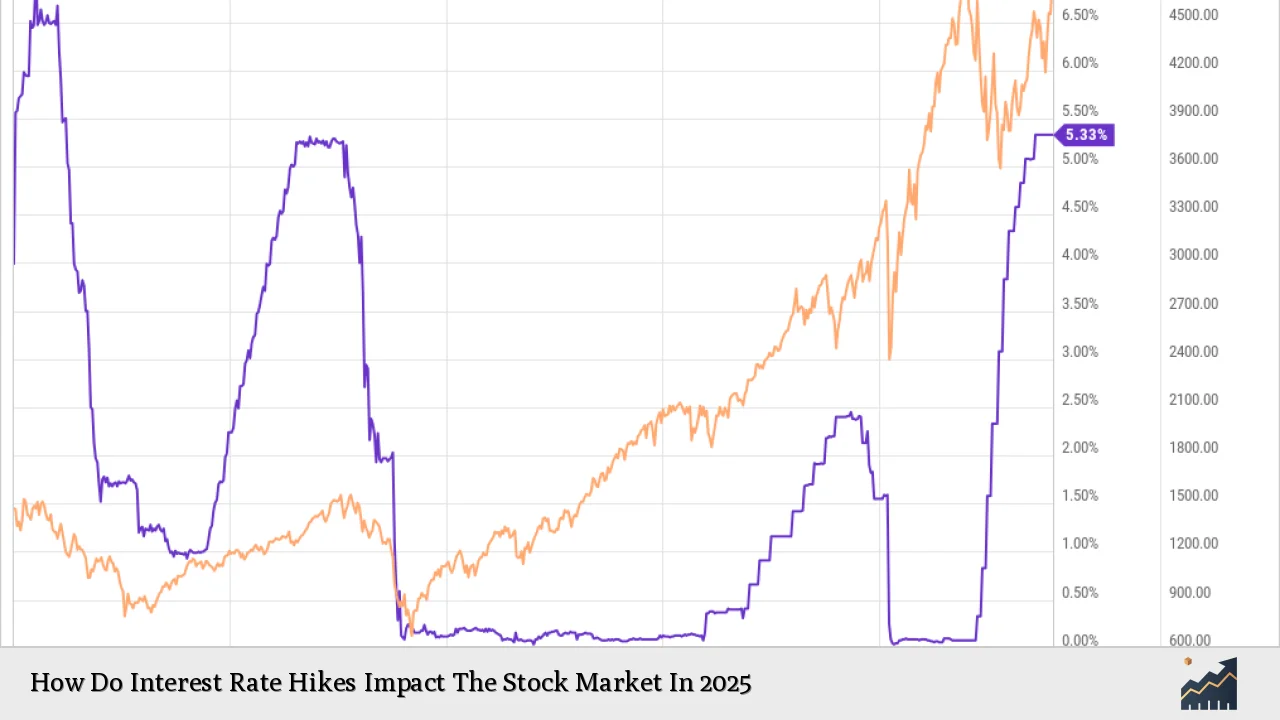
Interest rate hikes by central banks, particularly the Federal Reserve, have profound implications for the stock market. As we approach 2025, understanding this relationship is crucial for investors navigating an evolving economic landscape. Interest rates influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, and ultimately corporate profits, which are fundamental drivers of stock prices. This article delves into the anticipated effects of interest rate changes on the stock market in 2025, supported by current market statistics and expert analysis.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Interest Rates and Economic Growth | Higher interest rates typically slow down economic growth as borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to reduced consumer spending and business investments. |
| Stock Valuations | Increased rates lead to higher discount rates for future cash flows, reducing stock valuations as investors anticipate lower earnings growth. |
| Sector Performance | Sectors such as financials may benefit from rate hikes due to increased lending margins, while growth sectors like technology may suffer due to higher capital costs. |
| Investor Sentiment | Rate hikes can lead to increased market volatility as investor sentiment shifts based on expectations of future economic conditions. |
| Inflation Considerations | Persistent inflation may limit the effectiveness of rate cuts in stimulating growth, complicating the investment landscape. |
Market Analysis and Trends
As we enter 2025, the U.S. economy is projected to grow modestly at around 2% amid persistent inflationary pressures. The Federal Reserve's recent actions indicate a cautious approach towards interest rate adjustments. Following a significant rate cut in late 2024, markets now anticipate limited additional cuts throughout 2025, with a 37% chance of only one further reduction. This scenario suggests that investors must brace for a potentially volatile year as the market adjusts to shifting monetary policies.
Current Economic Indicators
- GDP Growth: The Atlanta Fed's GDPNow indicator projects a robust growth rate of 3.3% for Q4 2024, reflecting underlying economic strength despite concerns about inflation.
