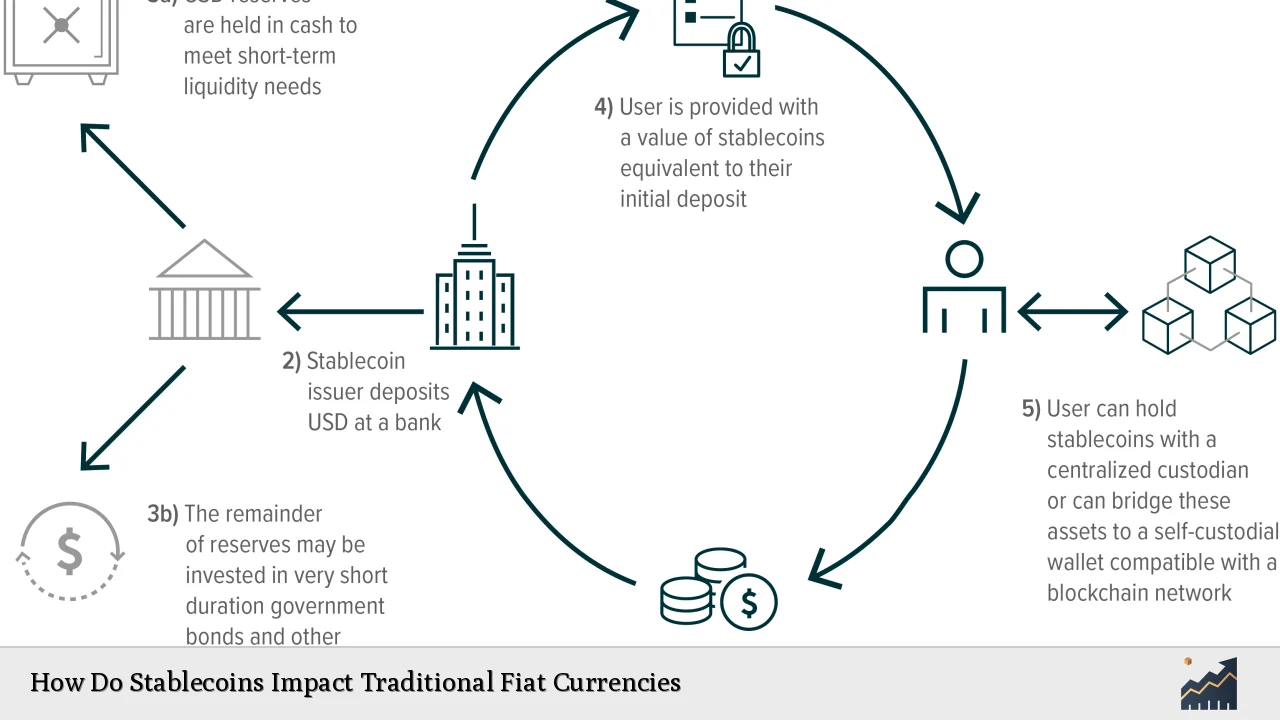
Stablecoins, a class of cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their worth to traditional fiat currencies or other assets, have emerged as a significant force in the financial landscape. Their rise has been propelled by the need for stability in an otherwise volatile cryptocurrency market, positioning them as a bridge between digital assets and traditional financial systems. This article explores the multifaceted impact of stablecoins on traditional fiat currencies, analyzing market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Market Stability | Stablecoins provide a reliable medium of exchange and store of value, reducing volatility compared to traditional cryptocurrencies. |
| Cross-Border Transactions | They facilitate faster and cheaper international transactions, impacting traditional remittance services. |
| Monetary Policy Implications | The issuance of stablecoins can influence money supply and monetary policy effectiveness in fiat economies. |
| Adoption in Emerging Markets | Stablecoins are increasingly used in regions with unstable currencies, offering a more stable alternative for transactions and savings. |
| Regulatory Challenges | The rapid growth of stablecoins poses regulatory challenges, necessitating frameworks to ensure consumer protection and financial stability. |
| Integration with Traditional Finance | Financial institutions are exploring the integration of stablecoins into payment systems, potentially reshaping the banking landscape. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The market for stablecoins has witnessed explosive growth, with their total market capitalization reaching approximately $200 billion as of December 2024. Tether (USDT) remains the dominant player, commanding a market share of around $139 billion, followed by USD Coin (USDC) at approximately $41 billion. This growth is driven by several factors:
- Increased Adoption: Stablecoins are increasingly viewed as practical solutions for everyday transactions, especially in regions experiencing economic instability or high inflation. In Latin America and Sub-Saharan Africa, for instance, retail adoption has surged due to their utility in remittances and as a hedge against local currency volatility.
