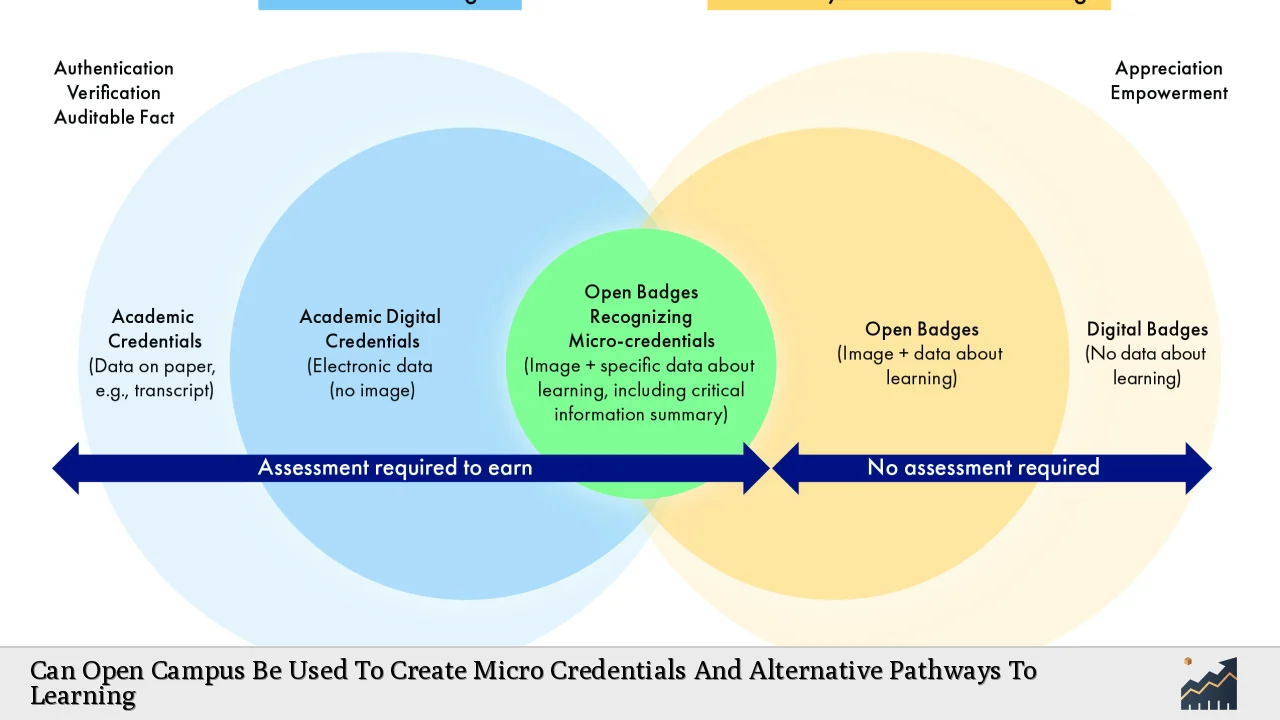
The landscape of education is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing workforce demands. One of the most significant trends in this evolution is the rise of micro-credentials—short, focused qualifications that validate specific skills or competencies. Open campuses, often associated with online learning environments, present a unique opportunity to facilitate the creation and dissemination of these micro-credentials. This article explores how open campuses can be leveraged to develop micro-credentials and alternative pathways to learning, examining market trends, implementation strategies, risk considerations, regulatory aspects, and future outlook.
| Key Concept | Description/Impact |
|---|---|
| Micro-Credentials | Short, targeted learning experiences that provide certification for specific skills, allowing for rapid upskilling and reskilling. |
| Open Campuses | Flexible online platforms that provide access to educational resources and courses from various institutions, enabling diverse learning pathways. |
| Stackability | The ability to combine multiple micro-credentials into larger qualifications or degrees, enhancing learner flexibility and career prospects. |
| Employer Recognition | Increasing acceptance of micro-credentials by employers as valid indicators of skills and competencies in hiring processes. |
| Regulatory Frameworks | The need for clear guidelines and standards to ensure the quality and recognition of micro-credentials across educational institutions. |
Market Analysis and Trends
The demand for micro-credentials has surged in recent years. According to a report by the OECD, the number of micro-credential offerings on major online platforms grew from approximately 600 in 2018 to nearly 1,900 by 2022. This trend reflects a broader shift towards more flexible learning options that cater to the needs of adult learners seeking to enhance their employability without committing to lengthy degree programs.
