Investing through a 401(k) plan is a powerful way to save for retirement while benefiting from tax advantages. A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement savings plan that allows employees to save a portion of their paycheck before taxes are taken out. This means that the money you contribute reduces your taxable income, and the funds grow tax-deferred until you withdraw them in retirement. Understanding how to effectively invest through your 401(k) can significantly impact your financial future.
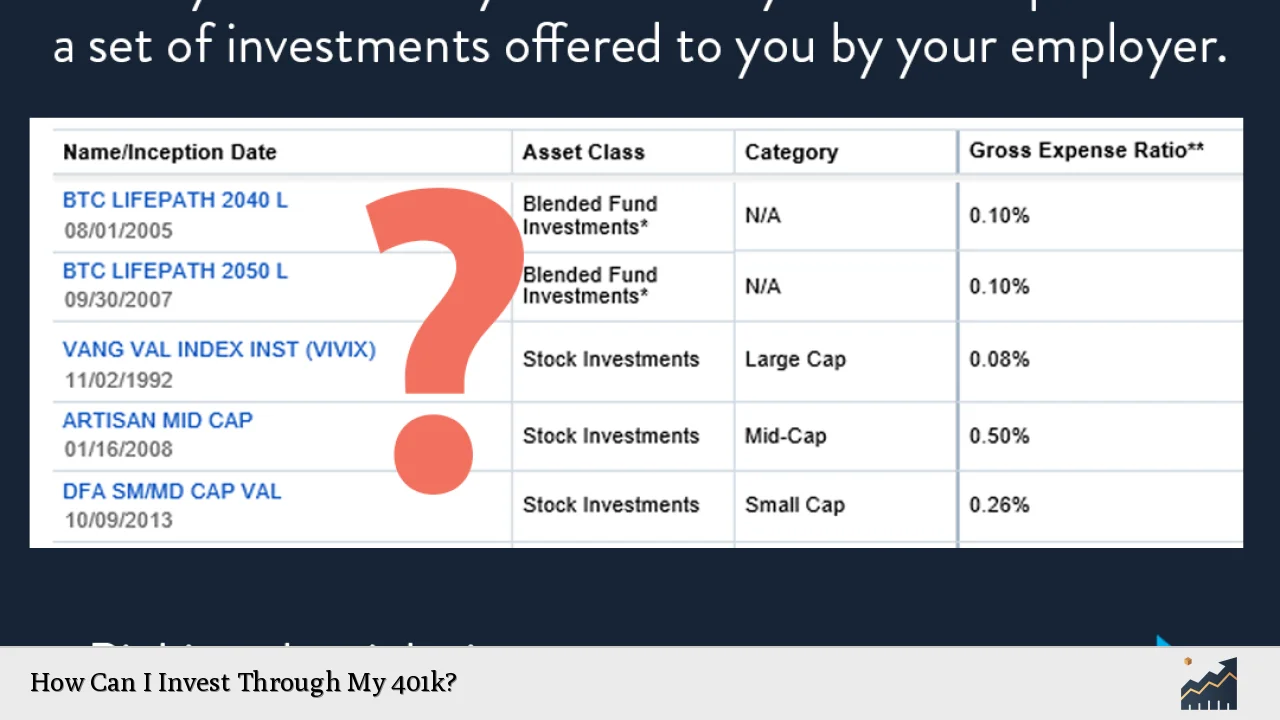
In a typical 401(k) plan, participants have access to a variety of investment options, including mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and target-date funds. The choices available can vary by employer and plan provider. It’s essential to evaluate these options carefully to align your investments with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
The following table summarizes key aspects of investing through a 401(k):
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Tax Benefits | Contributions are made pre-tax, reducing taxable income. |
| Investment Options | Includes mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and target-date funds. |
Understanding Your 401(k) Plan
Before diving into investment options, it’s crucial to understand the structure of your 401(k) plan. Each plan is unique and may offer different features and investment choices.
First, check if your employer offers matching contributions. Employer matching can significantly boost your retirement savings. For example, if your employer matches contributions up to a certain percentage, it’s wise to contribute at least enough to take full advantage of this benefit.
