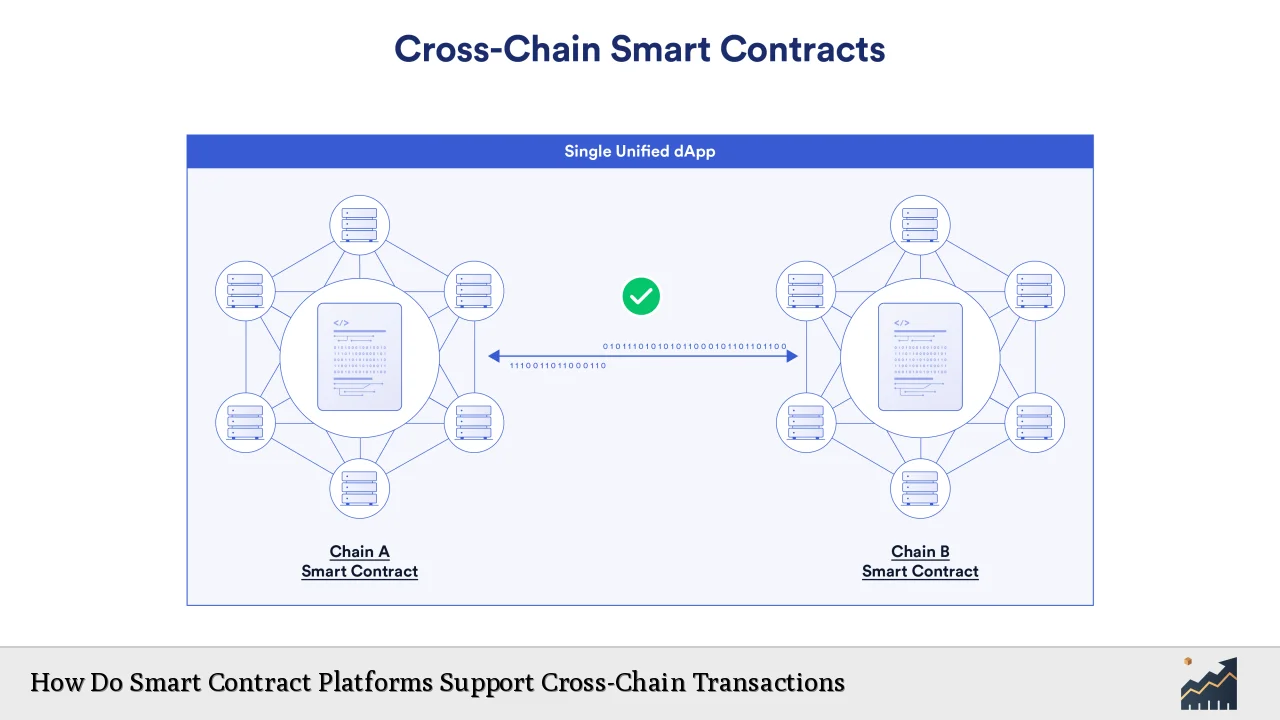
Smart contracts have emerged as a transformative technology within the blockchain ecosystem, enabling automated, self-executing agreements that facilitate transactions without the need for intermediaries. Their integration into cross-chain transactions is particularly significant, as it addresses the challenges of interoperability between different blockchain networks. This article explores how smart contract platforms support cross-chain transactions, the current market trends, implementation strategies, associated risks, regulatory considerations, and future outlook.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Cross-Chain Transactions | Facilitate the exchange of assets and data across different blockchain networks without centralized intermediaries, enhancing interoperability. |
| Smart Contracts | Self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code, automating processes and reducing reliance on intermediaries. |
| Blockchain Interoperability | The ability of different blockchain systems to communicate and interact seamlessly, increasing liquidity and usability of digital assets. |
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Financial services provided through decentralized platforms, leveraging smart contracts for lending, trading, and asset management. |
| Market Growth | The smart contract market is projected to grow from $2.14 billion in 2024 to $12.55 billion by 2032, highlighting increasing adoption across industries. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The demand for cross-chain transactions is rising as the blockchain ecosystem becomes increasingly fragmented. Different blockchains often serve specific purposes and utilize unique protocols, making interoperability essential for maximizing the utility of digital assets.
Recent studies indicate that the blockchain interoperability market is expected to grow significantly, reaching approximately $1.97 billion by 2028 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.4%. This growth is driven by several factors:
- Increased Liquidity: Cross-chain transactions enhance liquidity by allowing assets to move freely between blockchains.
