Smart contract platforms are at the forefront of blockchain technology, enabling decentralized applications (dApps) to execute automatically based on predefined conditions. However, as the number of blockchain networks continues to grow, interoperability—the ability of different blockchains to communicate and work together—has become a critical challenge. This article explores how smart contract platforms handle interoperability, analyzing current market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Interoperability | The ability of different blockchain networks to exchange information and value seamlessly, crucial for the expansion of decentralized applications. |
| Smart Contracts | Self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code, allowing for automated transactions without intermediaries. |
| Cross-Chain Protocols | Technologies that facilitate communication between different blockchains, enabling asset transfers and data sharing. |
| Sidechains | Separate blockchains linked to a main blockchain, allowing for the transfer of assets and functionalities across chains. |
| Oracles | Services that connect smart contracts with real-world data, enhancing their functionality by providing external information. |
| Market Trends | The blockchain interoperability market is projected to grow significantly, reaching $1.97 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 29.4%. |
| Security Risks | Increased interoperability may expose networks to vulnerabilities and breaches if not managed properly. |
| Regulatory Considerations | The evolving legal landscape requires clear guidelines for cross-chain interactions to ensure compliance and security. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The demand for interoperability in blockchain networks is rapidly increasing as businesses seek to leverage the unique advantages of multiple platforms. The global blockchain interoperability market is expected to expand from $0.54 billion in 2023 to $1.97 billion by 2028, driven by the rise in decentralized finance (DeFi), cross-border transactions, and multi-blockchain use cases. The market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.4%, reflecting the urgent need for solutions that enable seamless data exchange and asset transfers across various blockchain ecosystems.
Key trends influencing this market include:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The growth of DeFi applications necessitates interoperability for liquidity transfer between different platforms.
- Cross-Chain Solutions: Technologies such as cross-chain bridges and application programming interfaces (APIs) are being developed to facilitate communication between disparate blockchain systems.
- Layer 2 Solutions: These solutions enhance scalability and reduce transaction costs while maintaining security across multiple chains.
- Integration with Traditional Finance: As financial institutions explore blockchain technology, the demand for interoperable solutions that bridge traditional systems with decentralized networks is increasing.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively handle interoperability, smart contract platforms employ various strategies:
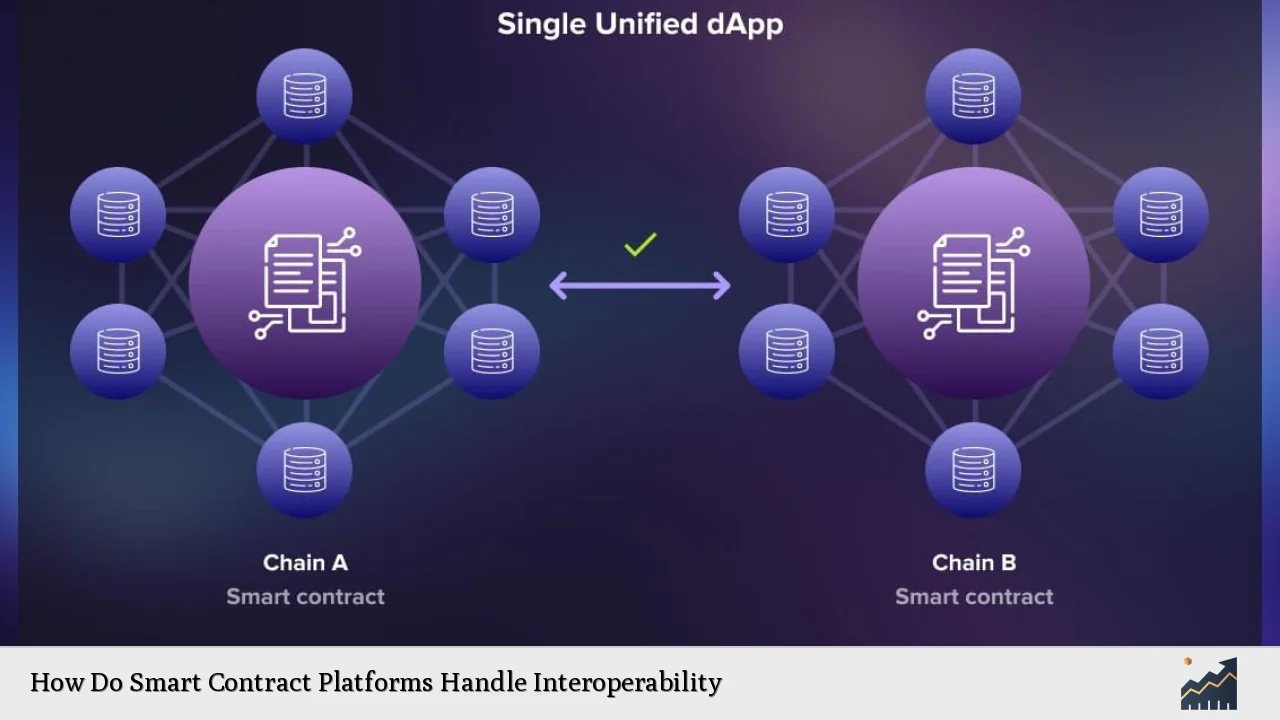
- Cross-Chain Protocols: Protocols like Polkadot and Cosmos allow different blockchains to communicate through shared standards and frameworks, enabling asset transfers without central intermediaries.
