Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and stablecoins are two innovative forms of digital currency that are reshaping the financial landscape. While they both aim to enhance payment systems and financial inclusion, they differ significantly in terms of governance, backing, and regulatory frameworks. This comprehensive analysis explores their characteristics, market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlook.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
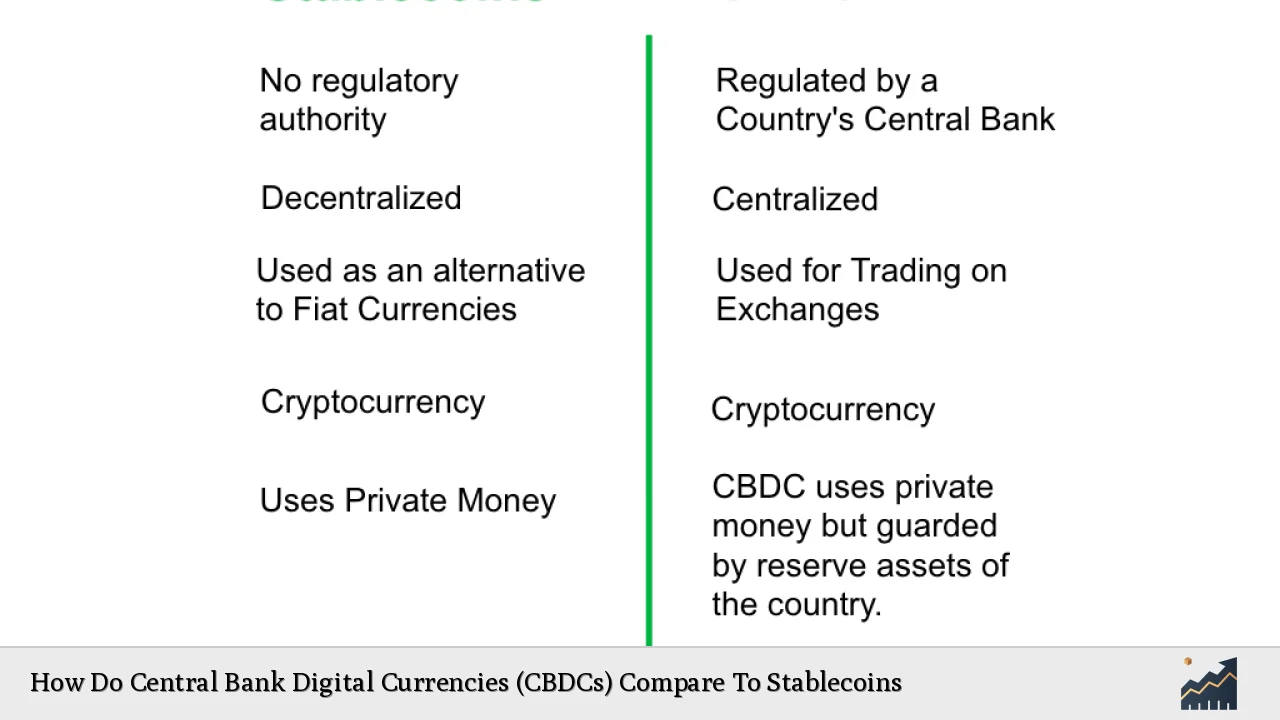
| CBDC Definition | A CBDC is a digital currency issued by a central bank, representing a digital form of a country’s fiat currency. It is regulated by the central authority, ensuring stability and trust. |
| Stablecoin Definition | Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their worth to traditional assets like fiat currencies. They are typically issued by private entities. |
| Governance | CBDCs are governed by central banks, while stablecoins are managed by private companies or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). |
| Backing | CBDCs are not backed by physical assets but rely on the trust in the issuing government. Stablecoins are usually backed by reserves of fiat currency or other assets. |
| Regulatory Framework | CBDCs operate under strict government regulations, while stablecoins face evolving regulatory scrutiny that varies by jurisdiction. |
| Market Trends | The stablecoin market has seen significant growth, with a total market capitalization reaching approximately $173 billion as of October 2024. Meanwhile, CBDC initiatives are being explored globally to enhance payment efficiency and financial inclusion. |
| Use Cases | CBDCs aim to improve payment systems and financial stability, while stablecoins are often used for trading and remittances due to their stability against fiat currencies. |
| Risks | CBDCs may pose risks related to privacy and cybersecurity, while stablecoins face challenges regarding transparency and reserve management. |
| Future Outlook | The future of both CBDCs and stablecoins is promising but will require careful management and collaboration between public and private sectors to mitigate risks and maximize benefits. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The digital currency landscape is rapidly evolving, with both CBDCs and stablecoins gaining traction. As of late 2024:
- Stablecoin Market Growth: The total market capitalization of stablecoins has increased steadily, reaching approximately $173 billion. This growth reflects rising demand for stable digital currencies that offer low volatility compared to traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
- CBDC Developments: Over 70% of central banks worldwide are exploring or implementing CBDCs as part of their monetary policy strategies. Countries such as China with its digital yuan (e-CNY) and India with its digital rupee are leading the way in CBDC adoption.
