The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the financial markets by investigating and prosecuting allegations of securities fraud. This process is vital for protecting investors and ensuring fair trading practices. The SEC’s approach to determining alleged securities fraud involves a structured investigation process, analysis of market trends, and regulatory compliance checks.
The SEC employs various methods to detect potential violations, including market surveillance, investor tips, and collaboration with other regulatory bodies. This article explores how the SEC determines alleged securities fraud, focusing on market analysis, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlook.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Rule 10b-5 | This rule prohibits any act or omission resulting in fraud or deceit in connection with the purchase or sale of any security. It sets the foundation for most securities fraud cases. |
| Material Misrepresentation | Involves false statements or omissions that could influence investor decisions. Establishing this is crucial for proving fraud. |
| Insider Trading | Trading based on non-public information is considered a serious violation. The SEC investigates both classical and misappropriation theories of insider trading. |
| Division of Enforcement | This division conducts investigations and prosecutes violations of securities laws, utilizing various tools to gather evidence. |
| Formal Investigations | When preliminary inquiries suggest wrongdoing, the SEC can initiate formal investigations, allowing them to subpoena documents and compel testimony. |
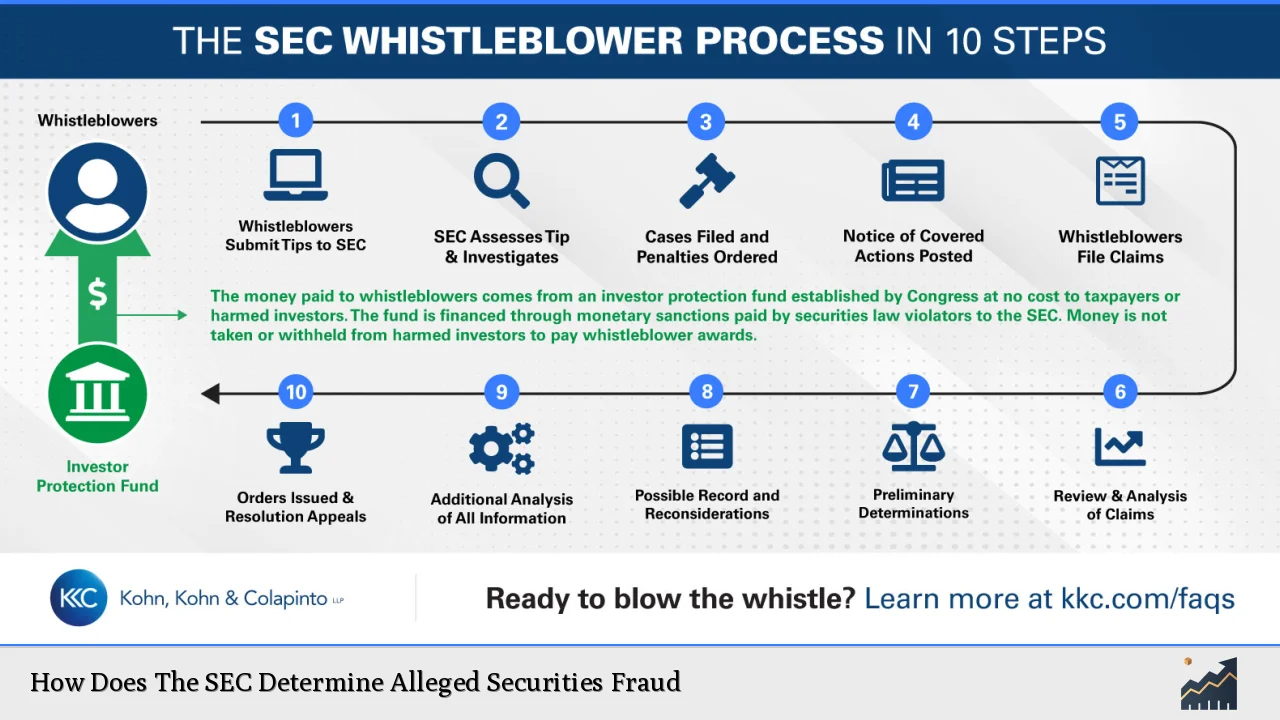
| Whistleblower Program | The SEC encourages individuals to report suspected violations by offering financial incentives for credible tips that lead to successful enforcement actions. |
| Settlement Agreements | Many cases are resolved through settlements where violators agree to penalties without admitting wrongdoing, which can expedite the process. |
| Public Disclosure | Once investigations conclude, the SEC publicly discloses its findings and actions taken against violators to maintain transparency and investor trust. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The landscape of securities fraud is continually evolving, influenced by technological advancements and changing market dynamics. In 2024, reported fraud incidents have increased significantly, with investors losing approximately $10 billion due to various scams according to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The SEC has responded by enhancing its surveillance capabilities and focusing on emerging threats such as digital asset fraud and scams perpetuated through social media platforms.
