Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is revolutionizing the financial landscape by leveraging blockchain technology to create an open, accessible, and transparent financial ecosystem. This innovative approach to finance has the potential to address longstanding issues of financial exclusion, particularly for the unbanked and underbanked populations worldwide. By removing traditional barriers and intermediaries, DeFi is paving the way for a more inclusive financial future.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
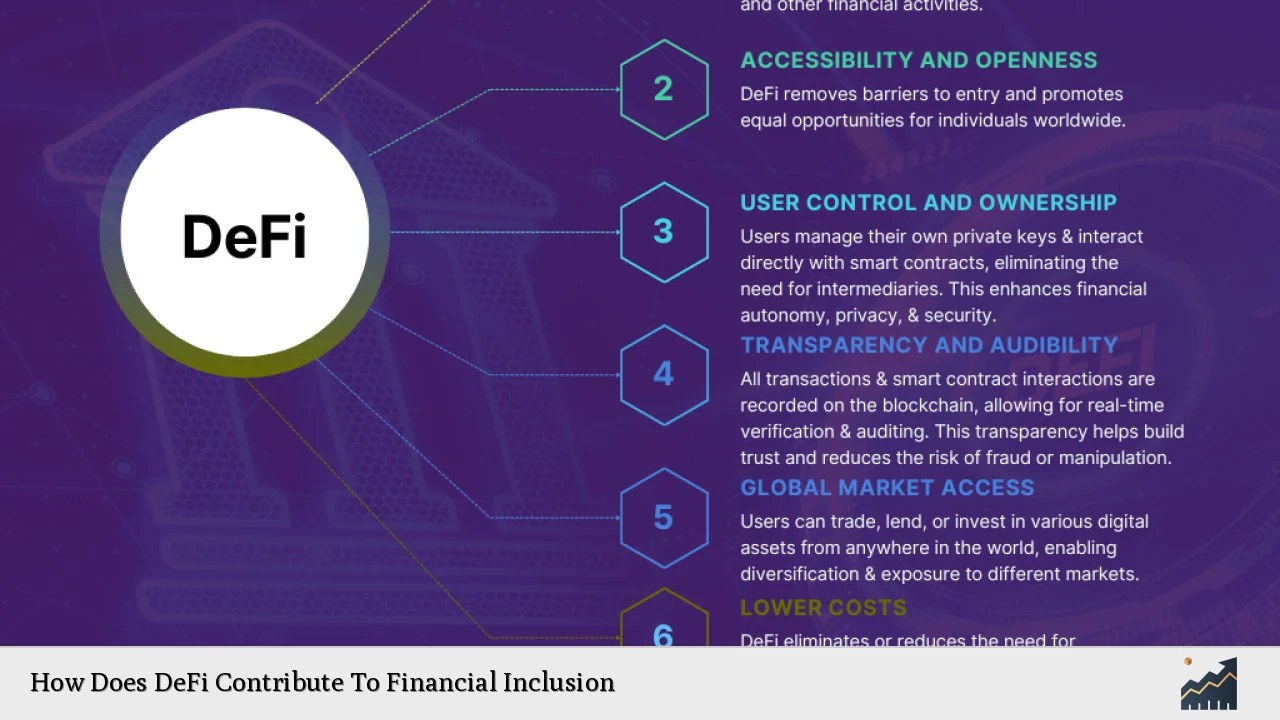
| Accessibility | DeFi platforms are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, eliminating geographical and institutional barriers |
| Disintermediation | Removal of traditional financial intermediaries reduces costs and increases efficiency |
| Transparency | Blockchain technology ensures all transactions are visible and verifiable, enhancing trust |
| Programmability | Smart contracts automate financial services, reducing human error and bias |
| Interoperability | DeFi protocols can interact seamlessly, creating a more integrated financial ecosystem |
Market Analysis and Trends
The DeFi market has experienced explosive growth in recent years, reflecting its potential to reshape the financial industry. As of 2024, the global DeFi market size is projected to reach $337.04 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 28.2% from 2023 to 2030. This rapid expansion underscores the increasing adoption and recognition of DeFi’s potential to address financial inclusion challenges.
Several key trends are driving the growth of DeFi and its impact on financial inclusion:
1. Increasing smartphone penetration: The widespread availability of smartphones, even in developing countries, provides a gateway for millions to access DeFi services without the need for traditional banking infrastructure.
2. Growing awareness of cryptocurrency: As more people become familiar with cryptocurrencies, the adoption of DeFi platforms is likely to accelerate, particularly in regions with unstable local currencies or limited access to traditional banking services.
3. Regulatory developments: While regulatory frameworks for DeFi are still evolving, there is a growing recognition among policymakers of the need to balance innovation with consumer protection, which could lead to more favorable regulations that promote financial inclusion.
4. Technological advancements: Ongoing improvements in blockchain scalability and user interface design are making DeFi platforms more accessible and user-friendly for a broader audience.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively leverage DeFi for financial inclusion, several implementation strategies can be employed:
1. Microloans and P2P Lending
DeFi platforms enable microloans and peer-to-peer lending without the need for traditional credit assessments. This approach can provide crucial access to capital for small businesses and individuals in underserved communities. By utilizing smart contracts, these loans can be processed quickly and with lower transaction costs compared to traditional financial institutions.