- Technological Innovations: Both CBDCs and stablecoins leverage blockchain technology to enhance transaction efficiency. However, CBDCs may also utilize traditional banking infrastructure alongside blockchain solutions for broader accessibility.
- Financial Inclusion: Both forms of digital currency aim to improve financial access for unbanked populations. CBDCs can facilitate government-backed payments directly to citizens, while stablecoins can provide an accessible means for transactions without reliance on traditional banking systems.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing CBDCs and stablecoins involves distinct strategies:
- For CBDCs:
- Pilot Programs: Many central banks initiate pilot programs to test the feasibility of CBDCs in controlled environments before full-scale rollout.
- Public Consultation: Engaging with stakeholders—including consumers, businesses, and financial institutions—to gather feedback on design and functionality.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that CBDCs can interact seamlessly with existing payment systems domestically and internationally.
- For Stablecoins:
- Regulatory Compliance: Issuers must navigate evolving regulations to ensure transparency in reserve management and operational practices.
- Partnerships with Financial Institutions: Collaborating with banks and payment processors to enhance acceptance and usability.
- Consumer Education: Educating users about the benefits and risks associated with using stablecoins compared to traditional currencies.
Risk Considerations
Both CBDCs and stablecoins present unique risks that need careful consideration:
- CBDC Risks:
- Privacy Concerns: The centralized nature of CBDCs raises questions about data privacy and surveillance.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As digital currencies become more prevalent, they may become targets for cyberattacks aimed at undermining confidence in the financial system.
- Stablecoin Risks:
- Reserve Transparency: The need for issuers to maintain adequate reserves poses risks if these reserves are not transparently reported or audited.
- Market Volatility: While designed to be stable, external factors can still affect the value of stablecoins if they lose their peg.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape for both CBDCs and stablecoins is complex:
- CBDC Regulation:
- Central banks have clear authority over CBDC issuance, ensuring compliance with national monetary policies.
- Regulatory frameworks are being developed globally to address issues such as consumer protection, anti-money laundering (AML), and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT).
- Stablecoin Regulation:
- Stablecoins face a patchwork of regulations that vary significantly across jurisdictions. Regulatory bodies like the SEC in the U.S. are increasingly scrutinizing these assets for compliance with securities laws.
- Recent proposals suggest that regulated stablecoins could be treated similarly to bank deposits if they meet specific criteria regarding reserve backing.
Future Outlook
The future of both CBDCs and stablecoins appears bright but will depend on several factors:
- Collaboration Between Sectors: Effective integration of CBDCs into existing financial systems will require collaboration between central banks, private sector players, and technology providers.
- Regulatory Clarity: Clear regulations will be crucial for fostering innovation while ensuring consumer protection. As governments refine their approaches to digital currencies, we may see more standardized frameworks emerge.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in blockchain technology could enhance the functionality of both CBDCs and stablecoins, making them more efficient and secure.
In conclusion, while CBDCs represent a sovereign approach to digital currency backed by government authority, stablecoins offer flexibility through private sector innovation. Understanding their differences is essential for investors navigating this rapidly changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Do Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) Compare To Stablecoins
- What is the primary difference between CBDCs and stablecoins?
CBDCs are issued by central banks as digital representations of fiat currency, while stablecoins are privately issued cryptocurrencies pegged to assets like fiat currencies. - Are CBDCs safer than stablecoins?
CBCDs generally offer more security due to government backing; however, they may raise privacy concerns. Stablecoins depend on the issuer’s transparency regarding reserves. - How do regulations differ between CBDCs and stablecoins?
CBCDs operate under strict government regulations; in contrast, stablecoin regulations vary widely across jurisdictions as they evolve. - Can I use both CBDCs and stablecoins for transactions?
Yes, both can be used for transactions; however, their acceptance may vary depending on the merchant or platform. - What impact do these digital currencies have on financial inclusion?
Both aim to improve access to financial services for unbanked populations by providing alternative means of transaction without relying on traditional banking systems. - How do market trends affect the adoption of these currencies?
The growing demand for efficient payment solutions drives interest in both forms; however, regulatory clarity will significantly influence adoption rates. - What future developments should we expect?
Expect ongoing developments in regulatory frameworks, technological advancements in blockchain integration, and increased collaboration between public/private sectors. - Are there risks associated with using either form of digital currency?
Yes; risks include cybersecurity threats for CBDCs and reserve transparency issues for stablecoins. Proper risk management practices will be essential.
This analysis provides a thorough overview of how Central Bank Digital Currencies compare with Stablecoins across various dimensions relevant to investors and finance professionals alike.