Next, review the investment options available within your plan. Most plans provide a selection of mutual funds that may include:
- Stock mutual funds: These invest in shares of companies and can be further categorized into large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap funds.
- Bond mutual funds: These invest in various types of bonds and are generally considered less risky than stock funds.
- Target-date funds: These funds automatically adjust their asset allocation based on the target retirement date.
Understanding these options will help you make informed decisions about where to allocate your contributions.
Choosing Your Investments
Selecting the right investments within your 401(k) is critical for long-term growth. Here are some steps to consider:
1. Assess Your Risk Tolerance: Determine how much risk you are willing to take with your investments. Younger investors may opt for more aggressive growth strategies by investing heavily in stocks, while those closer to retirement might prefer conservative approaches with more bonds.
2. Diversify Your Portfolio: Diversification helps minimize risk by spreading investments across various asset classes. A well-diversified portfolio might include a mix of domestic stocks, international stocks, bonds, and possibly alternative investments.
3. Consider Target-Date Funds: If you prefer a hands-off approach, target-date funds can be an excellent option. These funds automatically adjust their investment mix as you approach retirement age, becoming more conservative over time.
4. Monitor Performance: Regularly review the performance of your investments. While it’s important not to react impulsively to market fluctuations, staying informed about how your investments are doing can help you make necessary adjustments.
5. Rebalance as Needed: Over time, some investments may perform better than others, which can skew your intended asset allocation. Periodically rebalancing your portfolio ensures that it aligns with your original investment strategy.
Making Contributions
To invest through your 401(k), you must first decide how much you want to contribute from each paycheck. Most plans allow you to set a percentage or a fixed dollar amount for contributions.
- Contribution Limits: Be aware of annual contribution limits set by the IRS. For 2024, the limit is $23,000 for employees under age 50 and $30,000 for those aged 50 and over (including catch-up contributions).
- Automatic Contributions: Many employers offer automatic enrollment in their 401(k) plans. This means that a portion of your salary will be automatically deducted and contributed unless you opt out.
- Adjusting Contributions: You can typically change your contribution amount at any time throughout the year. Consider increasing contributions during salary increases or bonuses to maximize savings.
Understanding Fees
When investing through a 401(k), it’s important to understand the fees associated with the investment options available in your plan. Fees can eat into your returns over time; therefore:
- Expense Ratios: Look for funds with low expense ratios since these fees are charged annually based on the total assets in the fund.
- Administrative Fees: Be aware of any administrative fees charged by the plan provider for managing the account.
- Transaction Costs: Some plans may charge fees for buying or selling certain investments within the plan.
Understanding these costs will help you choose more cost-effective investment options that align with your financial goals.
Tax Implications
Investing through a 401(k) has significant tax advantages:
- Tax-Deferred Growth: The money in your 401(k) grows tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement when it is taxed as ordinary income.
- Roth Option: Some plans offer a Roth 401(k) option where contributions are made after-tax but qualified withdrawals are tax-free in retirement.
- Early Withdrawal Penalties: Be cautious about withdrawing money from your 401(k) before age 59½; doing so typically incurs a penalty unless specific conditions are met (e.g., financial hardship).
Understanding these tax implications can help you make strategic decisions about when and how much to withdraw from your account during retirement.
FAQs About How Can I Invest Through My 401k
- What types of investments can I choose in my 401(k)?
You can typically choose from stock mutual funds, bond mutual funds, target-date funds, and sometimes individual stocks or ETFs. - How much should I contribute to my 401(k)?
A good rule of thumb is to contribute enough to get any employer match available; aim for at least 10% if possible. - Can I change my investments anytime?
Yes, most plans allow you to change your investment choices at any time. - What happens if I leave my job?
You can typically roll over your 401(k) into an IRA or another employer’s plan without incurring taxes. - Are there penalties for early withdrawal from my 401(k)?
Yes, withdrawing before age 59½ usually incurs a penalty unless specific exceptions apply.
Investing through a 401(k) plan is an effective way to prepare for retirement while enjoying tax benefits. By understanding how to navigate investment options and making informed decisions based on personal financial goals and risk tolerance, individuals can maximize their savings potential and secure their financial future.