The relationship between the stock market and the UK economy is intricate, with each influencing the other in significant ways. The stock market serves as a barometer for economic health, reflecting investor sentiment and corporate performance. When stock prices rise, it often indicates optimism about future economic growth, which can lead to increased consumer spending and business investment. Conversely, a declining market can signal economic troubles, leading to reduced consumer confidence and spending.
Understanding this dynamic is crucial for investors, policymakers, and anyone interested in the broader economic landscape. This article delves into how the stock market impacts the UK economy, examining current trends, implementation strategies for investors, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Stock Market as Economic Indicator | The stock market reflects the health of publicly traded companies and overall economic conditions. Rising stock prices often correlate with increased consumer confidence and spending. |
| Investment and Employment Growth | When companies experience rising share prices, they gain access to capital for expansion, leading to job creation and increased employment rates. |
| Consumer Confidence | A robust stock market can enhance consumer confidence, encouraging spending and investment in goods and services. |
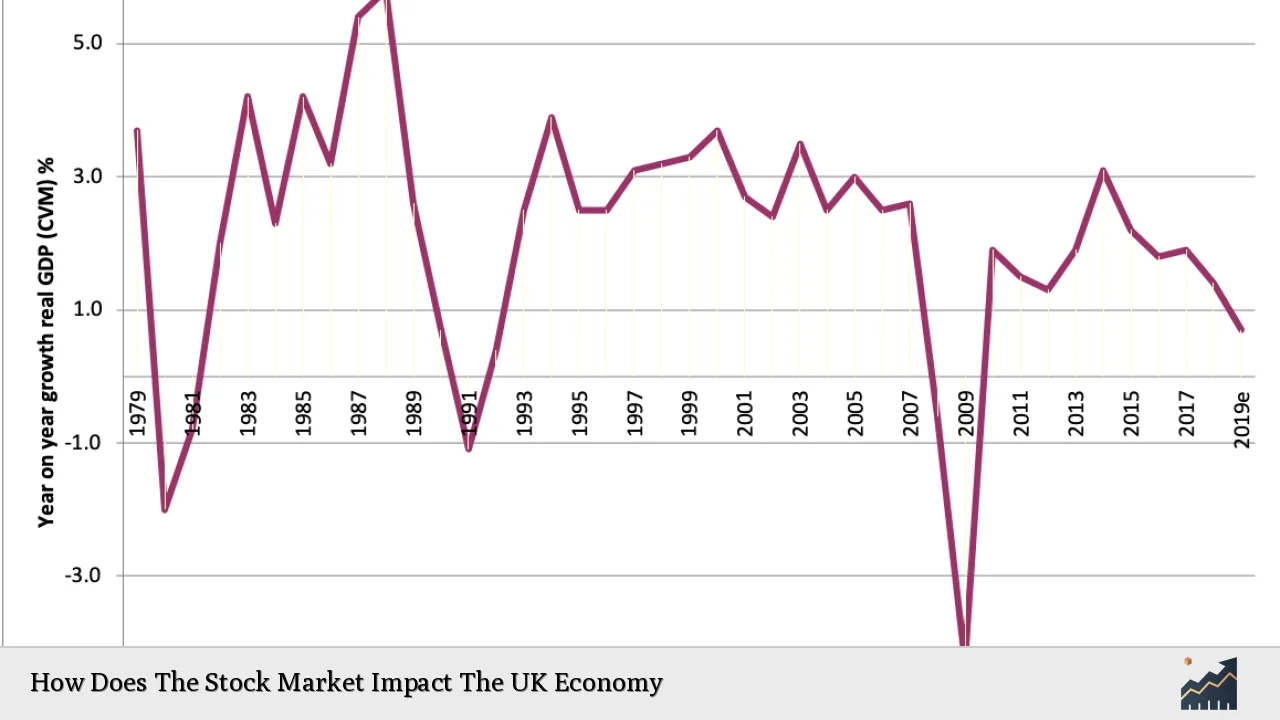
| Impact on GDP | The performance of the stock market influences Gross Domestic Product (GDP) through increased corporate profits, which can lead to higher economic activity. |
| Wealth Effect | As stock prices rise, individuals’ perceived wealth increases, prompting them to spend more, which further stimulates economic growth. |
| Market Volatility and Economic Stability | Significant drops in the stock market can lead to economic downturns as companies cut back on investment and consumers reduce spending due to decreased confidence. |
| Regulatory Influence | Government policies and regulations can impact stock market performance, influencing investor behavior and capital flows. |
| Global Market Interconnectedness | The UK stock market is influenced by global trends; fluctuations in major markets like the US can affect investor sentiment in the UK. |
Market Analysis and Trends
Recent trends indicate that the UK stock market has been on a recovery path after years of underperformance compared to global peers. The FTSE 100 index reached record highs in 2024 due to various factors including improving economic conditions, rising merger and acquisition (M&A) activity, and a decline in inflation rates. Analysts suggest that UK stocks are currently trading at significant discounts compared to their global counterparts—approximately 40% lower than US stocks—making them attractive for investors looking for value opportunities.