Current Market Statistics
- Growth Rate: The adoption of micro-credentials is increasing, with a 13% rise in institutions reporting mature adoption from 2021 to 2023.
- Employer Preferences: A study indicated that 72% of employers are more likely to hire candidates with micro-credentials, highlighting their growing importance in the job market.
- Learner Demand: Post-pandemic shifts have led to a greater preference for flexible learning pathways among students, with many seeking alternatives to traditional degrees.
These statistics underscore the potential for open campuses to fill gaps in the educational landscape by offering tailored micro-credential programs that align with industry needs.
Implementation Strategies
To effectively utilize open campuses for creating micro-credentials, several strategies can be employed:
Collaborative Partnerships
Educational institutions can partner with industry leaders to design micro-credential programs that address specific skill gaps. This collaboration ensures that the content is relevant and meets current market demands.
Modular Learning Design
Micro-credentials should be structured as modular units that can be taken independently or stacked towards larger qualifications. This flexibility allows learners to customize their educational paths according to their career goals.
Technology Integration
Leveraging technology platforms for course delivery can enhance accessibility. Open campuses can utilize Learning Management Systems (LMS) to provide asynchronous learning opportunities, enabling students to learn at their own pace.
Marketing and Awareness
Effective marketing strategies are essential for promoting new micro-credential offerings. Institutions should highlight the benefits of these credentials in terms of career advancement and skill acquisition.
Risk Considerations
While the potential for micro-credentials is significant, several risks must be considered:
Quality Assurance
There is a lack of standardization in micro-credential offerings. Institutions must implement rigorous quality assurance processes to ensure that credentials are recognized and valued by employers.
Market Saturation
As more institutions enter the micro-credential space, there is a risk of market saturation. Institutions need to differentiate their offerings through unique content or partnerships.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating regulatory frameworks can be complex. Institutions must stay informed about changes in policies regarding credential recognition and ensure compliance with national education standards.
Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory environment surrounding micro-credentials is still developing. Key considerations include:
Accreditation Standards
Establishing clear accreditation standards for micro-credential programs is crucial for maintaining quality and ensuring employer recognition. Organizations like the European Commission are exploring frameworks for international recognition.
Data Privacy Regulations
As open campuses collect data on learners’ progress and achievements, compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR becomes essential.
Funding Opportunities
Governments may provide funding or incentives for institutions developing innovative credentialing systems. Institutions should explore these opportunities to support their initiatives.
Future Outlook
The future of education appears increasingly aligned with flexible learning models such as those offered by open campuses. As workforce demands continue to evolve:
Enhanced Personalization
Micro-credentialing will likely become more personalized, allowing learners to tailor their educational experiences based on individual career aspirations and market needs.
Integration with Traditional Education
Institutions may begin integrating micro-credentials into traditional degree programs, allowing students to earn credits towards their degrees while acquiring valuable skills along the way.
Global Recognition
As more countries recognize the value of micro-credentials, we may see a shift towards standardized global frameworks that facilitate easier transferability of credentials across borders.
Frequently Asked Questions About Can Open Campus Be Used To Create Micro Credentials And Alternative Pathways To Learning
- What are micro-credentials?
Micro-credentials are short certifications that validate specific skills or competencies acquired through targeted learning experiences. - How do open campuses facilitate learning?
Open campuses provide flexible online platforms where learners can access courses from various institutions without geographical limitations. - Are employers recognizing micro-credentials?
Yes, many employers increasingly recognize micro-credentials as valid indicators of skills during hiring processes. - Can micro-credentials lead to traditional degrees?
Micro-credentials can be stackable; they may count towards larger qualifications or degrees depending on institutional policies. - What risks are associated with micro-credentialing?
Key risks include quality assurance challenges, potential market saturation, and navigating complex regulatory environments. - How can institutions ensure quality in their micro-credential offerings?
Institutions should implement robust quality assurance processes and seek accreditation from recognized bodies. - What is the future outlook for micro-credentials?
The future looks promising with increased personalization, integration into traditional education systems, and potential global recognition frameworks. - How do I choose a reputable provider for micro-credentials?
Look for providers with established partnerships with industry leaders and those offering accredited programs recognized by employers.
In conclusion, open campuses represent a significant opportunity for creating innovative pathways through micro-credentials. By leveraging technology and collaborative partnerships while addressing regulatory challenges and ensuring quality assurance, educational institutions can meet the evolving demands of learners and employers alike. The future holds promise as these alternative pathways gain traction in an increasingly competitive job market.