- User Flexibility: Users gain greater access to various assets across multiple networks, improving their investment options.
- DeFi Expansion: The rise of decentralized finance platforms has further fueled the need for seamless cross-chain interactions.
Current trends show that projects like Wormhole have facilitated over 1 billion messages and $39 billion in transfers since their inception, underscoring the importance of cross-chain technology in enhancing blockchain connectivity.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively implement cross-chain transactions using smart contracts, several strategies can be adopted:
- Cross-Chain Bridges: These are decentralized applications (dApps) that allow users to transfer assets between different blockchains. They typically use smart contracts to lock tokens on one chain while minting equivalent tokens on another. This ensures that the total supply remains consistent across networks.
- Interoperability Protocols: Protocols such as the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) enable secure communication between blockchains. They facilitate the execution of smart contracts across different environments, allowing developers to create applications that can operate seamlessly on multiple chains.
- Multi-Chain Development: Developers are increasingly deploying their applications across multiple blockchains rather than limiting them to a single network. This approach not only broadens their user base but also allows for experimentation with new features on lower-cost networks.
Risk Considerations
While cross-chain transactions offer numerous benefits, they also come with inherent risks:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Cross-chain bridges can be susceptible to attacks if not properly secured. The complexity of managing multiple chains increases the potential attack surface.
- Smart Contract Bugs: Flaws in smart contract code can lead to significant financial losses if exploited. Rigorous testing and audits are essential to mitigate these risks.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can pose challenges for cross-chain implementations. Companies must stay informed about compliance requirements in different jurisdictions.
Regulatory Aspects
As smart contracts and cross-chain technologies become more prevalent, regulatory bodies are beginning to establish frameworks to govern their use:
- Compliance Requirements: Organizations must ensure that their cross-chain implementations comply with existing regulations regarding anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) practices.
- Tax Implications: Cross-border transactions may have tax implications that vary by jurisdiction. Understanding these requirements is crucial for businesses operating in multiple regions.
- Consumer Protection: Regulatory bodies are increasingly focused on consumer protection in the cryptocurrency space. Clear guidelines will help foster trust among users engaging in cross-chain transactions.
Future Outlook
The future of smart contract platforms supporting cross-chain transactions looks promising:
- Increased Adoption: As more businesses recognize the benefits of interoperability, adoption rates for cross-chain technologies are expected to rise significantly.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing innovations in blockchain technology will likely lead to more robust solutions for cross-chain interactions, enhancing security and efficiency.
- Integration with Traditional Finance: There is potential for hybrid systems that combine traditional financial services with decentralized solutions powered by smart contracts. This could lead to more efficient processes and broader acceptance of blockchain technology in mainstream finance.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Do Smart Contract Platforms Support Cross-Chain Transactions
- What are cross-chain transactions?
Cross-chain transactions allow digital assets and data to be exchanged between different blockchain networks without needing centralized intermediaries. - How do smart contracts enhance cross-chain transactions?
Smart contracts automate processes involved in cross-chain transactions, ensuring secure and transparent transfers while minimizing reliance on intermediaries. - What are the main challenges of implementing cross-chain solutions?
Key challenges include security vulnerabilities, potential bugs in smart contract code, and regulatory uncertainties across different jurisdictions. - What role do decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms play in cross-chain transactions?
DeFi platforms leverage smart contracts to facilitate various financial services across multiple blockchains, enhancing liquidity and user access. - How is the market for smart contracts expected to grow?
The global smart contract market is projected to grow from $2.14 billion in 2024 to $12.55 billion by 2032 due to increasing adoption across various industries. - What regulatory considerations should businesses keep in mind?
Businesses must comply with AML/KYC regulations and stay informed about tax implications and consumer protection laws related to cryptocurrency transactions. - What is the future outlook for smart contracts in finance?
The future looks promising with increased adoption rates, technological advancements enhancing security and efficiency, and potential integration with traditional financial systems. - How can developers ensure the security of their cross-chain implementations?
Developers should conduct rigorous testing and audits of their smart contracts and utilize best practices for securing cross-chain bridges against vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, smart contract platforms play a crucial role in facilitating cross-chain transactions by providing automated solutions that enhance interoperability among diverse blockchain networks. As this technology continues to evolve, it will likely reshape how digital assets are managed and exchanged across various ecosystems.