- Oracles: By providing real-time data from external sources, oracles enable smart contracts on different platforms to interact with real-world events, enhancing their functionality.
- Sidechains: These are independent blockchains that run parallel to a main chain. They facilitate asset transfers while allowing developers to build specialized applications without congesting the main network.
- Automated Gateways: A novel framework proposed in recent studies integrates smart contracts directly into existing blockchain infrastructures, minimizing reliance on third-party services while enhancing operational efficiency.
Risk Considerations
While interoperability presents numerous opportunities, it also introduces significant risks:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Increased connectivity between blockchains can expose networks to new attack vectors. Ensuring robust security measures is critical to protect against potential breaches.
- Complexity in Integration: Integrating different protocols often requires extensive technical knowledge and resources, which can be a barrier for smaller developers or institutions.
- Transaction Finality Issues: Different blockchains may have varying consensus mechanisms, complicating the finality of transactions across chains.
- Regulatory Compliance: As interoperability grows, so does the need for clear regulatory frameworks that address cross-chain transactions and ensure consumer protection.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain interoperability is evolving. Key considerations include:
- Legal Frameworks: Governments are beginning to establish guidelines that define the legal status of smart contracts and cross-chain transactions. Clear regulations will encourage broader adoption by providing legal certainty.
- Consumer Protection: As users engage with interoperable platforms, regulations must ensure that consumer rights are safeguarded against fraud or misuse.
- Standardization Efforts: Industry-wide standards are necessary to promote compatibility among various blockchain systems, facilitating smoother interactions across platforms.
Future Outlook
The future of smart contract platforms in terms of interoperability looks promising but requires ongoing innovation and collaboration among stakeholders. Key developments expected include:
- Enhanced Cross-Chain Functionality: As more robust cross-chain protocols emerge, users will benefit from improved transaction speeds and reduced costs.
- Broader Adoption in Financial Services: Financial institutions are likely to increasingly adopt interoperable smart contracts as they recognize their potential to streamline operations and reduce costs.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: The convergence of AI with smart contracts could lead to more sophisticated applications capable of handling complex transactions autonomously.
- Global Collaboration: International cooperation will be essential in establishing regulatory frameworks that support interoperability while fostering innovation across borders.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Do Smart Contract Platforms Handle Interoperability
- What is blockchain interoperability?
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate with each other seamlessly, allowing for data exchange and asset transfers. - Why is interoperability important for smart contracts?
Interoperability enhances the utility of smart contracts by enabling them to interact with multiple blockchain platforms, thereby broadening their application scope. - What are some common methods for achieving interoperability?
Common methods include cross-chain protocols, sidechains, oracles, and automated gateways that facilitate communication between different blockchains. - What risks are associated with blockchain interoperability?
Risks include security vulnerabilities due to increased connectivity, complexity in integration processes, transaction finality issues across chains, and regulatory compliance challenges. - How does regulation impact smart contract interoperability?
Regulations provide legal clarity and consumer protection guidelines that can encourage or hinder the adoption of interoperable solutions in the market. - What future trends can we expect in smart contract interoperability?
Future trends may include enhanced cross-chain functionality, broader adoption in financial services, integration with emerging technologies like AI, and global regulatory collaboration. - How can businesses benefit from interoperable smart contracts?
Businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs associated with transaction delays or intermediaries, and leverage diverse blockchain capabilities through interoperable smart contracts. - What role do oracles play in enhancing interoperability?
Oracles connect smart contracts with real-world data sources, allowing them to function effectively across different platforms by providing necessary external information.
In conclusion, as the landscape of blockchain technology evolves rapidly, addressing the challenges of interoperability will be pivotal for maximizing the potential of smart contracts. By fostering collaboration among developers, regulators, and industry stakeholders while embracing innovative solutions like cross-chain protocols and automated gateways, the future holds significant promise for a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem.