The integration of blockchain technology into educational systems, particularly through initiatives like Open Campus, represents a transformative shift in how credentials and certifications are issued, verified, and managed. Open Campus aims to empower learners by providing them with control over their educational identities and ensuring that their credentials are verifiable and immutable on the blockchain. This innovation addresses the growing need for secure, transparent, and efficient verification processes in an increasingly digital world.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Verifiable Credentials | Credentials stored on the blockchain that can be easily verified by employers or institutions without needing to contact the issuing authority. |
| Self-Sovereign Identity | Users control their own data and credentials, allowing for privacy-preserving verification processes. |
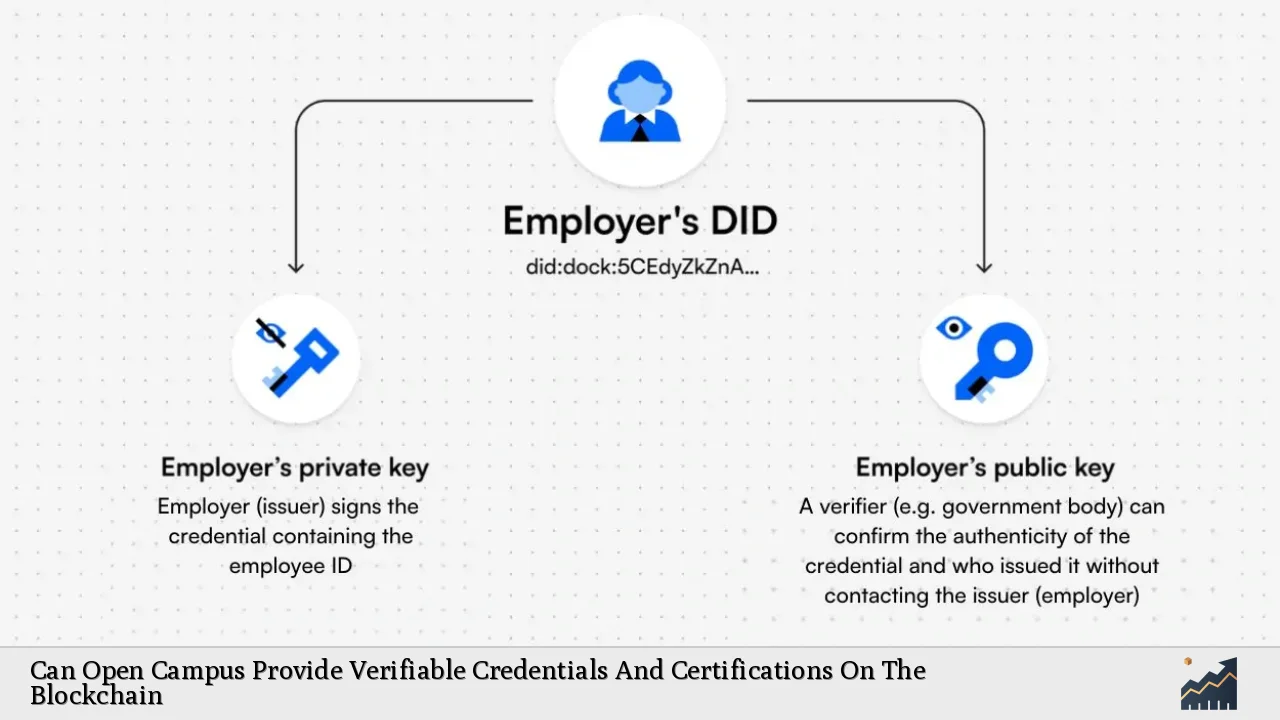
| Decentralized Identifier (DID) | A unique identifier that enables users to manage their digital identities securely and privately on the blockchain. |
| Immutable Records | Once recorded on the blockchain, credentials cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring authenticity. |
| Market Growth | The global blockchain ecosystem in education is projected to grow from USD 240 million in 2023 to USD 3.07 billion by 2030, reflecting increasing adoption of blockchain for credential verification. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The use of blockchain technology in education is rapidly gaining traction, driven by the need for enhanced security and efficiency in credential verification. Recent statistics indicate that the adoption of blockchain for credential verification has increased by 40% over the past three years. Educational institutions are increasingly issuing tamper-proof digital diplomas and transcripts, which significantly reduces fraud and simplifies the verification process.
Current Trends
- Increased Adoption: Institutions are recognizing the benefits of blockchain for certification verification, leading to a surge in adoption rates across various sectors.
- Integration with E-Learning: As online education continues to expand, there is a growing demand for secure and verifiable certificates for online courses.
- Government Support: Governments worldwide are endorsing blockchain in education, with policies and funding initiatives aimed at fostering transparency and efficiency.
- Micro-Credentials: The shift towards lifelong learning is driving demand for micro-credentials and badges that represent specific skills or achievements.
Implementation Strategies
To successfully implement blockchain-based credentialing systems like Open Campus, several strategies should be considered:
- Developing a Robust Infrastructure: Establishing a secure and scalable blockchain infrastructure is crucial. This includes integrating decentralized identifiers (DIDs) that allow users to manage their credentials securely.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Educational institutions should collaborate with technology providers to develop platforms that facilitate seamless credential sharing and verification.
- User Education: Educating users about the benefits of blockchain technology and how to manage their digital identities is essential for widespread adoption.
- Standardization: Developing standardized protocols for issuing and verifying credentials can enhance interoperability between different platforms.
Risk Considerations
While the potential benefits of using blockchain for credential verification are significant, several risks must be addressed:
- Data Privacy Concerns: Ensuring that personal information remains private while allowing for credential verification is paramount. Utilizing cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs can help mitigate these concerns.
- Vulnerability to Fraud: Although blockchain offers enhanced security, vulnerabilities still exist, particularly if proper authentication measures are not implemented. For instance, impersonation attacks can occur if issuing institutions do not have robust identity verification processes in place.
- High Implementation Costs: The initial costs associated with developing and maintaining a blockchain infrastructure can be significant. Institutions must weigh these costs against the long-term benefits of improved efficiency and security.
Regulatory Aspects
The implementation of blockchain technology in education must also navigate various regulatory frameworks:
- Compliance with Data Protection Laws: Institutions must ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR when handling personal data on the blockchain.
- Accreditation Standards: Educational institutions must align their blockchain credentialing practices with existing accreditation standards to ensure recognition of their credentials by employers and other institutions.
- Government Initiatives: Support from governmental bodies can facilitate the adoption of blockchain technology in education by providing funding and establishing clear regulatory guidelines.
Future Outlook
The future of verifiable credentials on the blockchain looks promising. As more educational institutions adopt this technology, we can expect:
- Widespread Adoption: The trend towards digital credentialing will likely continue as institutions recognize the importance of secure and efficient verification methods.
- Enhanced Interoperability: Development of standards will facilitate interoperability between different educational platforms, making it easier for students to share their credentials across borders.
- Increased Focus on Lifelong Learning: As job markets evolve, there will be a greater emphasis on continuous education and skill acquisition. Blockchain technology will play a crucial role in validating these ongoing learning experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions About Can Open Campus Provide Verifiable Credentials And Certifications On The Blockchain
- What is Open Campus?
Open Campus is a Web3 education protocol designed to provide learners with control over their educational identities while ensuring that their credentials are verifiable on the blockchain. - How does blockchain enhance credential verification?
Blockchain provides a secure, immutable ledger for storing credentials that can be easily verified by employers or institutions without needing to contact the issuing authority. - What are decentralized identifiers (DIDs)?
DIDs are unique identifiers that allow users to manage their digital identities securely on the blockchain while maintaining privacy. - What challenges does Open Campus face?
Challenges include data privacy concerns, vulnerability to fraud, high implementation costs, and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks. - How is the market for blockchain-based education evolving?
The global market for blockchain in education is expected to grow significantly, reaching USD 3.07 billion by 2030 due to increasing adoption rates. - What role do governments play in this space?
Governments are increasingly endorsing blockchain technology in education through funding initiatives and regulatory support aimed at fostering transparency. - Can individuals control their data on Open Campus?
Yes, individuals have full control over their academic certifications and personal data through self-sovereign identity mechanisms provided by Open Campus. - What is the significance of micro-credentials?
Micro-credentials represent specific skills or achievements acquired through short courses or workshops, supporting lifelong learning initiatives.
The integration of blockchain technology into education through platforms like Open Campus not only enhances security but also empowers learners by giving them control over their credentials. As this landscape continues to evolve, it will likely reshape how educational achievements are recognized globally.