- Inflation Rates: Core inflation is expected to remain above 2.5% for most of 2025 due to factors such as fiscal spending and possible tariff hikes.
- Interest Rates: Following recent cuts, the Federal Reserve's target rate is projected to stabilize around 4% through 2025.
Historical Context
Historically, interest rate hikes have led to declines in stock prices as higher borrowing costs dampen corporate earnings. For instance, during previous tightening cycles, sectors reliant on consumer spending often faced significant headwinds. However, some sectors like financials benefited from improved lending margins.
Implementation Strategies
Investors should consider several strategies in response to anticipated interest rate movements:
- Diversification: Maintaining a diversified portfolio can help mitigate risks associated with sector-specific downturns due to rising rates.
- Focus on Value Stocks: In an environment of higher rates, value stocks may outperform growth stocks as investors seek stability and dividends.
- Bond Allocation: With yields expected to remain elevated, incorporating bonds into portfolios can provide a buffer against stock market volatility.
Tactical Adjustments
Investors might also consider tactical adjustments based on economic indicators:
- Monitor Inflation Trends: Keeping an eye on inflation data will be critical in assessing the likelihood of further rate hikes or cuts.
- Sector Rotation: Shifting investments towards sectors that historically perform well during periods of rising rates—such as financials and energy—can enhance returns.
Risk Considerations
While navigating interest rate changes presents opportunities, it also introduces various risks:
- Market Volatility: Rate hikes can lead to increased volatility as markets react to new economic data and Fed announcements.
- Earnings Pressure: Higher interest expenses can squeeze corporate profit margins, particularly for companies with significant debt loads.
- Consumer Behavior: Changes in consumer spending patterns in response to higher borrowing costs can impact revenue for many companies.
Long-term vs. Short-term Risks
Investors should differentiate between short-term volatility risks and long-term structural changes in the economy. While immediate reactions may be negative during rate hikes, long-term investments in fundamentally strong companies can still yield positive returns over time.
Regulatory Aspects
Understanding regulatory frameworks is essential for investors:
- Federal Reserve Policies: The Fed's dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices influences its interest rate decisions significantly. Investors should stay informed about potential policy shifts that could impact market conditions.
- Global Economic Policies: International trade policies and geopolitical tensions can also affect U.S. interest rates and stock market performance. For instance, potential trade tariffs could exacerbate inflationary pressures and influence Fed decisions.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead into 2025, several scenarios could unfold based on interest rate movements:
- Continued Economic Growth with Controlled Inflation: If supply-side factors continue to drive productivity without triggering excessive inflation, both equities and bonds could perform well.
- Inflationary Pressures Leading to Further Rate Hikes: Should inflation persist beyond expectations, the Fed may need to implement additional rate increases, negatively impacting stock valuations across various sectors.
Investment Opportunities
Despite potential challenges posed by rising rates:
- Growth in Financial Sector: Financial institutions are likely to benefit from higher interest margins as borrowing costs rise.
- Infrastructure Investments: Increased fiscal spending on infrastructure could provide investment opportunities in related sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Do Interest Rate Hikes Impact The Stock Market In 2025
- What are interest rate hikes?
Interest rate hikes refer to increases in the benchmark interest rates set by central banks like the Federal Reserve, aimed at controlling inflation and stabilizing the economy. - How do interest rate hikes affect stock prices?
Higher interest rates generally lead to lower stock prices as they increase borrowing costs for companies and reduce consumer spending. - Which sectors benefit from rising interest rates?
The financial sector typically benefits from rising rates due to improved lending margins; however, sectors reliant on consumer spending may suffer. - What is the expected impact of interest rate changes in 2025?
The impact will largely depend on inflation trends and economic growth; limited further cuts are anticipated amid persistent inflation pressures. - How should investors prepare for rising interest rates?
Diversifying portfolios, focusing on value stocks, and adjusting bond allocations are effective strategies for managing risks associated with rising rates. - Can rising interest rates lead to a recession?
If rates rise too quickly or too high, they can stifle economic growth and potentially trigger a recession if consumer spending declines significantly. - What indicators should investors watch regarding interest rates?
Investors should monitor inflation data, employment figures, and Federal Reserve statements for insights into future rate movements. - Is it advisable to invest during periods of rising interest rates?
Yes, investing during such periods can still yield positive returns if focused on fundamentally strong companies or sectors that thrive in higher-rate environments.
In conclusion, understanding how interest rate hikes impact the stock market is crucial for investors looking to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape in 2025. With careful analysis and strategic planning, individuals can position themselves effectively amidst changing economic conditions.