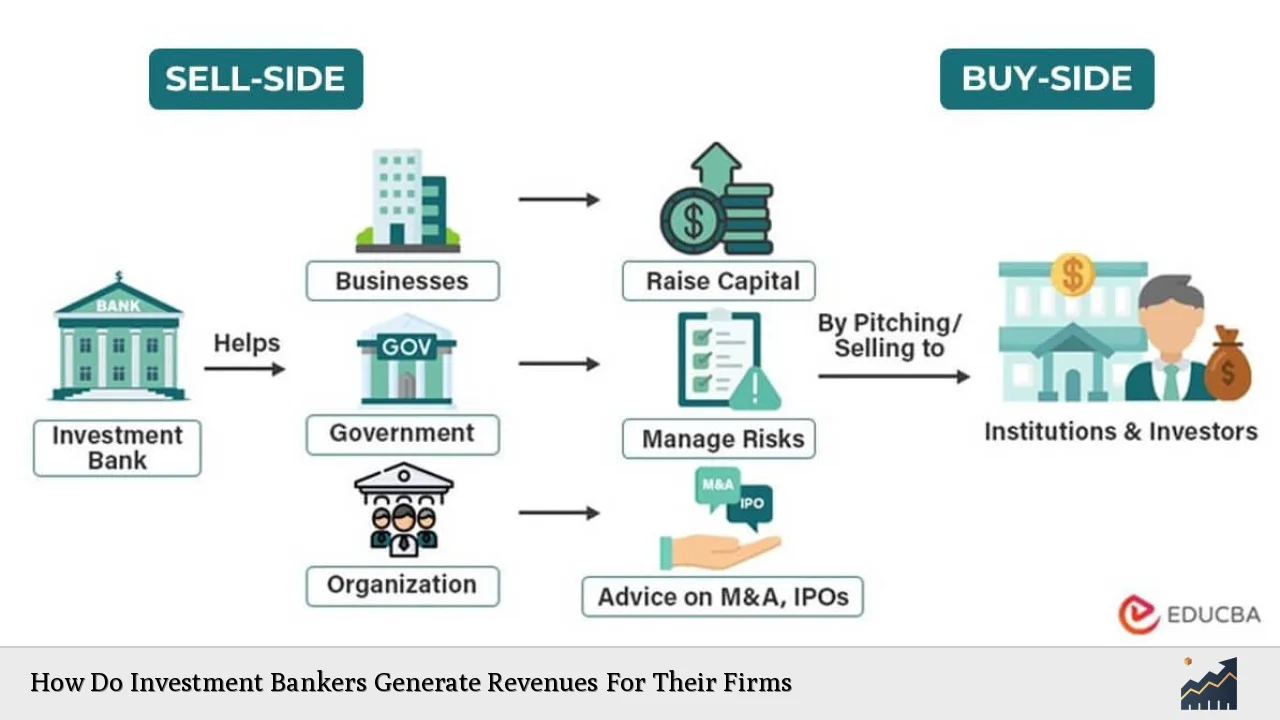
Investment bankers play a critical role in the financial ecosystem, serving as intermediaries between entities seeking capital and investors looking for opportunities. Their revenue generation is multifaceted, encompassing various services that cater to corporations, governments, and institutional investors. This article delves into the primary ways investment bankers generate revenues, providing a comprehensive analysis of market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlooks.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Underwriting Services | Investment banks facilitate the issuance of new securities by underwriting them. They assume the risk of buying the entire issue and reselling it to the public, earning substantial fees based on the size of the offering. |
| Advisory Fees | These fees are charged for providing strategic guidance on mergers and acquisitions (M&A), restructurings, and other financial transactions. The advisory role often leads to lucrative commissions. |
| Trading and Market-Making | Investment banks engage in trading securities for their own accounts or act as market makers, earning money from the bid-ask spread. This includes proprietary trading where banks invest their own capital. |
| Securitization | This involves pooling various financial assets (like loans) and creating new securities backed by these assets. Investment banks earn fees for structuring these deals and selling them to investors. |
| Research Services | Investment banks provide research reports that inform clients about market trends and investment opportunities. These reports can be monetized through subscriptions or fees. |
| Asset Management | Many investment banks have asset management divisions that manage portfolios for clients, charging management fees based on assets under management (AUM). |
| Private Equity Investments | Some investment banks invest in private equity deals, earning returns on their investments as well as management fees from funds they manage. |
| Fees from Financial Innovations | As markets evolve, investment banks develop new financial products (like derivatives) that can generate significant revenue through trading or advisory services. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The investment banking sector has seen considerable fluctuations over recent years due to changing economic conditions, interest rates, and regulatory environments. As of 2024, major U.S. and European investment banks are projected to experience a 30% increase in advisory and underwriting revenues, driven by a resurgence in M&A activity and capital markets engagement. This uptick is attributed to favorable market conditions and anticipated interest rate cuts that are expected to boost corporate deal-making activities.