2. Stablecoin Integration
Integrating stablecoins into DeFi platforms can provide a bridge between traditional fiat currencies and the crypto ecosystem. This can help mitigate volatility concerns and make DeFi more attractive to risk-averse users, particularly in developing economies where currency stability is a significant issue.
3. Mobile-First Approach
Developing mobile-optimized DeFi applications is crucial for reaching underbanked populations in regions with high smartphone penetration but limited access to traditional banking services. These applications should focus on simplicity and user-friendliness to overcome potential technological barriers.
4. Education and Outreach
Implementing comprehensive education programs and community outreach initiatives is essential to increase awareness and understanding of DeFi among underserved populations. This can include partnering with local organizations, offering tutorials, and providing multilingual support.
Risk Considerations
While DeFi offers significant potential for financial inclusion, it also comes with inherent risks that must be carefully considered:
1. Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: The reliance on smart contracts introduces the risk of coding errors or vulnerabilities that could be exploited, potentially leading to loss of funds.
2. Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market’s volatility can pose risks for users, particularly those in economically vulnerable situations.
3. Regulatory Uncertainty: The evolving regulatory landscape for DeFi creates uncertainty and potential compliance challenges for both users and platform providers.
4. User Error: The self-custodial nature of many DeFi platforms places a significant responsibility on users to manage their own keys and transactions, which can lead to irreversible mistakes.
5. Scalability Issues: As DeFi adoption grows, blockchain networks may face scalability challenges, potentially leading to higher transaction fees and slower processing times.
To mitigate these risks, DeFi platforms focusing on financial inclusion should prioritize security audits, implement user-friendly interfaces with built-in safeguards, and provide clear risk disclosures and educational resources.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape for DeFi is complex and rapidly evolving. While the decentralized nature of DeFi presents challenges for traditional regulatory approaches, there is growing recognition of the need for balanced oversight to protect consumers while fostering innovation.
Key regulatory considerations include:
1. KYC/AML Compliance: Balancing the need for anonymity with regulatory requirements for Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures.
2. Consumer Protection: Developing frameworks to protect users from fraud, market manipulation, and unfair practices without stifling innovation.
3. Cross-Border Transactions: Addressing the regulatory challenges posed by DeFi’s ability to facilitate seamless cross-border transactions.
4. Tax Implications: Clarifying the tax treatment of DeFi transactions and yields to ensure compliance and fairness.
5. Regulatory Sandboxes: Implementing regulatory sandboxes to allow controlled testing of DeFi innovations in a supervised environment.
As the DeFi ecosystem matures, collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulators, and policymakers will be crucial in developing regulatory frameworks that promote financial inclusion while addressing potential risks.
Future Outlook
The future of DeFi in promoting financial inclusion looks promising, with several key developments on the horizon:
1. Improved User Experience: Ongoing efforts to simplify DeFi interfaces and processes will make these platforms more accessible to a broader audience, including those with limited technical knowledge.
2. Integration with Traditional Finance: The growing trend of traditional financial institutions exploring DeFi integration could lead to hybrid solutions that combine the benefits of both centralized and decentralized finance.
3. Expansion of Use Cases: Beyond lending and borrowing, DeFi is likely to expand into areas such as insurance, derivatives, and tokenized real-world assets, providing a more comprehensive suite of financial services to underserved populations.
4. Technological Advancements: Continued improvements in blockchain scalability, interoperability, and privacy features will enhance the efficiency and security of DeFi platforms.
5. Regulatory Clarity: As regulatory frameworks evolve, clearer guidelines are expected to emerge, potentially leading to greater institutional adoption and trust in DeFi solutions.
6. Financial Education Initiatives: Increased focus on financial literacy programs tailored to DeFi could empower more individuals to participate in the decentralized economy confidently.
As DeFi continues to evolve, its potential to drive financial inclusion remains significant. By addressing current challenges and leveraging emerging technologies, DeFi has the power to create a more equitable and accessible financial system for people around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Does DeFi Contribute To Financial Inclusion
- What are the main advantages of DeFi for financial inclusion?
DeFi offers global accessibility, lower costs, faster transactions, and innovative financial products without requiring traditional bank accounts or credit histories. - How does DeFi address the needs of the unbanked population?
DeFi provides access to financial services through smartphones and internet connections, bypassing the need for physical bank branches and traditional identification requirements. - What role do stablecoins play in DeFi’s contribution to financial inclusion?
Stablecoins offer a bridge between volatile cryptocurrencies and traditional fiat currencies, providing a more stable store of value and medium of exchange for users in developing economies. - How does DeFi lending differ from traditional lending in terms of financial inclusion?
DeFi lending platforms often use alternative credit scoring methods and collateralization models, potentially opening up borrowing opportunities for those excluded from traditional lending systems. - What are the main challenges in adopting DeFi for financial inclusion?
Key challenges include technological barriers, regulatory uncertainty, security risks, and the need for widespread education on DeFi concepts and usage. - How can governments and regulators support DeFi’s role in financial inclusion?
Governments can create supportive regulatory frameworks, implement sandbox programs for testing DeFi innovations, and collaborate with industry stakeholders to develop inclusive policies. - What future developments in DeFi could further enhance financial inclusion?
Advancements in user interface design, integration with traditional finance, expansion of use cases, and improved blockchain scalability could all contribute to making DeFi more accessible and beneficial for financial inclusion efforts.