- Institutional Interest: Major financial institutions are beginning to recognize the potential of stablecoins for liquidity management and cross-border settlements. The integration of stablecoins into existing financial infrastructures is expected to enhance transaction efficiency.
- Regulatory Developments: As regulatory clarity improves in regions like the UK and EU, institutional adoption is anticipated to accelerate. For example, the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is developing a framework for regulating stablecoin issuers and custodians.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively leverage stablecoins within traditional finance systems, several strategies can be adopted:
- Integration with Payment Systems: Financial institutions can integrate stablecoin payments into their existing platforms to facilitate faster transactions. This could involve partnerships with stablecoin issuers to create seamless payment solutions.
- Utilization in Remittances: By adopting stablecoins for remittance services, companies can reduce transaction costs and improve transfer speeds. This is particularly beneficial in areas where traditional banking services are limited or costly.
- Investment Products: Financial firms can create investment products backed by stablecoins, allowing investors to earn yields while maintaining exposure to fiat currencies.
Risk Considerations
While stablecoins offer numerous advantages, they also present several risks that must be managed:
- Market Risk: The stability of a stablecoin is contingent upon the assets backing it. If these reserves are mismanaged or if there is a loss of confidence among users, it could lead to a rapid decline in value.
- Regulatory Risk: As governments worldwide grapple with how to regulate cryptocurrencies, changes in regulations could impact the viability and acceptance of stablecoins.
- Operational Risks: Technical failures or security breaches could undermine trust in stablecoin systems. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to mitigate these risks.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape for stablecoins is evolving rapidly. Key considerations include:
- Consumer Protection: Regulators are focusing on ensuring that consumers have adequate protections when using stablecoins. This includes transparency regarding reserves and redemption processes.
- Financial Stability: The potential systemic risks posed by large-scale adoption of stablecoins necessitate oversight similar to that applied to traditional banks. Regulatory bodies are exploring frameworks that would hold issuers accountable for maintaining adequate reserves.
- Cross-Border Regulations: Given that many stablecoin transactions occur across borders, international regulatory cooperation will be essential to address potential loopholes and ensure compliance with various jurisdictions.
Future Outlook
The future of stablecoins appears promising but will depend on several factors:
- Continued Growth: Analysts predict that the market capitalization of stablecoins could reach upwards of $400 billion by 2025, contingent on favorable regulatory developments and increased adoption by both consumers and businesses.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in blockchain technology could enhance the functionality and security of stablecoins, making them more appealing for everyday use.
- Integration into Traditional Finance: As traditional financial institutions increasingly adopt digital currencies, we may see a significant shift in how money is perceived and utilized globally.
In conclusion, while stablecoins present unique opportunities for enhancing transaction efficiency and providing stability in volatile markets, their impact on traditional fiat currencies will largely depend on how effectively they are integrated into existing financial systems and regulated by authorities worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Do Stablecoins Impact Traditional Fiat Currencies
- What are stablecoins?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a fixed value by pegging them to traditional fiat currencies or other assets. - How do stablecoins affect monetary policy?
The issuance of stablecoins can impact money supply dynamics by removing funds from traditional banking systems when backed by reserves like U.S. Treasury securities. - Are stablecoins safe?
While they offer price stability compared to volatile cryptocurrencies, risks exist related to reserve management and regulatory scrutiny. - What role do regulators play in the use of stablecoins?
Regulators aim to ensure consumer protection and financial stability by overseeing stablecoin issuers and establishing guidelines for their use. - How can businesses benefit from using stablecoins?
Businesses can leverage stablecoins for faster transactions, reduced fees on cross-border payments, and enhanced liquidity management. - What challenges do stablecoins face?
Challenges include regulatory uncertainty, market volatility risks associated with underlying assets, and potential operational vulnerabilities. - Will traditional banks adopt stablecoin technology?
The trend indicates that many banks are exploring ways to integrate stablecoin technology into their services as regulatory frameworks become clearer. - How do emerging markets utilize stablecoins?
In emerging markets with unstable currencies, individuals often use stablecoins as a reliable means for saving value and conducting transactions.
This comprehensive exploration highlights the growing significance of stablecoins within the global financial ecosystem while emphasizing their potential implications for traditional fiat currencies. As this sector continues to evolve, ongoing analysis will be critical for understanding its long-term effects on finance worldwide.