Geopolitical tensions in the Middle East have long been a significant factor influencing global financial markets. The region’s complexities, characterized by historical conflicts, resource control, and international alliances, create an environment of uncertainty that can lead to volatility in stock prices. Investors closely monitor these tensions as they can affect oil prices, inflation rates, and overall economic stability. This article explores the multifaceted impacts of Middle Eastern geopolitical tensions on the stock market, providing a comprehensive analysis of current trends, strategies for investors, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlook.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Geopolitical Risk | Heightened geopolitical risk often leads to increased market volatility as investors react to uncertainties surrounding military conflicts and diplomatic relations. |
| Oil Prices | Conflicts in the Middle East can disrupt oil supply chains, leading to spikes in oil prices which directly impact energy stocks and inflation rates globally. |
| Investor Sentiment | Geopolitical events typically trigger a risk-off sentiment among investors, leading to sell-offs in equities and increased demand for safe-haven assets like gold and government bonds. |
| Sector Performance | Sectors such as energy and defense often see gains during periods of heightened tension, while consumer discretionary sectors may suffer due to reduced spending confidence. |
| Market Reactions | The stock market often reacts negatively to immediate geopolitical events but may recover over time as the situation stabilizes or as corporate earnings come into focus. |
Market Analysis and Trends
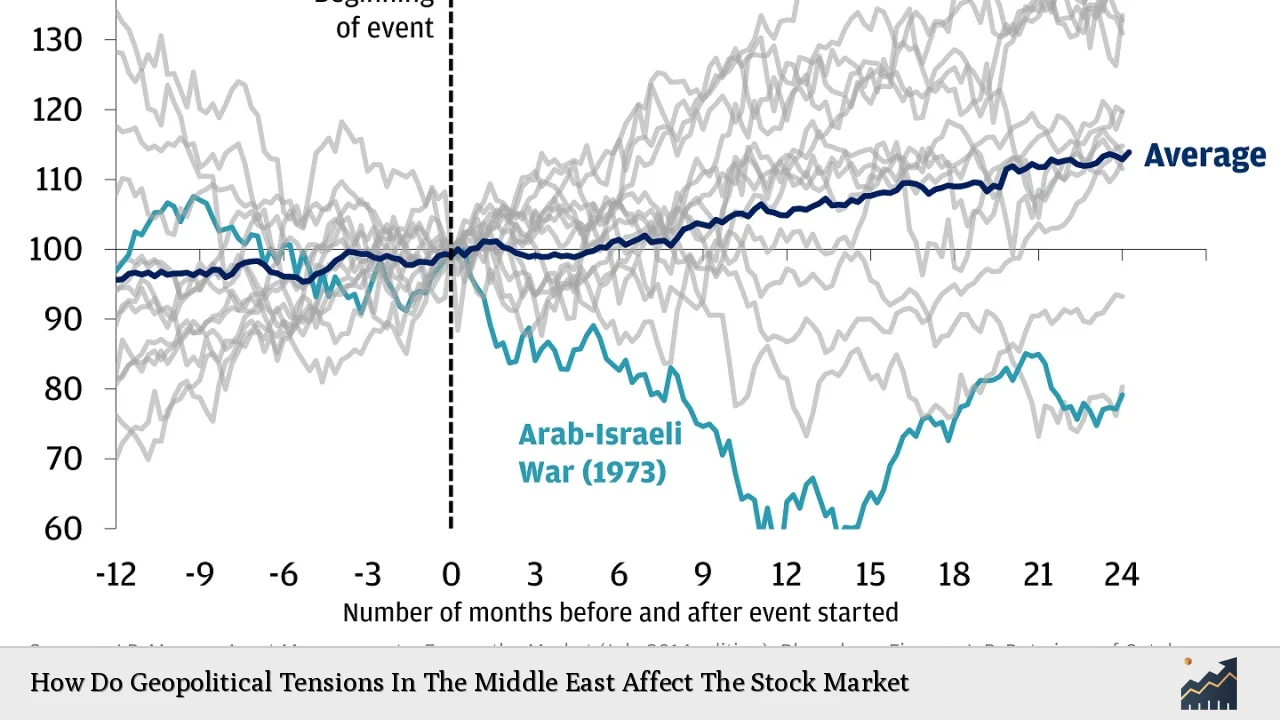
The stock market’s response to geopolitical tensions in the Middle East is often immediate and pronounced. For instance, following significant escalations such as the recent Israel-Hamas conflict that began in October 2023, global markets experienced notable fluctuations. The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell by 0.71% while the S&P 500 dropped by 0.67%, reflecting broader investor anxiety.
Current Market Statistics
- Oil Prices: Crude oil prices surged by approximately 7% during recent conflicts due to fears of supply disruptions. This spike has historically correlated with increased inflation pressures globally.