Recent statistics reveal that in fiscal year 2024, the SEC filed 583 enforcement actions, recovering $8.2 billion in financial remedies—the highest amount in its history. This reflects a shift towards more robust enforcement strategies against fraudulent activities while also highlighting a decline in total enforcement actions compared to previous years.
The increase in whistleblower tips—over 24,000 received in 2024—demonstrates heightened awareness among investors regarding potential fraudulent activities. The SEC’s Interagency Securities Council has been instrumental in coordinating efforts across federal, state, and local levels to combat financial fraud effectively.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively combat securities fraud, the SEC employs a multi-faceted approach:
- Market Surveillance: Continuous monitoring of trading activities to identify unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent behavior.
- Investor Education: Providing resources and guidance to help investors recognize potential scams and report suspicious activities.
- Collaboration: Working with other regulatory bodies and law enforcement agencies to share information and best practices.
- Technology Utilization: Leveraging advanced data analytics tools to detect anomalies in trading data that may suggest fraudulent transactions.
- Whistleblower Incentives: Encouraging individuals with knowledge of securities violations to come forward by offering financial rewards for credible tips.
These strategies are designed not only to detect fraud but also to deter potential violators by creating an environment of accountability.
Risk Considerations
Investors must be aware of the risks associated with securities fraud:
- Financial Loss: Victims of securities fraud can suffer significant financial losses due to deceptive practices.
- Legal Consequences: Individuals or firms found guilty of securities fraud face severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
- Reputational Damage: Companies involved in fraudulent activities may experience long-lasting damage to their reputation, impacting their market position.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Firms suspected of wrongdoing may face increased scrutiny from regulators, affecting their operations and profitability.
Understanding these risks is essential for both individual investors and finance professionals as they navigate the complexities of the investment landscape.
Regulatory Aspects
The SEC operates under a framework designed to enforce compliance with federal securities laws:
- Enforcement Actions: The SEC can initiate civil actions against violators in federal court or through administrative proceedings. These actions may result in monetary penalties, disgorgement of profits, or bans from serving as corporate officers.
- Reporting Requirements: Public companies must adhere to strict reporting standards to ensure transparency. Failure to comply can lead to legal repercussions.
- Investor Protection Initiatives: The SEC has implemented various programs aimed at protecting retail investors from fraudulent schemes.
- Annual Reports: The SEC publishes annual enforcement reports detailing its activities, which provide insights into trends in securities law violations.
These regulatory measures are critical for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring fair market practices.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the SEC is expected to continue adapting its strategies in response to emerging trends in securities fraud:
- Increased Focus on Technology-Based Fraud: With the rise of digital assets and online trading platforms, the SEC will likely enhance its focus on cyber-related fraud schemes.
- Strengthened Whistleblower Program: Anticipated expansions in whistleblower protections may encourage more individuals to report misconduct.
- Global Collaboration: As financial markets become more interconnected globally, the SEC will likely increase collaboration with international regulatory bodies to address cross-border fraud issues.
- Enhanced Data Analytics: Continued investment in technology will enable more effective detection and prevention of fraudulent activities within the markets.
By staying ahead of these trends, the SEC aims to protect investors while fostering a transparent and trustworthy financial environment.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Does The SEC Determine Alleged Securities Fraud
- What is securities fraud?
Securities fraud involves deceptive practices related to trading or issuing securities that mislead investors about a company’s financial status or prospects. - How does the SEC investigate alleged fraud?
The SEC conducts investigations through market surveillance, investor complaints, formal inquiries, and collaboration with other agencies. - What are common types of securities fraud?
Common types include insider trading, Ponzi schemes, misrepresentation of information, and pump-and-dump schemes. - What penalties do violators face?
Penalties can include hefty fines, disgorgement of profits gained through fraudulent activities, bans from serving as corporate officers, or imprisonment. - How can investors protect themselves from fraud?
Investors should conduct thorough research before investing, stay informed about potential scams, and report suspicious activities to authorities. - What role does technology play in detecting securities fraud?
The SEC uses advanced data analytics tools for real-time monitoring of trading patterns that may indicate fraudulent behavior. - Can whistleblowers receive rewards?
The SEC offers financial incentives for whistleblowers who provide actionable information leading to successful enforcement actions against violators. - What is Rule 10b-5?
This rule prohibits any act or omission resulting in fraud or deceit in connection with the purchase or sale of any security.
This comprehensive overview provides insights into how the SEC determines alleged securities fraud while highlighting current trends and future outlooks within this critical area of finance. Understanding these processes is essential for individual investors and finance professionals navigating today’s complex investment landscape.