Current Market Statistics
- The global investment banking market is projected to grow from $131.25 billion in 2023 to $142.16 billion in 2024, reflecting a CAGR of 8.3%.
- By 2028, this market is expected to reach approximately $194.05 billion, driven by factors such as integration of sustainable finance practices and increased private equity activity.
Implementation Strategies
Investment banks employ several strategies to enhance revenue streams:
- Diversification of Services: By offering a wide range of services—from underwriting to asset management—investment banks can mitigate risks associated with reliance on any single revenue source.
- Technological Integration: Utilizing data analytics and digital platforms allows banks to better understand client needs, customize offerings, and improve operational efficiencies.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with fintech firms or other financial institutions can expand service offerings and reach new markets.
- Focus on High-Growth Sectors: Investment banks are increasingly targeting sectors like technology and renewable energy, which are expected to see significant growth.
Risk Considerations
While the potential for revenue generation is substantial, investment bankers must navigate various risks:
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in market conditions can impact trading revenues and the success of underwriting efforts.
- Regulatory Risks: Compliance with evolving regulations can impose additional costs and operational challenges.
- Credit Risks: In underwriting debt securities or securitization transactions, there is always a risk that borrowers may default.
- Reputational Risks: High-profile failures or unethical practices can damage an investment bank’s reputation, affecting client trust and future business opportunities.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape for investment banking continues to evolve:
- In 2024, significant changes are anticipated in capital markets regulations in both the UK and EU. Investment banks will need to adapt their compliance frameworks accordingly.
- Regulatory bodies such as the SEC in the U.S. impose stringent requirements on transparency and risk management practices that impact how investment banks operate.
- The Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB) will require banks to enhance their capital calculations related to market risks by January 2025.
Future Outlook
The future for investment banking appears robust but requires adaptability:
- Increased M&A Activity: As interest rates stabilize or decline, M&A activity is expected to surge further, creating opportunities for advisory revenues.
- Sustainable Finance Growth: The integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into financing decisions is becoming increasingly important for investors.
- Technological Advancements: Continued innovation in fintech will reshape how investment banking services are delivered, potentially lowering costs while enhancing client engagement.
Conclusion
Investment bankers generate revenues through a diverse array of services that cater to various client needs across different sectors. By understanding current trends and implementing effective strategies while managing associated risks, they position themselves for sustained growth in an evolving financial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Do Investment Bankers Generate Revenues For Their Firms
- What are the primary revenue streams for investment banks?
The main sources include underwriting fees from issuing securities, advisory fees from M&A transactions, trading profits from market-making activities, securitization fees from pooling assets into new securities, research services subscriptions, asset management fees, private equity investments returns, and income from financial innovations. - How do underwriting services work?
Underwriting involves an investment bank purchasing all or part of a new issue of securities from a company before reselling them to investors. The bank assumes the risk if not all securities are sold but earns substantial fees based on the total amount issued. - What role do advisory fees play?
Advisory fees are charged for providing expert guidance on complex transactions such as mergers and acquisitions. These fees can be significant depending on the size of the deal. - How does trading contribute to revenue?
Investment banks earn money through trading by buying securities at lower prices and selling them at higher prices (proprietary trading) or by facilitating trades between buyers and sellers (market-making). - What risks do investment bankers face?
The primary risks include market volatility affecting trading revenues, regulatory compliance costs impacting operations, credit risks associated with underwriting debt securities, and reputational risks stemming from unethical practices. - How are regulatory changes impacting investment banking?
Regulatory changes require investment banks to enhance their compliance frameworks which can lead to increased operational costs but also drive improvements in risk management practices. - What is the future outlook for investment banking?
The future looks promising due to anticipated increases in M&A activity driven by favorable economic conditions along with growing emphasis on sustainable finance practices. - How do technological advancements affect revenue generation?
Technology enhances efficiency through data analytics that allows better client targeting and service customization while potentially lowering transaction costs.
This comprehensive analysis provides insights into how investment bankers generate revenues while navigating complex market dynamics. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for stakeholders involved in finance or considering investments within this sector.