alongside economic models that factor in variables like supply-demand dynamics and macroeconomic indicators to forecast potential impacts.
In conclusion, understanding how the stock market reacts to changes in oil prices requires a nuanced approach that considers various economic factors, sector-specific dynamics, and global events. By employing strategic investment practices while remaining aware of potential risks and regulatory influences, investors can better navigate this complex landscape.