Current Economic Indicators
- GDP Growth: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects UK GDP growth at 1.5% for 2025, an increase from previous years due to improved domestic conditions.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation has moderated significantly; consumer price inflation was reported at 2.3% in April 2024, down from higher levels earlier in the year.
- Employment Trends: As companies gain capital from rising share prices, employment rates are expected to improve as businesses expand operations.
The interplay between these indicators highlights how a thriving stock market can contribute positively to overall economic conditions.
Implementation Strategies
For individual investors looking to capitalize on these trends within the UK stock market, several strategies can be employed:
- Diversification: Investing across various sectors can mitigate risks associated with volatility in specific industries.
- Focus on Small-Cap Stocks: Smaller companies often have greater exposure to domestic economic conditions and may offer higher growth potential compared to large-cap stocks.
- Utilize Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Leveraging accounts like ISAs (Individual Savings Accounts) allows investors to maximize returns without incurring tax liabilities on gains.
- Monitor Regulatory Changes: Staying informed about changes in listing rules or financial regulations can provide insights into emerging investment opportunities.
Risk Considerations
Investing in the stock market carries inherent risks that need careful consideration:
- Market Volatility: Sudden drops in stock prices can lead to significant losses. Investors should be prepared for fluctuations.
- Economic Downturns: A recession or negative economic news can adversely affect stock prices and investor sentiment.
- Regulatory Risks: Changes in government policies or regulations can impact specific sectors or overall market performance.
Risk management strategies such as setting stop-loss orders or maintaining a diversified portfolio can help mitigate these risks.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory environment plays a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the UK stock market:
- FCA Reforms: The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has implemented significant reforms aimed at simplifying listing rules to attract more companies to list on UK exchanges. This includes reducing barriers for new listings and enhancing transparency requirements.
- Capital Buffer Regulations: The Bank of England’s countercyclical capital buffer helps ensure that banks maintain sufficient capital during economic fluctuations, promoting stability within financial markets.
These regulatory measures are designed not only to protect investors but also to foster a more vibrant capital market conducive to long-term economic growth.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, several factors will influence the relationship between the UK stock market and its economy:
- Continued Economic Recovery: As inflation stabilizes and consumer confidence improves, further growth in the stock market is anticipated.
- Increased Foreign Investment: A favorable valuation of UK equities may attract foreign investors seeking diversification from US markets.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations within financial technology could enhance trading efficiency and accessibility for retail investors.
Overall, while challenges remain—such as geopolitical tensions and potential recessionary pressures—the outlook for the UK economy appears cautiously optimistic given current trends in the stock market.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Does The Stock Market Impact The UK Economy
- What is the primary way that the stock market affects the economy?
The stock market impacts the economy primarily through its influence on corporate investment decisions. Rising share prices enable companies to raise capital more easily for expansion projects that create jobs and stimulate consumer spending. - How does consumer confidence relate to stock market performance?
A strong stock market boosts consumer confidence as individuals feel wealthier due to rising asset values. This increased confidence often leads to higher consumer spending, which drives economic growth. - What role do interest rates play in this relationship?
Interest rates affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Lower interest rates typically encourage borrowing and investing, which can lead to higher stock prices and vice versa during periods of rising rates. - Can a declining stock market lead to a recession?
Yes, a significant decline in the stock market can erode consumer confidence and spending power, potentially leading to reduced economic activity and even recession if sustained over time. - How do regulatory changes impact investor behavior?
Changes in regulations can either encourage or deter investment by altering perceived risks associated with investing in certain sectors or types of securities. - What should investors consider when investing during volatile periods?
Diversification across asset classes and sectors is crucial during volatile periods. Investors should also stay informed about macroeconomic indicators that could influence market movements. - Are there specific sectors that are more sensitive to stock market fluctuations?
Cyclical sectors such as consumer discretionary and financials tend to be more sensitive to fluctuations in the stock market compared to defensive sectors like utilities or healthcare. - How does foreign investment affect the UK economy?
Foreign investment brings capital into the UK economy, supporting business expansion and job creation while also contributing positively to trade balances.
This comprehensive analysis underscores how intertwined the UK economy is with its stock market dynamics. Understanding these relationships equips investors with insights necessary for making informed decisions amidst changing economic landscapes.