- Sector Performance: Energy stocks have generally benefitted from rising oil prices; for example, Shell’s shares rose by 6% amid escalating tensions. Conversely, luxury consumer stocks like LVMH saw declines of nearly 6% as consumer confidence waned.
Historical Context
Historically, geopolitical events have led to sharp declines in stock markets. For example:
- September 11 Attacks: The S&P 500 fell by nearly 4.9% immediately following the attacks but recovered within months.
- Iraq War: Initial market reactions included a drop of approximately 1.1%, with longer-term effects varying significantly based on subsequent economic conditions.
Implementation Strategies
Investors looking to navigate the complexities of geopolitical tensions should consider several strategies:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various sectors can mitigate risks associated with specific geopolitical events.
- Focus on Defensive Stocks: Investing in sectors that typically perform well during crises (e.g., utilities and consumer staples) can provide stability.
- Use of Derivatives: Options and futures can be employed to hedge against potential downturns in volatile markets.
- Monitoring Geopolitical Developments: Staying informed about ongoing conflicts and diplomatic negotiations is crucial for timely investment decisions.
Risk Considerations
Investing during periods of heightened geopolitical tension carries inherent risks:
- Market Volatility: Stock prices can fluctuate dramatically based on news cycles related to conflicts or diplomatic resolutions.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Companies reliant on stable supply chains may face increased costs or operational challenges due to regional instability.
- Inflationary Pressures: Rising oil prices can lead to broader inflationary trends that affect consumer spending and corporate profitability.
Economic Indicators
Key economic indicators that investors should monitor include:
- Oil Price Fluctuations: As a primary driver of inflation and economic activity.
- Consumer Confidence Index (CCI): Reflects how willing consumers are to spend money amidst uncertainties.
- Interest Rates: Central banks may adjust monetary policy in response to inflation driven by geopolitical tensions.
Regulatory Aspects
Regulatory bodies play a critical role in stabilizing markets during times of crisis:
- Central Bank Interventions: Institutions like the Federal Reserve may implement measures such as interest rate adjustments or quantitative easing to manage economic fallout from geopolitical tensions.
- Market Surveillance: Regulatory bodies monitor trading activities for signs of manipulation or excessive speculation during volatile periods.
Compliance Considerations
Investors must also ensure compliance with relevant regulations when trading during heightened geopolitical risks:
- Insider Trading Laws: Awareness of laws surrounding insider information is crucial, especially when trading based on non-public information related to geopolitical events.
- Investment Advisories: Consulting with financial advisors who understand geopolitical risks can help tailor investment strategies appropriately.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the interplay between geopolitics and financial markets is expected to continue evolving:
- Increased Geopolitical Tensions: With ongoing conflicts in regions like Ukraine and the Middle East, investors should prepare for potential market volatility.
- Shifts in Energy Policies: As countries seek energy independence or alternative sources due to instability in oil-rich regions, investment opportunities may arise in renewable energy sectors.
- Long-Term Market Resilience: Historically, while short-term reactions are often negative, stock markets tend to recover over time as underlying economic fundamentals reassert themselves.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Do Geopolitical Tensions In The Middle East Affect The Stock Market
- What are the immediate effects of geopolitical tensions on the stock market?
The immediate effects typically include increased volatility and declines in stock prices as investors react to uncertainty. - How do oil prices influence stock market performance?
Rising oil prices can boost energy sector stocks while increasing inflationary pressures that negatively affect consumer spending. - What sectors perform well during geopolitical crises?
Sectors such as energy and defense often see gains during crises, while consumer discretionary sectors may suffer. - Can investors protect themselves from geopolitical risks?
Diversification, investing in defensive stocks, and using hedging strategies can help mitigate risks associated with geopolitical events. - How do central banks respond to geopolitical tensions?
Central banks may adjust interest rates or implement other monetary policies to stabilize economies affected by rising inflation due to geopolitical crises. - What historical examples illustrate market reactions to geopolitical events?
Historical examples include significant drops following events like September 11 and the Iraq War; however, markets typically recover over time. - What role do regulatory bodies play during times of crisis?
Regulatory bodies monitor market activities for manipulation and may intervene through monetary policy adjustments to stabilize financial systems. - What is the long-term outlook for markets amid ongoing geopolitical tensions?
The long-term outlook suggests that while short-term volatility will persist, markets generally recover as economic fundamentals take precedence over time.
In conclusion, understanding how geopolitical tensions in the Middle East affect the stock market requires a nuanced approach that considers immediate impacts alongside long-term trends. Investors must remain vigilant about global developments while employing strategic measures to navigate this complex landscape effectively.